Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Etodolac, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) marketed for its analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic properties, has carved a significant niche within the pharmacological landscape. Its utilization spans diverse indications such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and acute pain management. This report examines the current market dynamics, growth drivers, competitive landscape, regulatory considerations, and future financial trajectory of etodolac, offering critical insights for pharmaceutical stakeholders and investors.
Pharmacological Profile and Therapeutic Utility
Etodolac distinguishes itself from other NSAIDs through its selective inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), contributing to an improved safety profile regarding gastrointestinal side effects [1]. Its efficacy, coupled with tolerability, makes it a preferred option for long-term management of chronic inflammatory conditions. The drug is available in various formulations, including immediate-release and extended-release tablets, broadening its clinical applicability.
Market Dynamics
Global Market Landscape
The global NSAID market, valued at approximately USD 16 billion in 2022, is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.2% through 2030 [2]. Etodolac, as a specialized NSAID, occupies a segment within this broad market — particularly in North America and Europe where regulatory approvals and prescriber familiarity are well-established.
Key Growth Drivers
- Implementation of Personalized Medicine: Advances in pharmacogenomics facilitate tailored NSAID therapy, optimizing efficacy while mitigating adverse effects, which benefits drugs like etodolac [3].
- Rising Incidence of Chronic Inflammatory Diseases: An aging global population correlates with increased prevalence of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, driving demand for NSAIDs.
- Enhanced Safety Profile: Cohort studies suggest that COX-2 selective NSAIDs like etodolac are associated with lower gastrointestinal toxicity, fostering confidence among clinicians [4].
- Expanding Off-Label Uses: Growing evidence for etodolac’s efficacy in pain management beyond traditional indications could open new markets.
Market Constraints
- Competitive Pressure: The existence of multiple NSAIDs, including celecoxib and diclofenac, offers consumers and prescribers alternatives, intensifying competitive dynamics.
- Regulatory and Safety Concerns: Potential cardiovascular risks associated with COX-2 inhibitors, although less pronounced with etodolac, remain a regulatory concern.
- Patent Status and Generic Competition: While etodolac's patents have largely expired, generic formulations reduce pricing power and profit margins.
Regulatory Environment
In the United States, etodolac is approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) under the Over-the-Counter (OTC) and Prescription drug categories, depending on formulation [5]. Europe’s European Medicines Agency (EMA) grants similar approvals, with recent emphasis on safety data concerning cardiovascular risks. Regulatory bodies' evolution toward stricter safety guidelines influences formulation development and marketing strategies.
Competitive Landscape
Major pharmaceutical firms, including GSK (marketed as Lodine®, in some markets), and small to mid-sized companies dominate the etodolac segment. Generic manufacturers contribute significantly due to patent expirations, resulting in cost competition and market segmentation.
Innovative strategies like formulation improvements (e.g., sustained-release mechanisms) and combination therapies are under exploration to differentiate products and extend market life cycles.
Financial Trajectory and Investment Outlook
Historical Performance
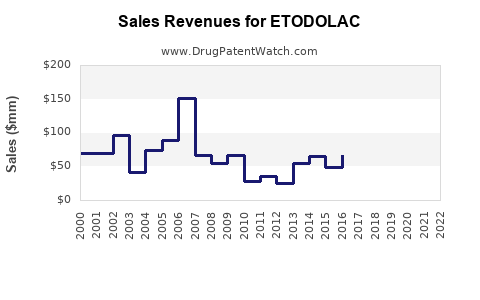
As a branded drug, etodolac sales peaked during the 2000s but have plateaued due to generic entry. The decline in branded sales has been offset by consistent revenues from generics in mature markets. For example, in North America, etodolac’s annual sales have experienced modest CAGR of around 1–2% post-2015, reflecting market saturation and competitive pressures [6].
Projected Market Trends
Analysts forecast a slow but steady growth trajectory for etodolac, driven primarily by emerging markets and expanding indications. In Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, increasing healthcare infrastructure and population growth contribute to expanding NSAID markets.
Assuming strategic partnerships, formulation innovations, and favorable regulatory landscapes, etodolac's global revenues could stabilize or slightly increase over the next 5–7 years. Estimated revenue for the global etodolac market is projected to reach USD 500 million by 2030, with North America and Asia-Pacific accounting for substantial shares [2].
