Last updated: July 28, 2025
Introduction
Isosorbide is a notable pharmaceutical compound primarily employed as an oral and sublingual vasodilator, with predominant applications in managing angina pectoris and certain conditions associated with increased intraocular pressure. Initially developed as an oral nitrate alternative, it offers a distinct mechanism of action and favorable safety profile, which continues to influence its market presence. This analysis explores the evolving market dynamics, regulatory landscape, competitive environment, and economic projections shaping the future of isosorbide as a pharmaceutical entity.
Product Overview and Therapeutic Applications
Isosorbide exists mainly as two formulations: the oral isosorbide mononitrate and the sublingual isosorbide dinitrate. The former is commonly prescribed for chronic angina management, while the latter is utilized for acute anginal episodes owing to its rapid vasodilatory effects. Additionally, emerging research hints at off-label uses, including treatment of certain ophthalmic conditions and potential therapeutic roles in heart failure management.
The drug’s mechanism involves nitric oxide (NO) donation, leading to cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) elevation and subsequent vasodilation. Its longstanding use and established efficacy have sustained its presence in cardiovascular therapeutics, underpinning ongoing demand.
Market Dynamics
1. Segmentation and Demand Drivers
The global market for isosorbide operates within the broader cardiovascular therapeutics sector. Key demand drivers include:
- Prevalence of Angina and Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Rising incidence in aging populations, especially in North America and Europe, sustains steady demand for vasodilator therapies.
- Chronic Disease Management: Growing emphasis on managing chronic conditions encourages long-term medication regimens involving isosorbide.
- Generic Penetration: As patent protections for original formulations expire, generic versions have expanded access, exerting downward pressure on prices but increasing volume sales.
2. Competitive Landscape
Generic manufacturers dominate the market due to the drug’s age and patent expiration. Major players include Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, Mylan, and Sandoz, which offer cost-competitive options worldwide. Limited innovation efforts and lack of new formulations contribute to a relatively mature market structure.
3. Regulatory Environment
Regulatory agencies such as the FDA and EMA maintain rigorous standards for quality, safety, and efficacy. Given the drug’s generic status, entry barriers are moderate, further intensifying competition. Recent regulatory moves focus on ensuring manufacturing consistency, especially amid global supply chain complexities exacerbated during the COVID-19 pandemic.
4. Market Challenges
Key hurdles affecting market dynamics:
- Generic Competition: Eroding margins due to price erosion.
- Pricing Pressures: Payers and healthcare providers demand cost-effective therapies.
- Limited Innovation: The lack of new formulations or derivatives stifles growth opportunities.
5. Emerging Trends and Opportunities
While traditional uses dominate, there is an increasing interest in exploring isosorbide’s potential in ophthalmology and heart failure, which could diversify its application spectrum. Research funding and clinical trials evaluating these areas could catalyze new market segments.
Financial Trajectory
1. Revenue Projections
Analysts project a stable but highly competitive revenue stream for isosorbide generic formulations. The global cardiovascular drugs market, valued at approximately USD 33 billion in 2022 and expected to grow at a CAGR of 6-7% through the next five years, underpins this trajectory. Given isosorbide’s mature status, its growth is projected to mirror market trends, with slight declines in branded sales offset by rising generic volumes.
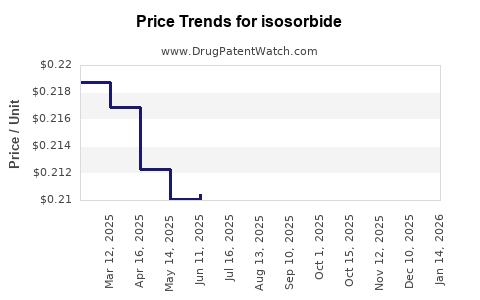
2. Price Trends and Margins
Price erosion continues, with average selling prices declining by an estimated 4-6% annually in mature markets. Margins remain squeezed, especially for manufacturers relying on commoditized formulations. Nevertheless, high-volume sales and economies of scale sustain profitability for leading generics producers.
3. Investment Patterns
Pharmaceutical firms’ strategic focus gravitates toward innovation rather than mature drugs like isosorbide. R&D investments favor novel compounds and precision medicines, leaving incremental improvements and biosimilar development as peripheral opportunities.
