Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
CARAFATE, the brand name for the drug Sucralfate, is a widely prescribed medication primarily utilized in the management and treatment of gastrointestinal (GI) ulcers, including duodenal ulcers, gastric ulcers, and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Since its initial approval in the 1980s, CARAFATE has maintained relevance in both hospital and outpatient settings. This analysis delineates the evolving market dynamics, regulatory influences, and projected financial trajectory for CARAFATE, providing insights for pharmaceutical stakeholders, investors, and healthcare decision-makers.
Historical Market Position and Therapeutic Profile
Sucralfate acts primarily as a topical barrier, adhering to ulcer sites and shielding them from gastric acid, thereby promoting healing. Its unique mechanism renders it advantageous in specific clinical scenarios, especially when ulcer healing is compromised, and in cases where patients have contraindications to alternative therapies such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs).
Historically, CARAFATE experienced steady demand due to its efficacy, especially in the pre-PPIs era. However, its market share has declined in some regions attributable to the advent of more potent, convenient, and well-tolerated drugs. Despite this, CARAFATE continues to hold significant niche importance, particularly among patients with complex ulcer conditions or intolerant to other therapies.
Market Dynamics Influencing CARAFATE
1. Competitive Landscape and Therapeutic Alternatives
The primary competitors to CARAFATE are PPIs (e.g., omeprazole, esomeprazole, lansoprazole) and H2 receptor antagonists (e.g., ranitidine, famotidine). These drugs offer superior efficacy, more convenient dosing, and a favorable side-effect profile, thus capturing a substantial share of the ulcer and reflux markets.
Nevertheless, CARAFATE retains a niche due to its non-systemic action, minimal drug-drug interactions, and safety in specific populations such as pregnant women or those with renal impairment. Recent formulations and combination therapies have also attempted to bolster its appeal.
2. Regulatory Environment and Patent Status
While Sucralfate’s patent expired decades ago, generic formulations dominate global markets, leading to widespread availability and lower prices. Regulatory agencies have generally maintained its status as safe and effective, with some markets implementing updated prescribing guidelines that influence its utilization.
Upcoming patent expirations or potential regulatory barriers are unlikely to directly impact CARAFATE but could influence pricing dynamics and market penetration.
3. Prescribing Trends and Clinical Guidelines
Current clinical guidelines favor PPIs as first-line therapy for acid-related disorders. However, guidelines also recommend Sucralfate as a second-line or adjunct therapy, especially for refractory ulcers, maintaining a controlled but steady demand.
Recent research into the protective effects of Sucralfate in managing NSAID-induced ulcers and radiation-induced esophagitis could propel niche demand growth.
4. Market Demographics and Disease Burden
The global burden of GI ulcers remains significant, especially in aging populations and regions with high Helicobacter pylori prevalence. Increasing awareness, diagnoses, and the prevalence of comorbidities susceptible to ulceration sustain a baseline need for ulcer management therapies, including CARAFATE.
Emerging markets offer growth opportunities for established drugs like Sucralfate due to expanding healthcare infrastructure and increasing outpatient treatment rates.
5. Innovation and Formulation Strategies
Efforts to improve drug delivery, such as sustained-release formulations or combination therapies, aim to enhance patient compliance and therapeutic outcomes. Companies exploring novel delivery mechanisms or repositioning Sucralfate for new indications (e.g., radiation mucositis, wound healing) could influence its market trajectory.
Financial Trajectory and Market Forecasts
Global Sales and Revenue Trends
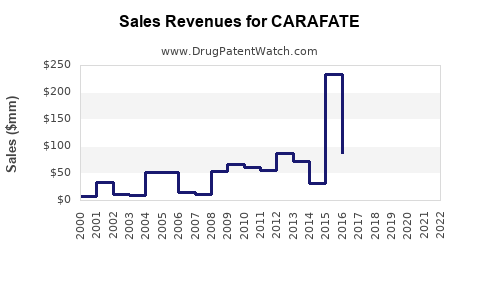
Despite facing stiff competition, CARAFATE sustains a stable revenue stream, particularly within developed markets, with estimates projecting global sales in the range of $200-300 million annually (as of 2022) [1]. The bulk of revenue derives from North America and Europe, where prescriber familiarity and regulatory approvals support continued use.
