Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Sulfasalazine, a disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug (DMARD), has maintained relevance in the management of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Originally developed in the 1950s, it has a long-standing history in pharmacotherapy. As demand for targeted, affordable treatments persists, understanding its market dynamics and financial trajectory is vital for stakeholders, including pharmaceutical companies, investors, and healthcare providers.
Pharmacological Profile and Clinical Utility
Sulfasalazine is a prodrug that metabolizes into 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) and sulfapyridine, exerting anti-inflammatory effects mainly in the gastrointestinal tract. Its primary indications include ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease, with secondary use in RA. Its efficacy, safety profile, and cost-effectiveness underpin its continued utilization, especially in regions with limited access to biologics.
Market Landscape and Competitive Positioning
Key Market Players
Major pharmaceutical manufacturers such as CDA Therapeutics, Solco Healthcare, and Teva Pharmaceuticals produce sulfasalazine formulations. Generic versions dominate the market globally, driven by extensive patent expirations and regulatory approvals worldwide. The widespread availability of generics has significantly suppressed prices, constraining revenue potential but expanding accessibility.
Market Drivers
- Prevalence of IBD and RA: Rising incidence rates across North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific sustain steady demand.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Sulfasalazine remains a preferred option in low- and middle-income countries due to its affordability compared to biologic therapies.
- Guideline Recommendations: Clinical guidelines continue endorsing sulfasalazine as first-line or adjunct therapy in specific cases of RA and IBD.
- Patient and Physician Preference: A long-established safety profile and familiarity support ongoing use.
Market Challenges
- Emergence of Biologics: Monoclonal antibodies and targeted DMARDs have demonstrated superior efficacy in some cases, leading to decreased sulfasalazine utilization.
- Toxicity Profile: Potential adverse effects, including hypersensitivity reactions, hepatotoxicity, and hematological issues, restrict widespread long-term use.
- Patient Compliance: Side effects such as gastrointestinal discomfort and alopecia may impact adherence.
Market Dynamics Influences
Regulatory Environment
Global regulatory agencies, including the FDA and EMA, continue to approve generic sulfasalazine formulations. They impose strict quality control, which sustains competition but also limits differentiation. Regulatory pathways for new formulations or combination therapies are complex, impacting innovation.
Pricing and Reimbursement Policies
In markets with government-controlled pricing and reimbursement schemes, sulfasalazine's affordability maintains its position. However, price pressures and reimbursement limitations in certain regions may constrain revenue growth.
Innovation and Formulation Developments
Current trends focus on improving formulations—such as extended-release or enteric-coated tablets—to enhance patient tolerability and compliance. Some research explores combination therapies or derivatives, but widespread adoption remains nascent.
Financial Trajectory and Revenue Outlook
Historical Revenue Analysis
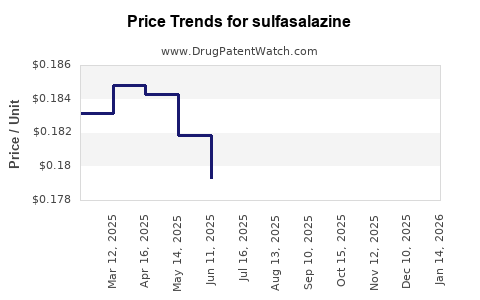
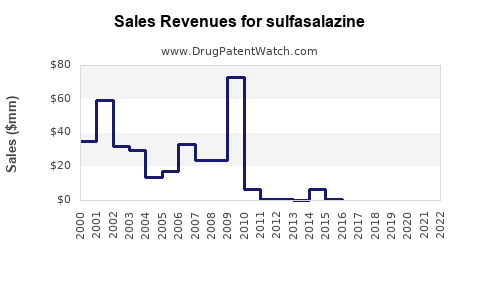
The global sulfasalazine market was valued at approximately USD 200 million in 2022, with steady growth driven predominantly by emerging markets. The revenue is underpinned by generic sales, with minimal branded premiums due to extensive patent expiries.
