IMIQUIMOD Drug Patent Profile
✉ Email this page to a colleague
Which patents cover Imiquimod, and what generic alternatives are available?
Imiquimod is a drug marketed by Apotex Inc, Cosette, Encube, Fougera Pharms, Glenmark Pharms Inc, Padagis Israel, Strides Pharma, and Taro. and is included in nine NDAs.
The generic ingredient in IMIQUIMOD is imiquimod. There are fourteen drug master file entries for this compound. Eight suppliers are listed for this compound. Additional details are available on the imiquimod profile page.
DrugPatentWatch® Litigation and Generic Entry Outlook for Imiquimod
A generic version of IMIQUIMOD was approved as imiquimod by FOUGERA PHARMS on February 25th, 2010.
AI Deep Research
Questions you can ask:
- What is the 5 year forecast for IMIQUIMOD?
- What are the global sales for IMIQUIMOD?
- What is Average Wholesale Price for IMIQUIMOD?
Summary for IMIQUIMOD
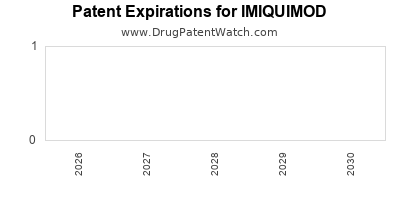
| US Patents: | 0 |
| Applicants: | 8 |
| NDAs: | 9 |
| Finished Product Suppliers / Packagers: | 5 |
| Raw Ingredient (Bulk) Api Vendors: | 1 |
| Clinical Trials: | 183 |
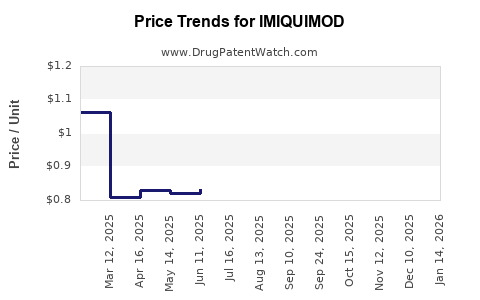
| Drug Prices: | Drug price information for IMIQUIMOD |
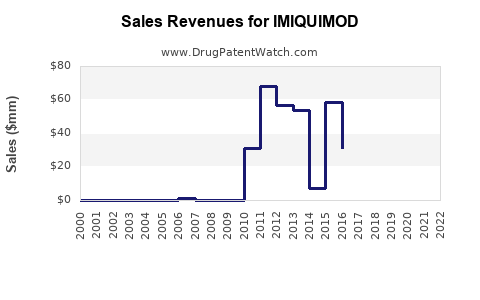
| Drug Sales Revenues: | Drug sales revenues for IMIQUIMOD |
| Patent Litigation and PTAB cases: | See patent lawsuits and PTAB cases for IMIQUIMOD |
| What excipients (inactive ingredients) are in IMIQUIMOD? | IMIQUIMOD excipients list |
| DailyMed Link: | IMIQUIMOD at DailyMed |
Recent Clinical Trials for IMIQUIMOD
Identify potential brand extensions & 505(b)(2) entrants
| Sponsor | Phase |
|---|---|
| Emory University | PHASE1 |
| Georgia Center for Oncology Research & Education | PHASE1 |
| University of Southern California | PHASE1 |
Pharmacology for IMIQUIMOD
| Mechanism of Action | Interferon Inducers |
| Physiological Effect | Increased Cytokine Activity Increased Cytokine Production |
Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) Classes for IMIQUIMOD
US Patents and Regulatory Information for IMIQUIMOD
| Applicant | Tradename | Generic Name | Dosage | NDA | Approval Date | TE | Type | RLD | RS | Patent No. | Patent Expiration | Product | Substance | Delist Req. | Exclusivity Expiration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apotex Inc | IMIQUIMOD | imiquimod | CREAM;TOPICAL | 091308-001 | Apr 6, 2012 | DISCN | No | No | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | ||||
| Strides Pharma | IMIQUIMOD | imiquimod | CREAM;TOPICAL | 202002-001 | Jun 24, 2014 | DISCN | No | No | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | ||||
| Fougera Pharms | IMIQUIMOD | imiquimod | CREAM;TOPICAL | 078548-001 | Feb 25, 2010 | AB | RX | No | No | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | |||
| Taro | IMIQUIMOD | imiquimod | CREAM;TOPICAL | 205971-001 | Jan 26, 2021 | AB | RX | No | No | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | |||
| Cosette | IMIQUIMOD | imiquimod | CREAM;TOPICAL | 200481-001 | Apr 18, 2011 | DISCN | No | No | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | ||||
| Encube | IMIQUIMOD | imiquimod | CREAM;TOPICAL | 091044-001 | Feb 28, 2011 | DISCN | No | No | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | ||||
| >Applicant | >Tradename | >Generic Name | >Dosage | >NDA | >Approval Date | >TE | >Type | >RLD | >RS | >Patent No. | >Patent Expiration | >Product | >Substance | >Delist Req. | >Exclusivity Expiration |
EU/EMA Drug Approvals for IMIQUIMOD
| Company | Drugname | Inn | Product Number / Indication | Status | Generic | Biosimilar | Orphan | Marketing Authorisation | Marketing Refusal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viatris Healthcare Limited | Aldara | imiquimod | EMEA/H/C/000179Imiquimod cream is indicated for the topical treatment of :External genital and perianal warts (condylomata acuminata) in adults.Small superficial basal cell carcinomas (sBCCs) in adults.Clinically typical, nonhyperkeratotic, nonhypertrophic actinic keratoses (AKs) on the face or scalp in immunocompetent adult patients when size or number of lesions limit the efficacy and/or acceptability of cryotherapy and other topical treatment options are contraindicated or less appropriate. | Authorised | no | no | no | 1998-09-18 | |
| Viatris Healthcare Limited | Zyclara | imiquimod | EMEA/H/C/002387Zyclara is indicated for the topical treatment of clinically typical, non-hyperkeratotic, non-hypertrophic, visible or palpable actinic keratosis of the full face or balding scalp in immunocompetent adults when other topical treatment options are contraindicated or less appropriate. | Authorised | no | no | no | 2012-08-23 | |
| Laboratoires 3M Santé | Zartra | imiquimod | EMEA/H/C/000180Imiquimod cream is indicated for the topical treatment of external genital and perianal warts (condyloma acuminata) in adult patients. | Withdrawn | no | no | no | 1998-09-18 | |
| >Company | >Drugname | >Inn | >Product Number / Indication | >Status | >Generic | >Biosimilar | >Orphan | >Marketing Authorisation | >Marketing Refusal |
Market Dynamics and Financial Trajectory of Imiquimod
More… ↓