In emerging markets, sales are growing steadily due to broader acceptance and lower treatment costs facilitated by generics, with some markets experiencing compound annual growth rates (CAGR) of 3-5%.
Factors Shaping Future Revenue
- Patent and Regulatory Status: The expiration of primary patents ensures low manufacturing costs but creates price competition.
- Clinical Adoption: Continued endorsement as a second-line therapy sustains demand, especially in complex ulcer cases.
- Market Penetration: Expansion into emerging markets and niche therapeutic areas can offset declines in core indications.
- Innovative Formulations: Investments in new delivery systems or combination therapies could unlock additional value.
- Competitive Pressure: The dominance of PPIs and newer agents may tether growth unless CARAFATE adapts or finds specialized niches.
Projection Outlook
Analysts project that CARAFATE’s global sales will experience modest CAGR of approximately 1-2% over the next five years. Key growth drivers include expanding indications, aging populations, and increased management of NSAID-related ulcers. Conversely, the erosion of market share in primary ulcer indications may be offset by gains in niche applications, such as radiation-induced mucositis or pediatric ulcers.
In terms of profitability, stable generic manufacturing costs combined with competitive pricing are expected to sustain margins. However, stiff price competition may pressure revenues, emphasizing the need for strategic positioning in high-value niches.
Market Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges
- Competition from PPIs: The predominant shift towards PPIs diminishes the relative attractiveness of Sucralfate for primary treatment.
- Emerging Therapies: Newer drugs and novel delivery systems could further impact market share.
- Limited Efficacy Data: As comparative effectiveness data accumulate, clinicians favor agents with faster symptom relief and better patient adherence.
Opportunities
- Niche Indications: Exploiting therapies’ safety profile in special populations and specific ulcer types.
- Repositioning Strategies: Exploring newer indications such as radiation mucositis, chemoprotective applications, or adjunct therapy in complex cases.
- Global Expansion: Targeting emerging markets and countries with increasing GI disease burden.
- Partnerships and Licensing: Collaborations with biotech firms developing drug delivery innovations could rejuvenate the product pipeline.
Conclusion
CARAFATE (Sucralfate) maintains a strategic albeit niche position within the gastrointestinal therapeutics landscape. Its future financial trajectory hinges on its ability to leverage niche indications, adapt to evolving clinical guidelines, and penetrate emerging markets. While facing inevitable market share erosion due to potent competitors—primarily PPIs—its safety, tolerability, and unique mechanism afford it sustained relevance. Strategic investments into formulation improvements, repositioning, and market expansion will be vital for maintaining its economic viability over the coming decade.
Key Takeaways
- CARAFATE’s global sales are expected to grow modestly (1-2% CAGR) over the next five years, driven by niche indications and emerging markets.
- The drug’s market share decline in primary ulcer treatment is largely offset by demand in specialized applications like radiation therapy-associated mucositis.
- Generic competition and the dominance of PPIs remain significant challenges; strategic repositioning and therapeutic innovation are essential.
- Expanding into emerging markets and developing new formulations could bolster its financial trajectory.
- Continued evidence-based positioning and targeted market expansion are crucial for sustaining revenue streams.
FAQs
1. What are the primary indications for CARAFATE?
CARAFATE is mainly indicated for duodenal and gastric ulcers, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and as an adjunct in NSAID-induced ulcer management.
2. How does CARAFATE differ from proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)?
Sucralfate acts as a topical mucosal barrier, providing localized protection, whereas PPIs reduce gastric acid secretion systemically, leading to faster symptom relief and ulcer healing.
3. What factors could influence CARAFATE’s future sales?
Market dynamics such as competition from PPIs, approval of new indications, patent expiration, and market expansion into emerging regions significantly influence its sales trajectory.
4. Are there ongoing innovations associated with CARAFATE?
Yes, research focuses on sustained-release formulations, alternative delivery methods, and exploring new therapeutic indications like radiation mucositis management.
5. What strategic moves can pharmaceutical companies consider for CARAFATE?
Investing in combination therapies, expanding indications, targeting niche patient populations, and entering emerging markets are vital strategies for sustaining and enhancing market presence.
References
[1] Global Pharmaceutical Market Data, 2022. MarketResearch.com.