Last updated: July 28, 2025
Introduction
Metolazone, a thiazide-like diuretic primarily prescribed for hypertension and edema, has maintained a niche yet critical role within the pharmaceutical landscape. Its unique pharmacokinetic profile, efficacy in resistant hypertension, and the evolving healthcare environment influence its market trajectory. This analysis examines the current market dynamics, key drivers, challenges, regulatory landscape, and financial prospects shaping metolazone's future.
Market Overview
Metolazone holds a longstanding position in the antihypertensive segment, often utilized when patients demonstrate resistance to other diuretics or require adjunct therapy. While not a new entrant—first approved in the 1960s—its role remains relevant, especially in specific patient subsets. The global demand correlates strongly with hypertension prevalence, aging populations, and healthcare protocols emphasizing diuretics as first-line or adjunct options for cardiovascular risk management.
The pharmaceutical market for diuretics, including metolazone, is competitive yet specialized. Conventional diuretics like hydrochlorothiazide dominate, but metolazone's distinct efficacy in certain resistant cases sustains its clinical relevance.
Market Drivers
1. Rising Prevalence of Hypertension
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), over 1.2 billion adults worldwide suffer from hypertension [1]. An aging global population escalates the demand for antihypertensives, including metolazone, especially for treatment-resistant subpopulations.
2. Increasing Incidence of Cardiovascular Diseases (CVD)
Hypertension remains a primary risk factor for strokes, ischemic heart disease, and heart failure. Healthcare protocols increasingly favor diuretics as foundational therapy due to their proven efficacy and cost-effectiveness, thereby supporting metolazone’s utilization.
3. Adoption in Resistant Hypertension Management
Metolazone’s potency in resistant hypertension cases propels its demand. Its pharmacological profile, characterized by strong sodium and water excretion with minimal renal impairment, makes it suitable in complex cases where other diuretics fall short.
4. Regulatory Approvals and Medical Guidelines
Updates in hypertension management guidelines, particularly those from the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association (ACC/AHA), emphasize the role of thiazide-like diuretics, indirectly boosting the demand for metolazone [2].
5. Off-Label and Adjunct Uses
Emerging off-label applications, such as in edema associated with certain malignancies or nephrotic syndrome, subtly expand the therapeutic scope.
Market Challenges
1. Competition from Generic Diuretics
Metolazone faces intense competition from well-established, low-cost generics like hydrochlorothiazide and chlorthalidone. These alternatives are widely prescribed owing to their affordability and extensive clinical experience, constraining metolazone’s market share.
2. Safety and Side Effect Profile
Potential adverse effects, including electrolyte imbalance, hypovolemia, and renal impairment, necessitate careful patient monitoring, discouraging broad over-the-counter or outpatient use in some regions.
3. Limited Brand-Specific Innovation
Compared to novel cardiovascular agents, limited innovation around metolazone reduces the impetus for new clinical trials or formulations, diminishing growth prospects.
4. Pricing and Reimbursement Dynamics
In highly regulated healthcare systems, reimbursement policies influence prescribing patterns. In markets where generic prices are aggressively driven down, sales volume becomes a critical revenue determinant.
5. Regulatory Variability
Different countries possess varying regulatory standards for approval, labeling, and indications. The lack of newer formulations or combination products with metolazone hampers global expansion.
Regulatory Environment and Patent Landscape
Metolazone's patent protections have long expired, rendering it a generic medication in most markets. Patent expiration led to a proliferation of generic options, which contribute to lower prices but also reduce revenue potential for original manufacturers. Nevertheless, certain formulations or combination drugs incorporating metolazone may still be under patent or regulatory exclusivity, offering niche opportunities.
Regulatory agencies continue to emphasize the importance of safety monitoring. In some countries, updated labeling mandates stricter electrolyte management protocols or contraindications, influencing clinical adoption.
