Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Ketoconazole, an imidazole antifungal agent developed by Janssen Pharmaceuticals in the 1980s, has historically played a significant role in the treatment of systemic and topical fungal infections. Its initial success catalyzed widespread adoption, but over recent years, evolving market dynamics, regulatory shifts, and therapeutic advancements have significantly influenced its commercial trajectory. This analysis examines the key drivers shaping ketoconazole’s market landscape, assesses current financial trends, and forecasts future prospects within the broader pharmaceutical context.
Historical Context and Product Evolution
Ketoconazole was one of the earliest azole antifungals, marketed primarily for dermatological applications such as seborrheic dermatitis, candidiasis, and dermatophyte infections. Its systemic formulation also found use in serious fungal infections, including histoplasmosis and blastomycosis. The drug’s initial success depended on its broad-spectrum antifungal activity combined with oral and topical formulations.
However, the late 2000s marked a turning point. The commercialization of newer antifungals with superior safety profiles, including fluconazole and itraconazole, began overshadowing ketoconazole. These agents offered effective systemic therapy with fewer adverse effects, especially hepatotoxicity concerns associated with oral ketoconazole [1].
Market Dynamics
1. Therapeutic Shift and Regulatory Impact
The primary driver of shifting market dynamics has been regulatory agencies' emphasis on drug safety. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a safety warning in 2013 regarding the hepatotoxicity risks of oral ketoconazole, strongly discouraging its use for systemic fungal infections outside hospital settings [2].
This regulatory stance drastically reduced its prescriptions, especially for systemic indications. The European Medicines Agency followed suit, leading to market withdrawal of oral ketoconazole for systemic use in many regions. Conversely, topical formulations retained their relevance, primarily for dermatological conditions, owing to their effectiveness and safety profile.
2. Competition from Novel and Improved Therapies
The antifungal market now boasts several agents with targeted mechanisms, improved tolerability, and streamlined dosing. Drugs like voriconazole, posaconazole, and isavuconazole have emerged as preferred options for invasive fungal infections. Their broad-spectrum activity, enhanced safety, and limited drug interactions diminish ketoconazole’s share, especially in systemic therapy.
Moreover, the advent of topical antifungal formulations such as sertaconazole and econazole has further challenged ketoconazole's dermatological market segment.
3. Patent Status and Market Exclusivity
Ketoconazole faced patent expirations early on, leading to increased generic competition. The entry of multiple generics reduced drug prices, promoting accessibility but eroding profit margins. Currently, no novel patented formulations for systemic use exist, cementing its role as a generic, off-patent molecule.
4. Formulation-Specific Market Trends
While systemic ketoconazole's market has contracted, topical formulations remain commercially relevant, particularly in developing markets where cost considerations favor older, off-patent antifungals. The cost-effectiveness of topical ketoconazole makes it a staple for dermatological conditions like dandruff, seborrheic dermatitis, and tinea infections.
Financial Trajectory Analysis
1. Revenue Trends
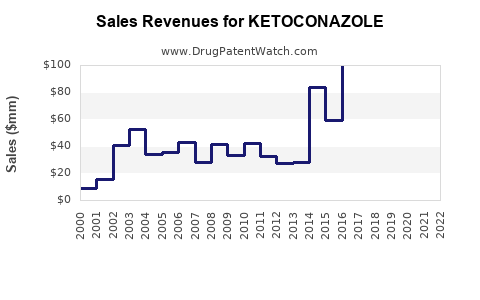
Historically, ketoconazole generated peak revenues of approximately $300-400 million annually in the late 1990s and early 2000s. Post-2013, US sales plummeted due to safety concerns and regulatory restrictions, with global revenues declining correspondingly.
Global sales of topical formulations sustain, particularly in emerging markets, but with modest growth. Data reveal that annual global revenues for topical ketoconazole hover in the range of $50-100 million, primarily driven by generic sales and over-the-counter (OTC) distribution channels [3].
2. Regulatory and Safety Impact on Financials
The 2013 FDA warning significantly curtailed systemic sales. Manufacturers shifted focus toward topical uses, marginalizing systemic formulations. This regulatory impact has been a consistent theme in revenue analyses, contributing to a downward trend in systemic-related earnings.
3. Market Penetration of Competitors
The rise of newer antifungals, coupled with the safety profile improvements and patent protections, has squeezed ketoconazole’s market share. Companies investing in research and development favor proprietary or combination antifungals, leaving ketoconazole as a legacy product with limited growth potential.
