Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Lamotrigine, marketed under brand names such as Lamictal and Lamictal XR, is a widely prescribed anticonvulsant and mood stabilizer primarily used in the management of epilepsy and bipolar disorder. Since its FDA approval in 1994, lamotrigine has experienced sustained demand driven by its efficacy, safety profile, and expanding therapeutic indications. This report examines the evolving market landscape, competitive forces, regulatory influences, and financial prospects shaping the future trajectory of lamotrigine within the global pharmaceutical industry.
Market Overview and Current Landscape
Global Market Size
The global antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) market was valued at approximately USD 4.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach USD 6.5 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of around 5.5% [1]. Lamotrigine accounts for a significant segment of this market, attributed to its dual indications and favorable safety profile compared to older AEDs like phenytoin and carbamazepine.
Key Indications and Demographics
Lamotrigine's primary indications include:
- Epilepsy: Especially generalized tonic-clonic and partial seizures.
- Bipolar Disorder: Particularly for type I and II depression phases.
The drug's utilization spans across adult and pediatric populations, with increasing awareness and diagnosis of bipolar disorder fueling demand in developed markets such as North America and Europe.
Market Drivers
Therapeutic Efficacy and Safety Profile
Lamotrigine's favorable adverse event profile, especially a lower risk of sedation and cognitive impairment, distinguishes it from older AEDs. Its efficacy in preventing mood episodes in bipolar disorder broadens its usage spectrum [2].
Expanding Indications and Off-Label Uses
Ongoing research exploring lamotrigine in neuropathic pain, borderline personality disorder, and migraine prophylaxis could unlock additional revenue streams, contingent upon successful clinical validation.
Regulatory Approvals and Label Expansions
Regulatory authorities, including the FDA and EMA, have approved various formulations (immediate and extended-release) and pediatric indications, enhancing market penetration [3].
Market Challenges and Constraints
Generic Competition and Price Erosion
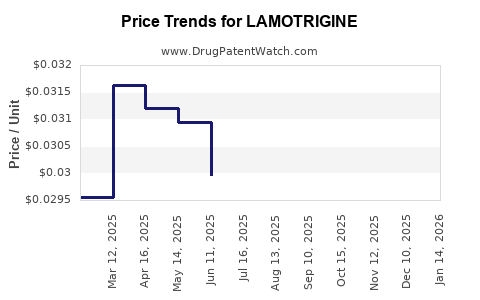
Once patent and exclusivity periods expire, generic manufacturers enter, intensifying price competition and compressing profit margins. Generic lamotrigine accounts for the majority of prescriptions globally, exerting downward pressure on branded formulations' revenue.
Safety Concerns and Adverse Effects
Risk of severe skin reactions (e.g., Stevens-Johnson syndrome) remains a concern, necessitating careful dosing and monitoring. Such safety considerations may influence prescribing patterns.
Regulatory and Patent Litigation Risks
Patent litigations, especially concerning formulation patents, can impact market exclusivity timelines and pricing strategies.
Competitive Landscape
Major pharmaceutical players include GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), Teva Pharmaceuticals, and Sun Pharma, which produce generic versions in addition to branded formulations. The consolidation of generic manufacturing has intensified price competition, typically leading to a stark decline in branded lamotrigine revenues upon patent expiry [4].
Innovative entities exploring novel delivery systems or combination therapies may alter the competitive landscape, but lamotrigine remains predominantly in the generic domain.
Financial Trajectory and Revenue Projections
Historical Revenue Trends
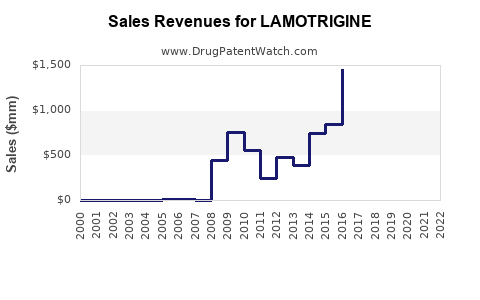
Branded lamotrigine sales peaked in the early 2010s, but with widespread generic availability by mid-2010s, revenues declined substantially in many markets. For example, GSK's branded lamotrigine monograph sales decreased by approximately 45% between 2013 and 2018 [5].
Forecast for 2023–2030
Given the industry trend toward commoditization post-generic entry, the revenue generated from lamotrigine is expected to decline further or stabilize at lower levels unless new formulations or indications are developed.
However, in emerging markets where generic penetration is less aggressive, the drug continues to generate robust revenues. Additionally, patent protections for specific formulations or delivery mechanisms could temporarily restrain generic competition and sustain higher profit margins.