Financial Trajectory and Growth Outlook
Historical Financial Performance
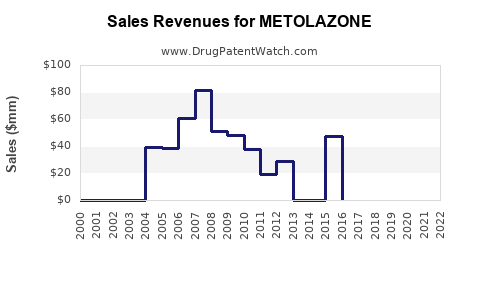
Given the drug's generic status, revenue streams for metolazone are modest compared to branded, patent-protected therapies. In the United States, the annual sales of diuretics like metolazone are estimated in the tens of millions USD, with a declining trend driven by competition from other diuretics and healthcare cost containment measures [3].
Future Revenue Drivers
- Niche Applications and Off-Label Use: While limited, these offer incremental revenue, especially in specialized centers.
- Combination Therapy Development: Pharmaceutical partnerships developing fixed-dose combinations incorporating metolazone with other antihypertensives could open new markets and improve patient adherence.
- Emerging Markets Growth: Countries with rising hypertension prevalence and healthcare expansion may increase demand, especially where healthcare plans favor cost-effective treatments.
Market Growth Forecast
Analysts project a slow-to-moderate decline in metolazone market share in mature regions due to generic competition. However, growth may persist marginally in emerging markets, driven by increased healthcare access and the aging population. The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for metolazone sales is forecasted to decline by approximately 2-3% over the next five years globally but balance in specific regional markets could occur due to healthcare infrastructure development [4].
Impact of Pricing Strategies and Policy Changes
Aggressive pricing, cost-containment policies, and stricter formulary controls are expected to suppress revenue. Conversely, strategic alliances with healthcare payers and value-based prescribing programs could sustain demand in key markets.
Technological Innovations and Market Evolution
Despite the lack of groundbreaking innovations specifically for metolazone, ongoing advancements in cardiovascular pharmacotherapy—such as implantable devices and personalized medicine—may marginally influence its role. The development of combination therapies with improved tolerability profiles could contribute to its sustained, albeit limited, market presence.
Conclusion
Metolazone's market dynamics are characterized by a mature, highly competitive landscape dominated by generic options. Its clinical niche—particularly in resistant hypertension—ensures ongoing but declining demand driven by demographic trends and evolving treatment guidelines. The financial outlook suggests limited growth potential, contingent upon niche applications, emerging markets, and strategic product developments like combination therapies. Regulatory considerations and healthcare policy reforms will continue to shape its market evolution.
Key Takeaways
- Stable Therapeutic Role: Metolazone remains a critical option in resistant hypertension management, though its market share is declining due to generic competition.
- Market Challenges: Pricing pressures, safety concerns, and limited innovation constrain revenue growth.
- Expansion Opportunities: Focus on niche indications, combination therapies, and emerging markets may sustain demand marginally.
- Regulatory and Policy Influence: Healthcare reforms and safety mandates influence prescribing patterns and revenue potential.
- Long-term Outlook: Expect modest decline in mature markets with potential growth in non-US regions driven by increasing hypertension prevalence.
FAQs
Q1: What factors primarily influence the declining market share of metolazone?
A1: The entry of low-cost generic diuretics, limited innovation, safety concerns, and healthcare cost containment policies predominantly drive market share decline.
Q2: Are new formulations or combination drugs with metolazone expected in the near future?
A2: While specific new formulations are limited, development of fixed-dose combination therapies with other antihypertensives is a strategic area that may expand its use.
Q3: How does the global burden of hypertension impact metolazone demand?
A3: Rising hypertension prevalence, especially in aging populations worldwide, sustains demand, particularly in regions with limited access to newer or branded therapies.
Q4: What regulatory challenges does metolazone face internationally?
A4: Variability in approval standards, labeling updates requiring safety monitoring, and absence of patent protections complicate global expansion.
Q5: What is the long-term revenue outlook for metolazone?
A5: Revenue is expected to decline gradually in mature markets but may stabilize or grow marginally in emerging markets, driven by demographic trends and healthcare infrastructure development.
Sources
[1] WHO. Hypertension. World Health Organization, 2021.
[2] American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Guidelines, 2017.
[3] IQVIA. Global Pharmaceutical Market Reports, 2022.
[4] MarketWatch. Diuretics Market Forecast, 2023-2028.