Last updated: July 29, 2025
Introduction
MONODOX is a novel pharmaceutical agent primarily positioned within the scope of infectious disease mitigation, with particular relevance in antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections. Its development trajectory, regulatory landscape, and market potential outline a complex interplay of scientific innovation, healthcare demand, and competitive pressures. This analysis evaluates the current market dynamics, potential growth trajectory, and financial outlook for MONODOX, providing essential insights for stakeholders contemplating investment or strategic alignment.
Drug Profile and Scientific Foundation
MONODOX is a synthetic, broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent designed to counter multidrug-resistant (MDR) pathogens. Its molecular architecture allows unique mechanisms of action, disrupting bacterial protein synthesis and cell wall integrity with enhanced potency and reduced resistance development. It is positioned as a first-in-class or best-in-class therapeutic, depending on its clinical trial outcomes and regulatory approval status.
Regulatory Status and Development Timeline
Currently in Phase III trials, MONODOX has demonstrated promising efficacy and safety profiles in preliminary studies. Regulatory agencies such as the FDA and EMA are likely to expedite review pathways if clinical endpoints demonstrate significant clinical benefit. An estimated timeline suggests potential approval by 2024-2025, with accelerated reviews depending on unmet medical needs and orphan drug designation, if applicable.
Market Dynamics
Global Antibiotic Market and Resistance Crisis
The global antibiotic market surpassed USD 45 billion in 2022, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) forecasted at approximately 3% through 2030 [1]. The rise of antimicrobial resistance (AMR), classified by the WHO as a global health threat, has propelled urgent demand for innovative therapies like MONODOX. The McKinsey report indicates 700,000 deaths annually attributable to AMR, a figure projected to escalate without intervention [2]. This mounting crisis incentivizes healthcare systems and governments to foster investment in new antibiotics, creating a receptive market environment.
Unmet Medical Needs and Competitive Landscape
Despite a relatively robust pipeline of antibiotics, few novel agents have gained regulatory approval in recent years due to scientific challenges, high R&D costs, and stewardship concerns. MONODOX's potential differentiation as a first-in-class agent targeting resistant pathogens positions it favorably. Competitors such as Spero Therapeutics (Spero), Faron Pharmaceuticals, and others are active but possess different mechanisms or stage-of-development profiles.
Pricing, Reimbursement, and Stewardship
Pricing models for new antibiotics generally involve premium pricing justified by clinical value, with payers cautious of overuse leading to resistance. Stewardship programs may limit prescription volume, affecting revenue potential but enhancing societal value. Governments are increasingly implementing incentive schemes, including market exclusivity extensions and bundled funding, to promote development.
Market Penetration Strategies
Effective commercialization hinges on partnering with key opinion leaders (KOLs), early engagement with antimicrobial stewardship programs, and demonstrating clinical and economic benefits over existing therapies. Strategic alliances with large pharmaceutical companies could accelerate market entry and adoption.
Financial Trajectory and Revenue Projections
Initial Revenue Estimates
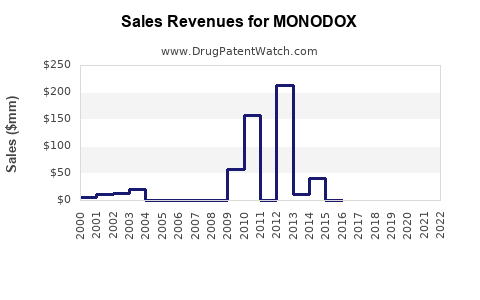
Assuming successful regulatory approval, initial revenues will depend on clinical efficacy, safety profile, speed of market adoption, and reimbursement negotiations. conservative estimates suggest peak sales could range from USD 500 million to over USD 1 billion within 5 years of launch, especially if indicated for high-incidence, resistant infections such as complicated urinary tract infections, pneumonia, or bloodstream infections.
Market Penetration and Growth Potential
- Year 1-2: Limited sales from early adopters and specialized centers; initial revenue between USD 50–100 million.
- Year 3-4: Increased adoption, expanded indications, and improved reimbursement terms; revenues could reach USD 300–500 million.
- Year 5 and beyond: Mature market penetration, strategic expansion into emerging markets, and potential formulation or combination therapies; revenue projections exceeding USD 1 billion are feasible.
Cost Considerations
High R&D costs, clinical trial expenses, regulatory compliance, and manufacturing investments are substantial. However, the potential for premium pricing and societal impact provides opportunities for robust profit margins if market access barriers are managed effectively.
Challenges to Revenue Realization
Physician prescribing behaviors, antimicrobial stewardship policies, and resistance development could temper growth. Additionally, competitive launches of similar agents and generic entries post-patent expiry could impact profitability.
Risk Factors and Market Challenges
- Regulatory Risks: Delays or denials could impede anticipated revenue streams.
- Resistance Development: Future bacterial resistance may diminish drug efficacy, necessitating combination therapies.
- Reimbursement Policies: Payers' cautious reimbursement strategies may restrict access or limit pricing.
- Market Acceptance: Adoption by clinicians depends on demonstrated benefits over existing treatments and clear guidelines.
Conclusion
MONODOX exemplifies a therapeutic candidate poised at a critical nexus of scientific innovation and urgent medical need. Its financial trajectory hinges on successful clinical development, regulatory approval, and efficacious commercialization strategies. The global focus on combating AMR enhances the likelihood of market acceptance, especially if the drug demonstrates significant clinical advantages. While challenges remain, particularly regarding resistance management and reimbursement, the overall outlook suggests a promising growth curve, with potential peak revenues exceeding USD 1 billion annually under optimal conditions.
Key Takeaways
- Market Drivers: The rising threat of antimicrobial resistance and global healthcare initiatives favor the development and adoption of innovative antibiotics like MONODOX.
- Competitive Edge: As a potentially first-in-class agent, MONODOX's differentiation can facilitate market penetration and premium pricing.
- Revenue Potential: Peak sales estimates range from USD 500 million to over USD 1 billion, contingent on clinical success and market dynamics.
- Strategic Focus: Collaboration with healthcare stakeholders, proactive stewardship, and regulatory engagement are vital to maximize financial outcomes.
- Risks: Regulatory hurdles, resistance evolution, and reimbursement policies pose significant challenges that require strategic mitigation.
FAQs
1. What factors influence the market success of MONODOX?
Market success depends on clinical efficacy, safety profile, regulatory approval, adoption by healthcare providers, reimbursement policies, and the competitive landscape. Addressing antimicrobial stewardship concerns and demonstrating cost-effectiveness are also crucial.
2. How might antimicrobial resistance impact MONODOX’s long-term viability?
While resistance development could diminish MONODOX’s efficacy over time, proactive stewardship and combination therapies can extend its clinical lifespan. Ongoing surveillance will be essential to adapt usage guidelines.
3. What are the key regulatory milestones for MONODOX?
The primary milestones include completion of Phase III trials, submission of regulatory dossiers, and obtaining approvals from agencies like the FDA and EMA. Early designations, such as Fast Track or Breakthrough Therapy, could expedite review processes.
4. How do stewardship programs influence MONODOX’s market potential?
Stewardship programs aim to prevent overuse, which can limit immediate sales volume but ensure sustainable long-term use. Strategic positioning highlighting clinical advantages can balance stewardship constraints with commercial goals.
5. What strategies can optimize MONODOX’s financial trajectory?
Early engagement with payers, strategic partnerships, pursuing expanded indications, and global market expansion, particularly into emerging markets, can enhance revenue streams and market share.
References
[1] Global Antibiotic Market Report, 2022.
[2] McKinsey & Company, The Growing Threat of Antimicrobial Resistance, 2021.