Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Lamivudine, commercially known as 3TC, is a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI), extensively utilized in the management of HIV/AIDS and hepatitis B virus (HBV) infections. Since its initial approval in the late 1990s, lamivudine has established itself as a cornerstone in antiretroviral therapy (ART), owing to its efficacy, safety profile, and affordability. This article analyzes the evolving market landscape and financial prospects of lamivudine within the global pharmaceutical sector, emphasizing driving forces, challenges, competitive dynamics, and future outlooks.
Market Overview
Historical Context and Market Penetration
Lamivudine was first approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1995 for HIV treatment. Its widespread adoption is attributed to its synergistic use in various multidrug regimens, particularly within fixed-dose combinations (FDCs) such as Epivir. Its dual activity against HBV further expanded its market scope, especially in regions with high HBV prevalence like Sub-Saharan Africa and Asia.
Despite the advent of newer antiretroviral agents boasting improved potency and resistance profiles, lamivudine remains a critical component in several treatment protocols due to its cost-effectiveness and established clinical data. The global HIV treatment market, valued at approximately $27 billion in 2022[1], continues to underpin demand for lamivudine-based products.
Geographical Market Distribution
The highest markets for lamivudine are concentrated in:
- North America and Europe: Mature markets with established healthcare infrastructure. Though competition from newer agents exists, lamivudine retains importance for generic formulations.
- Asia-Pacific: Rapidly expanding markets driven by large populations and increasing HIV/HBV testing and treatment initiatives.
- Africa: High HIV prevalence sustains demand, with WHO-initiated programs promoting generic formulations.
Market Drivers
1. Persistent HIV/AIDS Burden
According to UNAIDS, approximately 38 million people globally live with HIV/AIDS, with significant treatment coverage in developing regions. Lamivudine features in WHO-recommended ART regimens, ensuring steady market demand.
2. Cost-Effectiveness and Generics
Patents expiring over the last decade have accelerated the entry of generics, drastically reducing prices. In countries like India and China, affordable generic lamivudine supplies support large-scale treatment programs, particularly where healthcare budgets are constrained.
3. Hepatitis B Co-Infection Management
Chronic HBV infections impact over 290 million people worldwide[2]. Lamivudine’s antiviral activity against HBV solidifies its role in hepatitis management, especially in regions lacking access to newer agents like tenofovir.
4. Increasing Public-Private Initiatives
Global health agencies, such as WHO and Gilead Sciences, prioritize access to affordable antiretrovirals, bolstering lamivudine’s market stability.
Market Challenges
1. Resistance Development
Long-term monotherapy with lamivudine leads to high rates of viral resistance (notably the M184V mutation), compromising efficacy. Consequently, combination therapies incorporating tenofovir or emtricitabine are preferred, diminishing lamivudine’s standalone demand.
2. Competitive Landscape from Next-Generation Drugs
Drugs like tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) and tenofovir alafenamide (TAF) exhibit higher resistance barriers and better safety profiles, relegating lamivudine to adjunct or second-line therapy.
3. Patent Expirations and Market Saturation
While generics dominate, limited patent life extensions for some proprietary formulations influence pricing flexibilities and profitability margins.
4. Regulatory and Supply Chain Risks
Disruptions in supply chains, especially for low-cost generics from Asia, can impact market stability.
Competitive Dynamics
Major Market Players
- Gilead Sciences: Original developer of lamivudine; continues to hold significant market share through branded formulations.
- Indian Manufacturers: Companies such as Cipla, Hetero, and Mylan produce high-quality generics, expanding access in emerging economies.
- Other Players: Several local and regional manufacturers, especially in Africa and Southeast Asia, serve government and NGO procurement channels.
Strategic Movements
- Formulation Innovation: Fixed-dose combinations with lamivudine, tenofovir, and other agents consolidate market position.
- Pricing Strategies: Generics have driven prices down to less than $50 per patient/year in some regions, fostering wider access.
- Partnerships & Licensing: Multinational companies often partner with local manufacturers to navigate regional regulatory landscapes.