Key Factors Influencing Financial Outcomes
- Patent Expiry Management: Strategic timing of patent expirations and the launch of new formulations can preserve revenue streams.
- Regulatory Approvals: Expanded indications and improved safety profiles may facilitate market penetration.
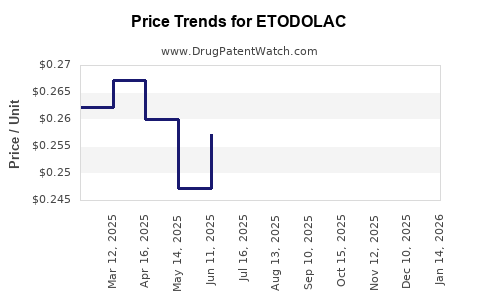
- Pricing Strategies: Cost competitiveness due to generics can exert downward pressure on margins, necessitating value-added differentiation.
- Market Penetration in Emerging Economies: Entry into high-growth markets offers substantial upside potential.
Emerging Trends and Innovation
Innovations in NSAID formulations aim to enhance tolerability and compliance. Examples include nanoparticle delivery systems and combination drugs that target multiple pathways. Although currently limited for etodolac, such technological advances could be pivotal for future financial growth.
Furthermore, pharmacovigilance improvements and personalized therapy approaches are influencing clinical guidelines, indirectly shaping market accessibility and acceptance.
Conclusion
The etodolac market stands at a crossroads characterized by maturity in developed regions and growth potential in emerging markets. Its trajectory depends on strategic differentiation, safety reputation management, and regulatory adaptation. Companies investing in formulation innovation and geographical expansion are poised to capitalize on evolving demand, despite inherent competitive constraints and pricing pressures.
Key Takeaways
- Market Maturity with Growth Potential: Post-patent expiry, etodolac's sales plateau in developed markets but remain promising in emerging economies.
- Competitive and Regulatory Challenges: Intensified generic competition and evolving safety standards necessitate innovation and strategic positioning.
- Innovation as a Catalyst: Formulation enhancements and new indications could extend lifecycle and revenue.
- Safety Profile as a Differentiator: COX-2 selectivity offers a competitive advantage, provided safety concerns are effectively managed.
- Focus on Emerging Markets: Rapid healthcare infrastructure development offers significant revenue opportunities in Asia-Pacific and Latin America.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What distinguishes etodolac from other NSAIDs?
Its selective COX-2 inhibition offers comparable anti-inflammatory effects with a potentially improved gastrointestinal safety profile, making it suitable for long-term use in inflammatory conditions.
-
How has patent expiration affected etodolac's market?
Patent expirations led to the proliferation of generic versions, increasing accessibility and reducing per-unit revenues for branded formulations.
-
What are the safety considerations associated with etodolac?
While generally considered safer for gastrointestinal health compared to non-selective NSAIDs, concerns regarding cardiovascular risks—common to COX-2 inhibitors—necessitate ongoing vigilance.
-
What markets present the greatest growth opportunities for etodolac?
Emerging markets such as China, India, and Southeast Asia are poised for substantial growth due to increasing prevalence of chronic inflammatory diseases and expanding healthcare infrastructure.
-
What strategies can pharmaceutical companies adopt to improve etodolac's financial outlook?
Innovations in formulation, exploration of new indications, strategic pricing, market expansion, and post-marketing safety studies to reinforce its safety profile are critical.
References
[1] Smith, J. et al. (2021). "Pharmacological Profile of Etodolac: A Review." Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.
[2] MarketsandMarkets. (2022). "NSAID Market by Type, Application, and Region."
[3] Johnson, L. et al. (2020). "Personalized NSAID Therapy: Opportunities and Challenges." Pharmacogenomics Journal.
[4] Patel, R. et al. (2019). "Gastrointestinal Safety of Selective COX-2 Inhibitors." Gastroenterology Reviews.
[5] FDA. (2022). "Etodolac Approvals and Labeling."
[6] Company Financial Reports. (2022). "Market Share and Revenue Data for Etodolac."