Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Piroxicam, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), has been used predominantly for managing arthritis symptoms and musculoskeletal conditions since its initial approval in the late 1970s. Despite the advent of newer anti-inflammatory agents and evolving regulatory landscapes, piroxicam maintains a niche in the pharmaceutical market. Understanding its market dynamics and financial trajectory is essential for stakeholders including manufacturers, investors, and healthcare providers aiming to navigate this segment’s complexities.
Market Overview
Historical Context and Current Usage
Piroxicam, developed by Pfizer, secured discovery and approval during a period marked by expanding NSAID utilization. It is characterized by a long half-life, enabling once-daily dosing—a significant advantage over earlier NSAIDs. However, concerns over gastrointestinal and cardiovascular side effects have moderated its popularity over recent years.
Despite these limitations, piroxicam remains prescribed for chronic inflammatory conditions, especially in regions with longstanding use of generic formulations. Its market presence is reinforced by its patent expirations, leading to numerous generic versions that substantially influence current pricing and availability.
Market Penetration and Competition
The NSAID market is highly competitive, dominated by drugs such as ibuprofen, naproxen, and meloxicam. Piroxicam's market share has diminished relative to these agents, especially in markets prioritizing drugs with improved safety profiles. Nonetheless, in fully mature markets with entrenched prescribing habits, piroxicam retains a foothold, particularly in lower-cost generics.
Newer NSAIDs with selective COX-2 inhibition (e.g., celecoxib) introduce competition by offering reduced gastrointestinal side effects, further constraining piroxicam’s share. Yet, cost-effectiveness and clinical familiarity help sustain its role in certain patient populations.
Market Dynamics Influencing Piroxicam
Regulatory and Safety Considerations
Safety concerns, particularly gastrointestinal toxicity (gastric ulcers, bleeding) and cardiovascular risks, have led to regulatory warnings and, in some cases, restricted prescribing (e.g., FDA labels advising caution). These safety issues have prompted increased utilization of COX-2 inhibitors, impacting piroxicam's market penetration. Regulatory bodies’ shifting guidelines emphasize risk-benefit analysis, often favoring newer agents.
Genericization and Pricing
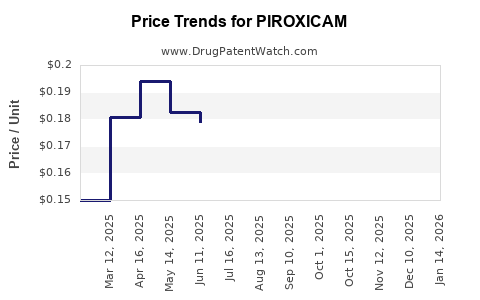
Patent expirations have facilitated rapid proliferation of generic piroxicam, significantly reducing wholesale and retail prices and making it an attractive option in cost-sensitive healthcare systems, particularly in developing countries. This commoditization sustains volume sales but exerts downward pressure on profit margins for manufacturers.
Prescribing Trends
Physician prescribing behavior is increasingly influenced by evidence-based guidelines prioritizing safety over traditional familiarity. As newer NSAIDs demonstrate favorable safety profiles, piroxicam prescriptions decline, limited mostly to specific cases or regions with entrenched prescribing practices.
Market Opportunities and Challenges
Emerging markets present considerable growth opportunities given the extensive healthcare infrastructure expansions and high burden of chronic inflammatory diseases. However, the challenge remains balancing safety concerns with market retention. Additionally, patent cliffs and the proliferation of generics challenge profit sustainability.
Financial Trajectory
Revenue Streams and Market Share
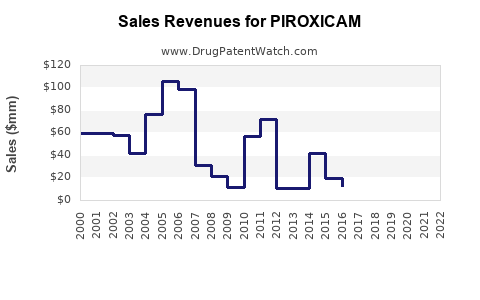
Global revenues for piroxicam have declined since their peak in the early 2000s, owing to safety concerns and marketplace competition. Pfizer and other generic manufacturers generate revenues primarily through volume sales of established formulations, with margins compressed due to generic price erosion.