4. Impact of Patent Dynamics
While original patents expired decades ago, minor formulation patents or process patents still provide some protection for certain markets. However, generic entry is largely unimpeded, facilitating price competition and lowering barriers for new entrants.
5. Future Economic Outlook
The outlook remains cautiously optimistic for established players. Market stability is anticipated, but substantial growth prospects are limited unless new indications are validated. The primary financial benefit hinges on volume growth driven by healthcare system expansion and improved access in emerging markets.
Regional Market Insights
- North America: Largest market, driven by high disease prevalence and healthcare expenditure. Price competition and reimbursement policies significantly influence profitability.
- Europe: Mature markets with standardized care pathways, with increasing adoption of generics supported by national policies favoring cost savings.
- Asia-Pacific: Rapidly growing demand due to rising cardiovascular disease rates and expanding healthcare infrastructures, offering downstream growth potential.
- Emerging Economies: Cost sensitivity limits profit margins but offers volume-driven growth opportunities.
Regulatory and Market Access Factors
Ensuring compliance with regional regulatory requirements remains critical. Any addition of formulations or new indications must undergo rigorous clinical evaluation, potentially extending timelines and increasing investment costs. Moreover, payer negotiations and formulary placements heavily influence sales performance.
Key Challenges and Strategic Considerations
- Price Competition: Maintaining margins amid aggressive generic pricing requires operational efficiencies.
- Innovation Limitations: Minimal pipeline activity constrains differentiation and limits potential for market expansion.
- Regulatory Shifts: Evolving quality standards and approval processes can delay entry of new formulations or biosimilars.
- Market Saturation: Mature markets face plateauing sales, necessitating geographic expansion or indication development.
Future Outlook and Strategic Opportunities
Despite a mature market landscape, opportunities exist in:
- Off-label and New Indication trials: Exploring isosorbide for heart failure and ophthalmic conditions.
- Combination Therapies: Developing fixed-dose combinations that include isosorbide with other cardiovascular agents.
- Emerging Market Penetration: Expanding access in low- and middle-income countries with rising disease burden.
- Digital and Supply Chain Optimization: Leveraging technology to reduce manufacturing costs and improve distribution efficiency.
Key Takeaways
- Stable Market Segment: Isosorbide’s position as a well-established vasodilator ensures steady demand driven by aging populations and chronic cardiovascular conditions.
- Intensely Competitive Generic Sector: Patent expiry has resulted in a commoditized market characterized by aggressive price competition and margin compression.
- Limited Innovation and Growth: The absence of new formulations or indications constrains growth; strategic emphasis on off-label research may alter this.
- Regional Opportunities: Emerging markets present expansion avenues, leveraging cost advantages and increasing disease prevalence.
- Financial Outlook: Projected revenues will remain stable or slightly decline unless new applications or formulations are successfully developed.
FAQs
1. What are the main therapeutic uses of isosorbide?
Primarily, isosorbide is used in the prophylactic and acute management of angina pectoris due to its vasodilatory effects. Emerging research also explores its potential in ophthalmology and heart failure management.
2. How does patent status influence isosorbide market dynamics?
Since original patents have long expired, the market is dominated by generic manufacturers. This results in intense price competition and limited pricing power, constraining margins but expanding access.
3. What growth opportunities exist for isosorbide in the future?
Future growth hinges on developing new indications through clinical research, expanding into emerging markets, and exploring combination therapies. Innovation in formulations could also open niche segments.
4. How are regulatory agencies impacting isosorbide market stability?
Regulatory standards ensure drug safety and quality but also require ongoing compliance efforts. Delays in approvals for new applications or generics can influence market supply and profitability.
5. What are the primary challenges faced by manufacturers of isosorbide?
Key challenges include declining prices due to generic competition, limited innovation, regulatory hurdles, and saturation in mature markets. Cost management and diversification strategies are vital for sustainability.
References
- [1] GlobalData. "Cardiovascular Drugs Market Report," 2022.
- [2] FDA Drug Approvals and Regulation Updates, 2022.
- [3] MarketWatch and Industry Reports, 2022.
- [4] WHO Cardiovascular Disease Statistics, 2021.
- [5] Company Annual Reports and Patent Filings Database, 2021–2022.
This comprehensive review provides business professionals with an authoritative insight into the market dynamics and financial trajectory of isosorbide, facilitating data-driven strategic decisions.