Forecast and Future Trends
Analysts project a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 2-3% over the next five years, primarily sustained by the increasing prevalence of IBD and RA. However, this growth is constrained by market saturation and competition from biologics.
Revenue Impact of Market Dynamics
- Pricing Pressures: Competitive generics reduce profit margins.
- Market Penetration: Expanding into under-served regions could offset mature-market stagnation.
- Therapeutic Alternatives: Rising confidence in biologic treatments may gradually supplant sulfasalazine use, especially in high-income markets.
Regional Market Insights
- North America: Despite mature markets, the high prevalence of RA and IBD sustains steady demand. However, biologics' dominance limits upside.
- Europe: Similar trends as North America, with regulatory constraints fostering generics' prominence.
- Asia-Pacific: Rapidly growing markets with increasing disease prevalence and cost sensitivity favor sulfasalazine's use, promising higher growth potential.
- LATAM and Africa: Lower treatment penetration and economic constraints maintain a steady or modest market size.
Market Entry Strategies
To capitalize on sulfasalazine's market potential, pharmaceutical companies focus on:
- Differentiated Formulations: Developing improved-tolerability versions.
- Market Expansion: Targeting regions with limited access to advanced therapies.
- Cost-Effective Packaging and Pricing: Ensuring affordability in price-sensitive markets.
- Partnerships and Collaborations: Working with local distributors and healthcare providers to increase distribution channels.
Conclusion
Sulfasalazine's market characteristics are shaped by its longstanding clinical utility, generic availability, and the evolving treatment landscape for IBD and RA. While current revenue growth is modest due to market saturation and competition from novel agents, targeted strategies focused on emerging markets and formulation innovations can bolster its financial trajectory. The drug’s role remains critical in resource-constrained settings, implying a continued, albeit moderated, market presence.
Key Takeaways
- Steady Demand: Sulfasalazine’s affordability and existing clinical guidelines uphold its relevance in IBD and RA treatment worldwide.
- Competition from Biologics: Innovations in therapies pose a risk to sulfasalazine’s market share, especially in high-income regions.
- Regional Variations: Emerging markets present growth opportunities due to rising disease prevalence and cost considerations.
- Price Sensitivity: Generics dominate, leading to suppressed profit margins but wider access.
- Innovative Formulations: Development of better-tolerated or extended-release versions can sustain interest and expand patient adherence.
FAQs
1. How does the patent status impact the sulfasalazine market?
Patent expirations in the past have facilitated widespread generic manufacturing, decreasing prices and limiting profit margins but broadening access globally.
2. What are the main competitors to sulfasalazine in the treatment of IBD and RA?
Biologics such as infliximab, adalimumab, and newer small molecules like tofacitinib offer superior efficacy in some cases, challenging sulfasalazine’s position.
3. Are there ongoing innovations or formulations that could extend sulfasalazine’s market life?
Yes, extended-release formulations and combination therapies are under investigation to improve tolerability and adherence, potentially extending its market viability.
4. How region-specific factors influence sulfasalazine’s market?
In low- and middle-income countries, cost-effective, easily accessible generics favor sulfasalazine. Conversely, in high-income regions, biologics’ superior efficacy may diminish its use.
5. What strategic moves can pharmaceutical companies adopt to maximize sulfasalazine’s market share?
Developing improved formulations, expanding into underserved markets, and implementing competitive pricing strategies are effective approaches.
References
- [1] Global Market Insights, “Pharmaceutical Drugs Market Report,” 2022.
- [2] World Health Organization, “Prevalence and Incidence of Inflammatory Bowel Disease,” 2021.
- [3] FDA Database, “Approved Generic Drugs,” 2022.
- [4] Clinical guidelines from the American College of Rheumatology, 2021.
- [5] Pharma intelligence, “Biologic Therapies in Rheumatology,” 2022.