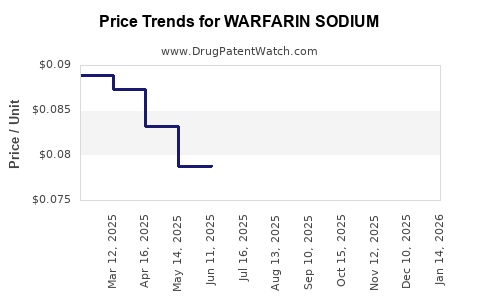
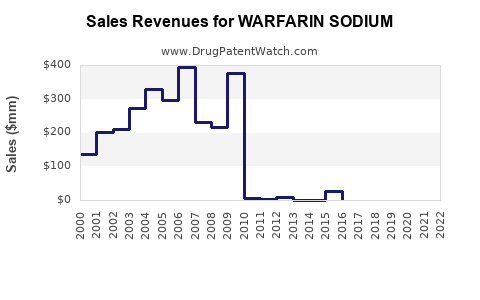
Last updated: July 28, 2025
Introduction
Warfarin Sodium, a widely used oral anticoagulant, has maintained a significant presence in clinical practice for decades. Originally introduced in the 1950s, warfarin's efficacy in preventing thromboembolic events has established it as a staple in the treatment of atrial fibrillation, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and prosthetic heart valve management. Despite the advent of novel anticoagulants, warfarin remains relevant due to its cost-effectiveness, long history of use, and well-understood pharmacodynamics. This article explores the current market dynamics influencing warfarin sodium’s financial trajectory, examining factors such as patent landscape, clinical competition, regulatory environment, and emerging technological trends.
Market Overview
The global warfarin market was valued at approximately USD 1.2 billion in 2021, with steady growth projected through 2030, driven primarily by rising cardiovascular disease prevalence and expanding anticoagulation indications [1]. North America retains the largest market share, owing to widespread clinical adoption and robust healthcare infrastructure, while Asia-Pacific is expected to register the fastest growth, propelled by increasing awareness and healthcare spending.
Despite the arrival of direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) like apixaban and rivaroxaban, warfarin continues to dominate in certain regions, mainly due to its low cost and extensive clinician familiarity. The drug’s versatility—requiring routine INR monitoring—further sustains its demand in healthcare settings that prioritize cost-containment.
Market Dynamics Influencing Warfarin Sodium
1. Patent Expiry and Generic Competition
A critical factor shaping warfarin's financial trajectory is patent expiration. Originator companies, such as Bristol-Myers Squibb and others, faced patent cliffs in the late 20th and early 21st centuries, leading to the widespread introduction of generic warfarin products. Generic manufacturers now account for the majority of the global supply, exerting downward pressure on pricing and margins.
The increased availability of affordable generics has significantly expanded accessibility, especially in emerging markets, but it has also compressed profit margins for branded formulations. Market saturation with low-cost generics underscores a mature product lifecycle, limiting avenues for premium pricing.
2. Clinical Competition from Novel Anticoagulants
In recent years, DOACs have revolutionized anticoagulation therapy by offering fixed dosing, fewer monitoring requirements, and improved safety profiles. As evidenced by clinical trials, drugs like dabigatran, apixaban, and rivaroxaban demonstrate comparable or superior efficacy with fewer bleeding risks [2].
However, despite these attributes, warfarin retains advantages that sustain its market position. These include its affordability, the ability to reverse its effects rapidly—particularly in emergencies using vitamin K—and superior cost-effectiveness in specific patient populations. Nevertheless, the shift toward newer agents in high-income markets poses an ongoing competitive challenge.
3. Regulatory Environment and Reimbursement Policies
Government agencies and payers significantly influence warfarin’s market trajectory. Health policies promoting cost-effective therapies may favor the continued use of warfarin, especially in publicly funded healthcare systems. Conversely, reimbursement policies that favor newer, branded anticoagulants or impose limitations on generic use can impact market share.
Furthermore, regulatory approvals for new formulations—such as extended-release versions or combination therapies—may create incremental revenue streams, although these are typically modest relative to the overall market size.
4. Technological Innovations and Digital Health Integration
Advancements in point-of-care INR testing, digital health platforms, and individualized dosing algorithms are transforming warfarin management. Automated monitoring and telemedicine integrations improve patient adherence and safety, potentially reducing hospitalization costs and enhancing overall clinical outcomes.
The integration of these technologies can extend warfarin’s relevance, especially in resource-limited settings, by improving its safety profile and convenience, thereby sustaining demand.
5. Public Perception and Prescribing Trends
Physician familiarity, patient preferences, and perceived safety influence prescribing behaviors. Although the complexity of INR monitoring and dietary interactions are drawbacks, educational initiatives and clinical guidelines continue to reinforce warfarin’s role in specific cases, particularly where cost considerations predominate.
