Last updated: July 30, 2025
Introduction
DILANTIN-125, a proprietary formulation of phenytoin sodium, is a widely recognized anticonvulsant used primarily in the management of seizure disorders. Given its longstanding presence in the pharmaceutical landscape, understanding its market dynamics and financial trajectory involves an analysis of regulatory status, competitive positioning, patent lifecycle, patent expiration impacts, manufacturing considerations, and evolving market demands. This report offers a comprehensive examination tailored for stakeholders seeking strategic insight.
Regulatory and Patent Status
DILANTIN-125, administered as a 125 mg phenytoin sodium capsule or injection, has been in clinical use for over five decades. Its regulatory status in key markets, notably the US, Europe, and emerging markets, as a generic and brand formulation influences its commercial trajectory. As of recent years, the original patent protections for Dilantin (the brand) expired or are nearing expiration, shifting the landscape toward generic manufacturing. This transition fosters increased competition, impacting drug pricing and market share.
Patent expiration significantly influences the immediate future of DILANTIN-125. The original patent expiry in major markets has led to a proliferation of generic equivalents, substantially reducing revenue streams for brand manufacturers. Nonetheless, formulations with specific delivery mechanisms or unique excipients may retain patent protection, providing temporary market advantages.
Market Demand and Therapeutic Landscape
The demand for DILANTIN-125 hinges on the prevalence of seizure disorders. According to WHO estimates, approximately 50 million people worldwide suffer from epilepsy, making anticonvulsants among the most prescribed neurological drugs [1]. Phenytoin remains a first-line therapy in many developing countries due to its effectiveness and cost-effectiveness, sustaining steady demand.
However, the therapeutic landscape is evolving. The advent of newer antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) with improved safety profiles and fewer drug interactions, such as levetiracetam and lamotrigine, has gradually eroded DILANTIN-125’s market share in advanced markets. Nonetheless, in resource-constrained settings, DILANTIN-125 remains a staple, providing resilient demand.
Additionally, the necessity for carefully monitored long-term therapy in epilepsy management sustains ongoing requirements. Nonetheless, concerns over side effects (gingival hyperplasia, cerebellar ataxia) may influence prescribing trends, with clinicians opting for newer agents where feasible.
Competitive Dynamics
The market for phenytoin-based therapies is characterized by high generic competition. Multiple manufacturers produce DILANTIN-125 formulations, including notable generic firms, significantly compressing margins.
Pricing pressure is prominent, driven by the commodification of the drug post-patent expiry. Price erosion directly impacts revenue and profitability for brand-name manufacturers. However, some differentiation persists via formulations with modified release features, specialty delivery mechanisms, or licensing arrangements with local regulatory bodies.
In addition, regulatory hurdles—such as bioequivalence requirements—create barriers to entry for new generic players but do not prevent existing competitors from offering similar products. Strategies like establishing manufacturing cost efficiencies and expanding into emerging markets can offset declining prices.
Moreover, market access and reimbursement policies heavily influence profitability. Countries with national health programs favor low-cost generics, further intensifying price competition.
Manufacturing and Supply Chain Considerations
Manufacturing costs for DILANTIN-125 vary based on source ingredients, scale efficiencies, and regulatory compliance. Ensuring robust quality control and supply chain integrity is essential, particularly to meet global demand and adhere to stringent Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) standards.
Supply chain disruptions—exacerbated during global crises like the COVID-19 pandemic—pose risks to consistent drug availability. Manufacturers investing in diversified supply chains and inventory buffers mitigate these risks, safeguarding market presence.
Furthermore, formulation innovations, such as sustained-release forms, necessitate additional R&D investment, potentially offering premium pricing but increasing operational complexity.
Financial Trajectory and Market Outlook
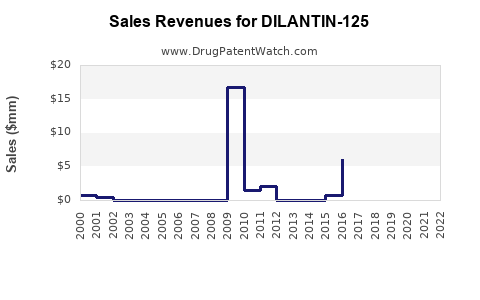
Historical revenue trends indicate a decline for proprietary DILANTIN brands post-patent expiry, with revenues increasingly supplanted by generics. This trend constrains profit margins but maintains volume-based revenues in high-demand regions.
Forecasting suggests that the global market for phenytoin formulations will see modest growth, primarily driven by emerging markets where cost-effective options remain essential. The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) is projected at approximately 2-3% over the next five years, influenced by the ongoing prevalence of epilepsy and the continued reliance on generic formulations.
Emerging markets constitute the principal growth avenue, with rising healthcare infrastructure and increasing epilepsy diagnoses. Here, pharmaceutical companies may engage in licensing, partnerships, or local manufacturing to capture market share.
Innovative formulations and combination therapies could unlock premium segments, although high R&D investment and regulatory approval processes pose challenges.
Strategic Considerations
For existing stakeholders, differentiation through lower-cost manufacturing, strategic regional partnerships, and enhancement of formulation stability remains key. Patents on specific delivery systems can provide short-term advantages. For companies contemplating entry, understanding regional legalities, compliance requirements, and local demand is vital.
Investment in clinical research exploring new indications or combination therapies may augment long-term viability. Additionally, post-expiry strategies like acquiring generics or developing biosimilars could offset declining revenues from original formulations.
Conclusion
The market dynamics for DILANTIN-125 are characterized by a mature lifecycle, intense generic competition, and shifting prescribing patterns influenced by newer therapies. Its financial trajectory is trending toward stabilization in high-demand, cost-sensitive markets, with modest growth driven by emerging economies. Strategic maneuvering, cost management, and diversification into innovative formulations or collaborations will define future profitability.
Key Takeaways
- Patent expiries have transitioned DILANTIN-125 from a proprietary product to a highly competitive generic market, exerting downward pressure on prices and margins.
- Demand remains stable in resource-limited settings, but premium markets are gradually shifting toward newer AEDs with better safety profiles.
- Market share opportunities exist in emerging economies via local partnerships, licensing, and cost-optimized manufacturing.
- Innovation and formulation differentiation can create short-term premium segments but require substantial R&D investment.
- Supply chain resilience remains critical amid global disruptions, impacting consistent market supply and revenue stability.
FAQs
1. How does patent expiration influence DILANTIN-125’s market share?
Patent expiry opens the market to generic manufacturers, drastically increasing competition, reducing prices, and eroding the brand's market share. Nevertheless, formulations with new delivery technologies or proprietary excipients can temporarily extend market exclusivity.
2. Which regions are likely to see growth in DILANTIN-125 demand?
Emerging markets like India, Africa, and parts of Southeast Asia are expected to continue significant demand, driven by cost considerations and the prevalence of epilepsy.
3. Can innovations in formulation improve DILANTIN-125’s market position?
Yes. Extended-release formulations or combination therapies could command premium pricing and address specific clinical needs, though they require substantial R&D investment and regulatory approval.
4. What are the main competitive strategies for sustaining profitability?
Cost optimization, regional licensing agreements, diversification through formulation innovation, and supply chain robustness are critical for maintaining profitability amidst generic competition.
5. What are the key risks to DILANTIN-125’s financial outlook?
Market saturation, regulatory changes, intellectual property challenges, shifting clinician preferences favoring newer therapies, and supply chain disruptions pose significant risks.
Sources:
[1] World Health Organization. Epilepsy Fact Sheet. 2022.