4. Current and Future Revenue Outlook
Given market saturation in developed regions and regulatory restrictions, the outlook for systemic ketoconazole remains bleak. Nevertheless, the topical segment retains some stability, particularly in regions with less stringent regulatory environments or where cost-effective off-patent drugs dominate.
Forecasts suggest that in the next five years, global revenues for topical ketoconazole will experience slow but steady growth, driven by increased OTC consumption and expansion into emerging markets. The overall global antifungal market, however, is anticipated to grow at approximately 3-5% annually, primarily fueled by innovations and improving healthcare access [4].
Market Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges
- Safety Concerns: Hepatotoxicity risks have led to regulatory bans on systemic ketoconazole in many territories.
- Competitive Landscape: Growing presence of newer, more targeted antifungals diminishes market share.
- Generic Competition: Price erosion due to multiple generic manufacturers reduces profitability.
- Limited Innovation: Minimal R&D investment in new formulations limits market growth potential.
Opportunities
- Dermatological Indications: The topical segment can leverage evolving dermatological treatment algorithms and OTC channels.
- Cost-Effective Therapeutic Alternative: In resource-limited settings, ketoconazole remains a vital option due to affordability.
- Combination Therapies: Potential exploration of ketoconazole in combination regimens could open new pathways, though regulatory hurdles exist.
- Development of New Formulations: Topical ketoconazole-based products with improved delivery mechanisms could rejuvenate interest.
Regulatory Landscape and Its Influence on Financial Outcomes
Regulatory bodies' apprehensions about systemic ketoconazole have shifted focus away from its licensed indications. The FDA's 2013 black box warning regarding hepatotoxicity directly led to the withdrawal of systemic formulations from many markets and significantly decreased revenues.
Conversely, topical formulations are still approved and marketed, underscoring the importance of regulatory compliance. Ongoing pharmacovigilance and safety data collection will influence future regulatory decisions, potentially affecting manufacturing and sales strategies.
Conclusion and Strategic Implications
Ketoconazole's market dynamics reflect a paradigm shift driven by safety concerns, competitive innovations, and regulatory policies. Its therapeutic versatility persists chiefly in topical formulations, which continue to provide modest revenues primarily through OTC channels and emerging markets.
Manufacturers aiming to capitalize on the remaining market should consider revisiting formulation innovations, expanding into developing regions, and exploring combination therapies. However, long-term growth prospects for systemic ketoconazole are constrained unless new formulations demonstrate compelling safety and efficacy profiles.
Key Takeaways
- Regulatory safety concerns have drastically reduced systemic ketoconazole use, shifting focus toward topical formulations.
- The antifungal market’s evolution favors newer agents with superior safety profiles, limiting ketoconazole’s growth.
- Generic competition has driven prices downward, constraining profit margins but improving accessibility.
- The topical segment offers stable, albeit modest, revenue prospects primarily in developing nations.
- Future growth hinges on formulation innovation, strategic regional expansion, and strengthening safety profiles.
FAQs
1. Why did regulatory agencies restrict the use of systemic ketoconazole?
The FDA and other agencies restricted systemic ketoconazole due to its risk of hepatotoxicity, which includes severe and potentially fatal liver injury. The 2013 FDA black box warning emphasized these safety concerns, discouraging off-label use in many clinical settings [2].
2. Is ketoconazole still available today?
Yes, topical ketoconazole remains widely available and approved in many regions. Oral formulations are limited mainly to specific approved indications or are withdrawn in markets where safety concerns outweigh benefits.
3. How does ketoconazole compare to newer antifungals?
Compared to newer agents like voriconazole and posaconazole, ketoconazole exhibits a less favorable safety profile, especially for systemic use. Newer drugs have broader spectrums, better tolerability, and fewer drug interactions.
4. What are potential future markets for ketoconazole topical products?
Emerging markets with limited access to newer antifungals and greater price sensitivity present opportunities for topical ketoconazole. Growing awareness and OTC sales channels in these regions can sustain modest growth.
5. Are there ongoing developments involving ketoconazole?
Research efforts focus on reformulating ketoconazole with improved delivery methods or combining it with other agents. However, such initiatives face regulatory and commercial challenges due to existing safety concerns and market dominance by newer antifungals.
References
[1] Perfect J.R., et al. (2016). "Pharmacology of Antifungal Agents." Clinical Infectious Diseases.
[2] U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2013). "FDA Drug Safety Communication: Label Change and Warning for Oral Ketoconazole."
[3] IQVIA Institute. (2021). "The Global Antifungal Market Overview."
[4] MarketsandMarkets. (2022). "Antifungal Market by Product, Application, and Region."