Last updated: July 30, 2025
Introduction
Coumadin, the brand name for warfarin, remains a cornerstone in oral anticoagulant therapy despite the advent of newer agents. As a vitamin K antagonist, warfarin has a complex regulatory history, significant clinical utility, and evolving market landscape driven by demographic shifts, regulatory considerations, and advances in anticoagulation management. This analysis explores the current market dynamics, competitive environment, regulatory factors, and projected financial trajectory for Coumadin over the coming years.
Historical Context and Clinical Significance
Since its FDA approval in 1954, warfarin has established itself as a mainstay in the prevention and treatment of thromboembolic disorders, including atrial fibrillation, deep vein thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism, and prosthetic heart valve management. Its long-standing clinical use, extensive safety data, and cost-effectiveness underpin its continued relevance, albeit with certain clinical management complexities, such as narrow therapeutic index and need for regular INR monitoring.
Market Dynamics
1. Demographics and Epidemiology
The global aging population drives demand for anticoagulants, including warfarin. Elderly patients, who have higher risks of atrial fibrillation and thromboembolic events, historically relied on warfarin due to cost considerations and familiarity. According to the World Health Organization, the population aged 65 and older is projected to reach over 1 billion by 2050[1], fueling sustained demand.
2. Competitive Landscape: Alternative Oral Anticoagulants
The advent of novel oral anticoagulants (NOACs)—such as dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban, and edoxaban—has significantly impacted the market for warfarin. These agents offer fixed dosing, fewer drug and dietary interactions, and do not require regular INR monitoring. As a result, they have gained favor in many clinical settings, especially among younger, lower-risk populations.
However, warfarin retains advantages in specific contexts:
- Cost-effectiveness remains a key driver in low-resource settings.
- Its reversal agents (vitamin K, fresh frozen plasma, prothrombin complex concentrates) are well established.
- In patients with mechanical heart valves or certain antiphospholipid syndrome cases, warfarin remains the preferred agent.
Despite the growing preference for NOACs, warfarin continues to dominate the anticoagulant landscape in many regions.
3. Regulatory and Reimbursement Factors
The market trajectory for Coumadin is sensitive to regulatory changes and reimbursement policies. The increasing adoption of NOACs influences prescribing patterns, especially where insurance coverage broadens access to newer agents. Conversely, policies favoring cost-sensitive care in public health systems sustain warfarin use.
Clinical guidelines, such as those from the American College of Cardiology (ACC) and European Society of Cardiology (ESC), continue to recognize warfarin as a viable option, particularly when NOACs are contraindicated or inaccessible.
4. Prescriber and Patient Preferences
Physicians balance efficacy, safety, monitoring burden, and patient compliance. Warfarin's requirement for frequent INR checks can deter compliance but also allows close monitoring, beneficial in certain high-risk groups. Patient preferences, often influenced by out-of-pocket costs and ease of use, influence market share.
Financial Trajectory
1. Revenue Sources and Market Share
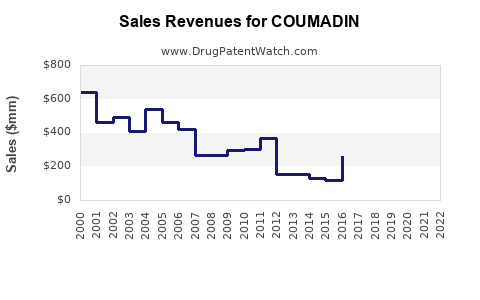
Despite the generic availability of warfarin, Coumadin still generates substantial revenue, especially in markets with limited access to NOACs. The global warfarin market was valued at approximately USD 1.3 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow modestly at a CAGR of 3%-5% until 2030[2].
The sustained demand in developing economies, where affordability is critical, contributes to steady revenue streams. North American and European markets are increasingly dominated by NOACs, but warfarin’s market share persists due to established clinical protocols and lower costs.