Financial Trajectory and Future Outlook
Revenue Trends
The global sales of lamivudine are primarily propelled by generic product sales, with estimates indicating annual revenues exceeding $3 billion globally. Compliance with public health initiatives and sustained HIV/AIDS prevalence underpin steady revenue streams.
Projection and Growth Opportunities
- Market Stability: Demand in existing markets is expected to remain steady due to ongoing treatment needs.
- Emerging Markets: Expanding access in Africa, Southeast Asia, and Latin America presents growth opportunities.
- Pipeline Developments: Advances in formulations—such as once-daily fixed-dose combinations—and potential novel indications could reinvigorate sales.
Potential Growth Drivers
- Broader integration into treatment guidelines for HBV and HIV.
- Increased procurement via global health programs.
- Continued patent expirations fostering price reductions and market expansion.
Threats to Growth
- Replacement by newer drugs with superior resistance profiles.
- Potential shifts toward tenofovir and emtricitabine-based regimens.
- Drug resistance necessitating combination therapy adjustments.
Economic Outlook
Forecasts predict a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 2-4% over the next five years, chiefly driven by generic sales and increased access initiatives, notwithstanding stagnant or declining revenue for proprietary formulations.
Regulatory Landscape
Global regulatory agencies continue to approve generic versions compliant with international standards, facilitating market entry. WHO prequalification status and stringent quality assurance underpin product acceptance in low- and middle-income countries.
Key Takeaways
- Steady Demand Amidst Competitive Shifts: Lamivudine remains vital in HIV and HBV management, especially within low-cost generic markets, despite competition from newer agents.
- Generics Driving Market Expansion: Patent expirations have catalyzed a surge in affordable formulations, broadening treatment access in underserved regions.
- Resistance Challenges: Long-term monotherapy limitations prompt reliance on combination therapies, limiting standalone lamivudine growth.
- Growth Opportunities in Emerging Markets: Expanding healthcare infrastructure and international aid programs bolster future sales prospects.
- Innovation and Formulation Development: Fixed-dose combinations and novel delivery mechanisms can enhance adherence and market share.
FAQs
1. How does resistance impact lamivudine’s market longevity?
Resistance development, particularly the M184V mutation in HIV, reduces lamivudine’s efficacy over time, leading clinicians to prefer combination regimens that include agents with higher resistance barriers. This has shifted demand from monotherapy to combination therapy, potentially limiting standalone lamivudine sales but sustaining its role in fixed-dose treatments.
2. What are the main markets for lamivudine in the coming decade?
Emerging markets in Africa, Asia-Pacific, and Latin America are poised for continued growth due to high HIV/HBV burdens and increasing access programs. Developed markets maintain demand through established generics and treatment guidelines integrating lamivudine within combination therapies.
3. Are there new formulations of lamivudine in development?
Current development efforts focus on fixed-dose combinations with other antiretrovirals to improve adherence and efficacy. Novel delivery systems or formulations are less prevalent due to existing patents on combination drugs, but generic manufacturers may explore bioequivalent formulations.
4. How do global health initiatives influence lamivudine’s market?
WHO and other agencies prioritize affordable access to essential medicines, massively supporting the production and distribution of generic lamivudine, especially in resource-limited settings, ensuring a stable demand trajectory.
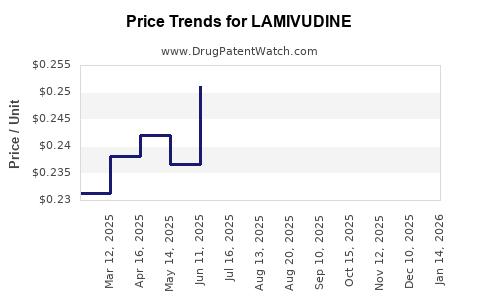
5. What are the key factors determining lamivudine’s price trends?
Generic competition, patent status, manufacturing costs, regulatory approvals, and procurement policies primarily influence pricing. Increased competition generally drives prices downward, making lamivudine a cost-effective choice.
References
[1] UNAIDS. (2022). Global HIV & AIDS statistics — 2022 fact sheet.
[2] World Health Organization. (2021). Global hepatitis report.