Revenue estimates:
- Developed Markets: Anticipated to experience a compound annual decline of 3-5% due to market saturation and generic competition.
- Emerging Markets: Potential growth of 4-6% driven by increasing epilepsy and bipolar disorder diagnoses, coupled with lower generic penetration.
Potential Revenue Growth Avenues
- Formulation Innovation: Extended-release or proprietary delivery systems could command premium pricing.
- New Indications: Validated off-label uses or novel approved indications may rejuvenate sales.
- Partnerships and Licensing: Collaborations with biotech firms exploring combination therapies could unlock additional revenue streams.
Regulatory and Patent Strategies
The expiration dates of key patents significantly influence market dynamics. For lamotrigine, patent protections for specific formulations or methods of use have largely lapsed or are nearing expiry, facilitating generic entry. However, pharmaceutical companies may seek to extend exclusivity via secondary patents or formulation patents—though these are increasingly scrutinized for patent evergreening practices [6].
Regulatory agencies also impose risk management obligations, including risk evaluation and mitigation strategies (REMS), for safe prescribing, which influence market access and compliance costs.
Future Outlook and Market Opportunities
Innovation in Drug Delivery
Development of once-daily extended-release formulations with improved tolerability could sustain higher pricing and market share.
Biomarker and Personalized Medicine Approaches
Advances in pharmacogenomics may facilitate tailored treatments, optimizing lamotrigine efficacy and safety, and potentially leading to premium products.
Expanding Global Access
Emerging markets offer significant growth opportunities due to increasing diagnoses of epilepsy and bipolar disorder, coupled with unmet treatment needs and lower generic market saturation.
Challenges to Watch
- Stringent regulatory environments may delay approvals of new formulations.
- Competitive pricing from low-cost generics diminishes profitability.
- Prescriber preference shifts towards newer agents with perceived superior efficacy or safety profiles, such as levetiracetam or carbamazepine.
Key Takeaways
-
Market Maturity and Competition: Over the past decade, lamotrigine's market in developed countries has transitioned into a mature, highly competitive landscape dominated by generics, leading to declining branded sales.
-
Revenue Optimization Strategies: Innovating with new formulations, targeted indications, and strategic partnerships can offset revenue declines in matured markets.
-
Emerging Market Potential: Growth opportunities in unpenetrated or underserved regions stem from increasing epilepsy and bipolar disorder prevalence and lower drug penetration.
-
Regulatory Dynamics: Patent expiries and regulatory decisions shape competitive timing and pricing strategies, influencing revenue trajectories.
-
Investment Implications: Companies should pivot towards innovation, emerging market expansion, and personalized medicine to maximize lamotrigine's financial potential beyond patent protection.
FAQs
1. How does patent expiry affect lamotrigine’s market revenues?
Patent expiration leads to widespread generic manufacturing, significantly reducing branded drug prices and revenues. Companies relying on branded formulations see declining sales unless they develop new formulations or indications that extend exclusivity.
2. Are there ongoing efforts to expand lamotrigine's indications?
Yes. Research is ongoing into off-label applications like neuropathic pain and migraine prophylaxis, which could provide new revenue opportunities if supported by clinical trials and regulatory approval.
3. What role do generics play in lamotrigine’s market?
Generics dominate the market due to significant cost advantages, accounting for the majority of prescriptions globally. They exert downward pressure on prices and limit profitability for branded manufacturers.
4. Can pharmaceutical innovation revive lamotrigine's market presence?
Potentially. Innovative delivery systems, combinations with other agents, or personalized medicine approaches can command premium pricing and offset declines from generics.
5. What are the primary challenges facing lamotrigine’s future growth?
Main challenges include price erosion from generics, safety concerns (notably skin reactions), regulatory hurdles, and competition from newer agents perceived as having improved efficacy or tolerability.
References
[1] Grand View Research. Antiepileptic Drugs Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report. 2022-2030.
[2] Stern, T. et al. Efficacy and safety of lamotrigine in bipolar disorder: a systematic review. J Clin Psychiatry, 2015.
[3] U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Lamictal (lamotrigine) Label. 2022.
[4] IMS Health. Global Brand and Generic Market Dynamics. 2018.
[5] GSK Annual Report. Market Performance and Revenue Trends. 2013-2018.
[6] Kesselheim, A.S. et al. Evergreening Strategies in Pharmaceutical Patents. JAMA, 2017.
In summary, lamotrigine remains a significant player in the epilepsy and bipolar disorder treatment landscape. While market maturation and generic competition challenge its revenue potential, strategic innovation and emerging market penetration offer pathways to sustain and enhance its financial trajectory. Recognizing these dynamics enables pharmaceutical stakeholders to make informed investment and development decisions.