2. Impact of Patent and Generics
Warfarin's patent expiration in the early 2000s led to widespread generic manufacturing, substantially reducing drug prices and increasing accessibility. This commoditization supports consistent volume sales but constrains profit margins for manufacturers.
3. Market Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges:
- Competition from NOACs reducing physician reliance on warfarin.
- Management complexities and adverse events associated with warfarin.
- Stringent regulatory monitoring for safety updates.
Opportunities:
- Integration into combination therapies for specific indications.
- Development of more precise formulation variants or delivery systems.
- Expansion into emerging markets with limited anticoagulant access.
4. Innovative Developments and Future Outlook
Although no significant formulation innovations are in late-stage development explicitly for Coumadin, ancillary innovations include digital monitoring tools to improve INR management. Additionally, pharmacogenetic testing methodologies aim to optimize warfarin dosing, potentially revitalizing its clinical utility.
The overall financial trajectory for Coumadin hinges on balancing ongoing demand, competitive pressures from NOACs, and regional healthcare policy dynamics. While revenue growth may slow in mature markets, emerging economies and certain therapeutic niches present continued revenue avenues.
Regulatory and Patent Outlook
The patent landscape for warfarin is mature, with no current patent protections in most jurisdictions. Regulatory agencies focus on safety and post-marketing surveillance, ensuring continued clinical relevance. The lack of patent barriers means no exclusive pricing advantages, influencing manufacturer profitability to primarily depend on volume sales.
Conclusion: Future Market Outlook
Coumadin's market position will gradually shift towards niche applications, cost-sensitive markets, and specific patient groups contraindicated for NOACs. Market share will likely decline in developed regions but remains important globally. Proprietary formulations or adjunct technological advancements could provide incremental growth opportunities.
The global anticoagulation market is predicted to evolve, with the NOAC segment expanding rapidly, but warfarin’s entrenched role ensures its continued financial footprint. Long-term, strategic engagement with healthcare providers, policymakers, and patients will determine Coumadin’s sustainable market trajectory.
Key Takeaways
- Steady Demand in Low-Resource Settings: Coumadin remains vital in regions where cost constraints favor generic, inexpensive anticoagulants.
- Market Share Decline in Developed Countries: Rising preference for NOACs diminishes warfarin’s dominance but sustains a baseline revenue.
- Regulatory Stability and Cost Advantage: Batch classifying warfarin as a low-cost generic supports continued sales despite clinical preferences.
- Potential for Niche Applications: High-risk or complex cases favoring warfarin preserve its clinical role and revenue.
- Innovation Focus: Digital INR monitoring and pharmacogenetics may extend warfarin’s clinical and commercial utility.
FAQs
1. What factors influence the shifting market share between warfarin and NOACs?
Clinical convenience, safety profiles, monitoring requirements, cost, and regulatory guidelines drive prescriber and patient preferences. NOACs offer fixed dosing and fewer interactions, leading to increased adoption, especially in high-resource settings, while warfarin remains prevalent where cost and access are concerns.
2. How does patent expiration impact the financial trajectory of Coumadin?
Patent expiration leads to generic manufacturing, significantly lowering drug prices and increasing volume sales. While this diminishes profit margins for manufacturers, it sustains overall revenue through high-volume sales, especially in emerging markets.
3. Are there regulatory threats to Coumadin’s market position?
Regulators focus on safety and efficacy updates. No imminent regulatory threats threaten its market exclusivity due to patents, but safety concerns and evolving clinical guidelines could influence prescribing practices.
4. What are the main regions driving Coumadin’s sales?
Developing countries and emerging markets, where affordability remains critical, sustain higher demand. North America and Europe see more NOAC-driven growth, reducing warfarin's relative market share.
5. What future innovations could influence Coumadin's market?.
Advances in digital health tools for INR management, pharmacogenetic dosing algorithms, and potentially new formulations could optimize use and extend its market viability, particularly in niche applications.
Sources:
[1] World Health Organization. Aging and Health. 2021.
[2] MarketsandMarkets. Anticoagulants Market Forecast. 2023.