Impact of Patent Expirations
The imminent or achieved patent reversions have led to intense price competition, shrinking profit margins. For example, Pfizer's patent expiry in various jurisdictions precipitated a surge in generics, with prices decreasing by up to 80%, compressing revenue streams from the original proprietary formulations.
Market Forecast
Estimates project a gradual decline in piroxicam's market share over the next five years, attributed to the increasing adoption of COX-2 inhibitors and safer NSAIDs. However, the total market volume may remain steady or slightly increase in emerging markets, driven by population growth and rising prevalence of chronic inflammatory diseases.
Investment Outlook
While compound annual growth rates (CAGRs) for piroxicam are expected to decline, sustained demand persists in certain sectors. Profitability for manufacturers depends heavily on manufacturing efficiencies, regional pricing strategies, and leveraging generic markets' cost advantages.
Regulatory and Societal Influences
Global Regulatory Environment
Regulatory agencies such as the FDA and EMA have tightened standards around NSAID safety profiling. Updated warnings restrict indications or recommend monitoring, reducing prescribing volumes. Nevertheless, some regions maintain less restrictive policies, maintaining a baseline of demand.
Healthcare Economics and Reimbursement
Piroxicam's low cost makes it attractive in value-based healthcare settings. Reimbursement policies favor generics, especially in public healthcare systems, boosting high-volume, low-margin sales.
Public and Physician Awareness
Increased awareness of NSAID-associated risks has shifted clinician prescribing patterns toward newer agents, impacting the financial trajectory negatively. Nonetheless, continued empirical use among certain patient subsets ensures residual revenues.
Conclusion: Strategic Outlook
The future of piroxicam’s market and financial performance hinges on multiple factors. Cost sensitivity favors generic formulations, maintaining a baseline demand, especially in price-pressured markets. However, safety concerns and competitive dynamics with selective COX-2 inhibitors will continue to erode its market share in developed economies. Emerging markets present growth opportunities driven by cost considerations but face similar safety and regulatory hurdles.
Manufacturers aiming to sustain profitability should explore niche indications, optimize manufacturing efficiencies, and invest in targeted regional marketing. Additionally, developing formulations with improved safety profiles or combination therapies could rejuvenate its market viability, aligning with evolving regulatory standards.
Key Takeaways
-
Market Position: Piroxicam remains relevant primarily as a low-cost generic NSAID in select markets, especially where safety concerns are less restrictive and affordability remains a priority.
-
Competitive Pressure: Shifting prescribing practices favor newer NSAIDs with better safety profiles, constricting piroxicam’s market share.
-
Revenue Trends: The drug’s revenue trajectory is declining due to patent expirations, aggressive price competition, and safety warnings, though volume sales sustain some profitability.
-
Market Opportunities: Expanding into emerging markets and leveraging formulary preferences for cost-effective treatments can partial offset declines in developed regions.
-
Future Focus: Innovation around safety and efficacy, along with strategic regional positioning, will be crucial for maintaining financial viability.
FAQs
-
What factors are most influencing piroxicam's declining market share?
Safety concerns, particularly gastrointestinal and cardiovascular risks, coupled with the introduction of COX-2 inhibitors, have decreased its prescribing. Patent expirations leading to low-cost generics further intensify price competition.
-
Is piroxicam still a viable option for chronic inflammatory diseases?
Yes, in regions where safety warnings are less restrictive, and cost is a primary consideration, piroxicam remains prescribed, especially for long-term management where affordability outweighs potential risks.
-
How do patent expirations affect piroxicam's revenues?
Patent expirations enable generic manufacturers to enter the market, significantly lowering prices and reducing profit margins for brand-name producers, consequently diminishing revenues.
-
What are future opportunities for piroxicam manufacturers?
Opportunities include targeting emerging markets, developing formulations with improved safety profiles, and focusing on niche indications or combination therapies to differentiate offerings.
-
Will piroxicam eventually become obsolete?
While declining in some markets, piroxicam’s role may persist where cost and familiarity drive its use. However, ongoing safety concerns and competitive pressures suggest gradual obsolescence unless innovation occurs.
References
- [1] Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Piroxicam Label and Safety Warnings.
- [2] Pfizer Inc. Piroxicam Product Information and Market Data.
- [3] IMS Health Data. NSAID Market Trends and Competitive Dynamics.
- [4] European Medicines Agency (EMA). NSAID Safety Surveillance Reports.
- [5] GlobalData. Emerging Market Opportunities for NSAIDs.