Financial Trajectory Analysis
The financial outlook for warfarin sodium hinges on several intertwined factors:
-
Market Maturation: The global market for warfarin is approaching maturity, with growth primarily driven by emerging markets and incremental technological improvements. The overtaken patents and commoditized manufacturing environment constrain revenue growth potential.
-
Competitive Pressure: The increasing adoption of DOACs poses a long-term risk, primarily in high-income countries. While warfarin remains cost-effective, shifts in clinical guidelines and insurance reimbursement favor newer agents, influencing market share.
-
Pricing Trends: Generic competition has driven prices downward, especially in regions with robust regulatory approval processes and generic manufacturing bases. As a result, profit margins are under sustained pressure, compelling manufacturers to innovate in delivery and management tools rather than price.
-
Regulatory and Policy Environment: Favorable policies in developing countries, emphasizing cost-effective therapies, sustain demand for warfarin. Conversely, stringent regulations or reimbursement restrictions in mature markets may constrain revenue streams.
-
Technological Adoption: Digital health innovations that improve safety and patient management could catalyze extended product life cycles. These innovations open new revenue avenues through device sales, digital services, and integration partnerships.
Projected Revenue Trends: Industry analysts forecast that the warfarin market will experience modest annual growth (~1-3%) over the next decade, driven largely by volume increases in emerging markets and the incorporation of management technologies. However, high-income regions may see stagnation or slight declines due to DOAC adoption.
Emerging Opportunities and Challenges
Opportunities
-
Personalized Medicine: Developing bespoke dosing algorithms utilizing genetic information (e.g., CYP2C9, VKORC1 genotyping) can optimize warfarin therapy, improving safety and efficacy, and thus sustaining demand.
-
Digital Health Integration: Collaborations with digital health firms to develop INR monitoring devices and telehealth platforms can differentiate products and retain competitiveness.
-
New Formulations: Innovations such as fixed-dose combination pills or extended-release formulations can offer convenience, potentially expanding the user base.
Challenges
-
Shift to Newer Agents: The increasing clinical preference for DOACs threatens to diminish warfarin’s market share further.
-
Regulatory Risks: Stringent regulations or adverse safety data can impact manufacturing licenses and prescribing practices.
-
Pricing Pressures: Intense intragroup and intercompany competition constrain profit margins, impacting long-term revenue potential.
Key Takeaways
-
Market Maturity and Generics: Patent expiries have shifted warfarin into a commoditized environment, with generics dominating supply and suppressing prices.
-
Competition from DOACs: While warfarin remains cost-effective, the growing preference for DOACs in high-income markets is a significant competitive challenge.
-
Technology and Management Tools: Innovations in digital health and personalized dosing are pivotal for extending warfarin’s lifecycle and profitability.
-
Regional Variability: Emerging markets offer growth opportunities, driven by cost considerations and expanding healthcare infrastructure.
-
Strategic Focus: Manufacturers should focus on enhancing patient management technologies, fostering regional growth, and exploring formulation innovations to mitigate declining margins.
Conclusion
Warfarin sodium’s market landscape is characterized by a mature, highly commoditized environment faced with increasing competition from novel oral anticoagulants. While generics and cost-effective management strategies sustain its global use, its long-term financial trajectory depends on technological innovation, regional market expansion, and adaptive regulatory strategies. Stakeholders who leverage digital health integrations and personalized medicine approaches can potentially prolong its relevance, maintain profitability, and capitalize on emerging opportunities within the anticoagulation space.
FAQs
Q1: Will warfarin be phased out due to emerging anticoagulants?
A1: Not immediately. While DOACs are increasingly preferred in many settings, warfarin remains essential, especially where cost constraints limit access to newer agents. Its well-understood reversal protocols and affordability sustain its use.
Q2: How do regulatory changes impact warfarin’s market?
A2: Regulations promoting cost-effective and generic medicines sustain warfarin’s market share. Conversely, restrictions or safety concerns can reduce prescriber confidence or limit market access, impacting sales.
Q3: Are there technological innovations that could revitalize warfarin’s market?
A3: Yes. Innovations like point-of-care INR devices, telehealth-enabled monitoring, and pharmacogenetic-guided dosing can improve safety, adherence, and convenience, potentially expanding its user base.
Q4: How does regional variability affect warfarin’s financial trajectory?
A4: Emerging markets with limited access to expensive drugs provide growth opportunities, driven by cost-conscious healthcare policies. In contrast, high-income markets are increasingly shifting toward DOACs, constraining revenue growth.
Q5: What strategic actions should manufacturers undertake to sustain profitability?
A5: Focus on integrating digital health solutions, developing personalized dosing tools, expanding into underserved regions, and exploring innovative formulations can help maintain competitiveness and profitability.
References
[1] MarketsandMarkets. (2022). Global Anticoagulants Market Report.
[2] Camm, A. J., et al. (2019). 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation. European Heart Journal, 42(5), 373-498.