Last updated: July 27, 2025
rket Dynamics and Financial Trajectory for the Pharmaceutical Drug: Metoprolol Tartrate
Introduction
Metoprolol tartrate, a beta-1 selective adrenergic receptor blocker, commands a pivotal position in cardiovascular therapeutics. Approved initially in the late 20th century, it remains a cornerstone in managing hypertension, angina pectoris, and heart failure. Understanding its market landscape and financial outlook involves a comprehensive analysis of clinical demand, competitive forces, regulatory considerations, and evolving healthcare paradigms.
Market Overview and Demand Drivers
Clinical Use and Therapeutic Role
Metoprolol tartrate is prescribed predominantly for hypertension and ischemic heart diseases. Its ease of administration, proven efficacy, and favorable safety profile underpin sustained demand. As per IQVIA reports, beta-blockers constitute a significant segment of cardiovascular medications, with metoprolol representing an approximately 25% share within this class globally [1].
Prevalence of Cardiovascular Diseases
The rising global burden of cardiovascular disease (CVD), projected to afflict over 1.4 billion people by 2030, sustains the therapeutic need for agents like metoprolol [2]. Aging populations in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia escalate prescription volumes.
Off-Label and Combination Use
Off-label utilization in arrhythmias and prophylactic migraine treatment, alongside combination therapies, also bolster volumes. The pharmaceutical interest pivots around such flexible applications, where patent protection no longer constraints market expansion.
Market Dynamics Influencers
Generic Competition and Market Penetration
Metoprolol tartrate's patent expired in the early 2000s, drastically increasing generic entry. Generic versions have maintained aggressive pricing strategies, constraining branded sales growth but expanding access and compliance due to lower costs. As a result, the market is predominantly driven by biosimilar and generic availability, pressuring profit margins for branded formulations.
Manufacturing and Supply Chain Factors
The production of metoprolol tartrate involves established synthesis pathways, but recent shortages—due to raw material disruptions, regulatory compliance issues, or manufacturing outages—have occasionally constrained supply. Such disruptions can momentarily influence pricing and procurement strategies, especially in emerging markets.
Regulatory Environment
Regulatory bodies like the FDA and EMA have streamlined approval pathways for generics, facilitating market entry and wider distribution channels. Conversely, evolving regulations around biosimilars, patent litigations, and quality standards influence competitive dynamics.
Emerging Markets and Demographic Trends
Emerging economies, particularly in Asia and Latin America, exhibit escalating uptake owing to increasing CVD prevalence and expanding healthcare infrastructure. Market penetration is further facilitated by local manufacturing, licensing agreements, and government-led initiatives for affordable medications.
Financial Trajectory and Growth Opportunities
Revenue Trends and Projections
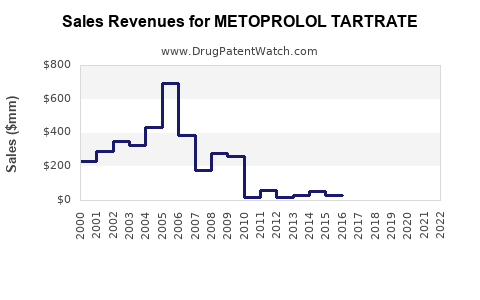
Global sales of metoprolol tartrate hovered around USD 1.2 billion in 2022, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 3% over the past five years, primarily due to generic proliferation and pricing pressures [3]. While branded sales have plateaued, volume-driven growth remains viable owing to widespread adoption and population aging.
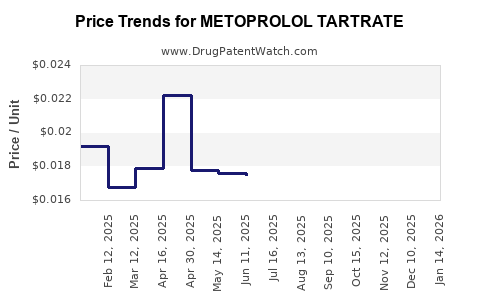
Pricing Strategies and Margins
Pricing is heavily influenced by generic competition; thus, profit margins are concentrated among early entrant manufacturers and regional players with lower cost structures. The shift towards biosimilars and generics sustains somewhat stable revenue streams despite intense price erosion.
Pipeline and Future Developments
Currently, no significant novel formulations or extended-release variants of metoprolol tartrate are in advanced development. However, innovations combining beta-blockers with novel agents or delivery systems could create targeted niche markets, potentially fostering incremental revenues.
Market Challenges and Risks
- Intense Price Competition: High generic penetration constricts revenue streams, compelling manufacturers to optimize operational efficiencies.
- Regulatory Barriers: Stringent quality standards and patent litigations can delay market entry of new competitors or formulations.
- Evolving Therapeutic Guidelines: The emergence of novel antihypertensives and device-based treatments might reduce reliance on traditional beta-blockers.
- Supply Chain Risks: Raw material shortages and manufacturing disruptions could impact availability, especially in low-income regions.
Strategic Outlook and Recommendations
- Focus on Cost Optimization: To sustain margins amid price erosion, manufacturers should streamline production and logistics.
- Diversify Portfolio: Introducing combination formulations or new delivery methods may mitigate risks associated with patent expiry.
- Expand in Emerging Markets: Tailored strategies to penetrate rapidly growing economies can sustain long-term revenue growth.
- Engage in Pharmacovigilance and Compliance: Maintaining regulatory alignment ensures uninterrupted market access.
Key Takeaways
- The global metoprolol tartrate market remains sizeable, driven by widespread use in cardiovascular conditions and demographic aging.
- Patent expirations and generic competition dominate the landscape, suppressing branded revenues but expanding access.
- Market growth pivots around demand in emerging markets, demographic shifts, and off-label applications.
- Price pressure necessitates operational efficiencies and product diversification to sustain profitability.
- Future opportunities lie in novel formulations, combination drugs, and strategic regional expansion, especially in markets with rising CVD burdens.
FAQs
1. What factors primarily influence the pricing of metoprolol tartrate in different markets?
Pricing is influenced by patent status, generic competition, regulatory standards, healthcare policies, and market-specific purchasing power.
2. How does patent expiration impact the financial trajectory of metoprolol tartrate?
Patent expiry typically leads to entry of generics, reducing branded drug revenues but expanding overall market volume and access, ultimately stabilizing or decreasing unit prices.
3. Are there any promising developments or alternative formulations for metoprolol tartrate?
While current pipelines lack major innovations, combination drugs and extended-release formulations could offer limited growth opportunities.
4. How does the rise of biosimilars and advanced antihypertensive agents influence the metoprolol market?
These developments intensify competition and may shift prescribing patterns, but metoprolol's established efficacy ensures continued relevance.
5. What strategies can pharmaceutical companies adopt to enhance profitability in this mature market?
Focusing on operational efficiencies, regional expansion, product line diversification, and exploring niche applications can offset declining margins.
References
[1] IQVIA. (2022). Global Cardiovascular Market Trends.
[2] World Health Organization. (2021). Cardiovascular Diseases Fact Sheet.
[3] MarketWatch. (2023). Metoprolol Tartrate Market Size and Forecast.