COTELLIC Drug Patent Profile
✉ Email this page to a colleague
Which patents cover Cotellic, and what generic alternatives are available?
Cotellic is a drug marketed by Genentech Inc and is included in one NDA. There are seven patents protecting this drug.
This drug has one hundred and ninety-seven patent family members in forty-four countries.
The generic ingredient in COTELLIC is cobimetinib fumarate. One supplier is listed for this compound. Additional details are available on the cobimetinib fumarate profile page.
DrugPatentWatch® Generic Entry Outlook for Cotellic
Cotellic was eligible for patent challenges on November 10, 2019.
By analyzing the patents and regulatory protections it appears that the earliest date
for generic entry will be December 30, 2036. This may change due to patent challenges or generic licensing.
Indicators of Generic Entry
AI Deep Research
Questions you can ask:
- What is the 5 year forecast for COTELLIC?
- What are the global sales for COTELLIC?
- What is Average Wholesale Price for COTELLIC?
Summary for COTELLIC
| International Patents: | 197 |
| US Patents: | 7 |
| Applicants: | 1 |
| NDAs: | 1 |
| Finished Product Suppliers / Packagers: | 1 |
| Raw Ingredient (Bulk) Api Vendors: | 10 |
| Clinical Trials: | 35 |
| Drug Prices: | Drug price information for COTELLIC |
| What excipients (inactive ingredients) are in COTELLIC? | COTELLIC excipients list |
| DailyMed Link: | COTELLIC at DailyMed |
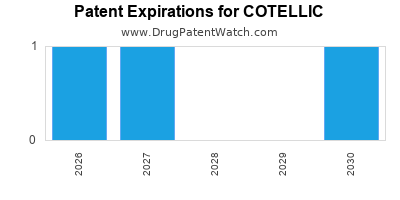

DrugPatentWatch® Estimated Loss of Exclusivity (LOE) Date for COTELLIC
Generic Entry Date for COTELLIC*:
Constraining patent/regulatory exclusivity:
NDA:
Dosage:
TABLET;ORAL |
*The generic entry opportunity date is the latter of the last compound-claiming patent and the last regulatory exclusivity protection. Many factors can influence early or later generic entry. This date is provided as a rough estimate of generic entry potential and should not be used as an independent source.
Recent Clinical Trials for COTELLIC
Identify potential brand extensions & 505(b)(2) entrants
| Sponsor | Phase |
|---|---|
| University of Manchester | Phase 2/Phase 3 |
| Hoffmann-La Roche | Phase 2/Phase 3 |
| University of Birmingham | Phase 2/Phase 3 |
Pharmacology for COTELLIC
| Drug Class | Kinase Inhibitor |
| Mechanism of Action | Kinase Inhibitors |
US Patents and Regulatory Information for COTELLIC
COTELLIC is protected by seven US patents and four FDA Regulatory Exclusivities.
Based on analysis by DrugPatentWatch, the earliest date for a generic version of COTELLIC is ⤷ Get Started Free.
This potential generic entry date is based on patent 10,590,102.
Generics may enter earlier, or later, based on new patent filings, patent extensions, patent invalidation, early generic licensing, generic entry preferences, and other factors.
| Applicant | Tradename | Generic Name | Dosage | NDA | Approval Date | TE | Type | RLD | RS | Patent No. | Patent Expiration | Product | Substance | Delist Req. | Exclusivity Expiration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genentech Inc | COTELLIC | cobimetinib fumarate | TABLET;ORAL | 206192-001 | Nov 10, 2015 | RX | Yes | Yes | 11,597,699 | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | ||||
| Genentech Inc | COTELLIC | cobimetinib fumarate | TABLET;ORAL | 206192-001 | Nov 10, 2015 | RX | Yes | Yes | 11,087,354*PED | ⤷ Get Started Free | Y | ⤷ Get Started Free | |||
| Genentech Inc | COTELLIC | cobimetinib fumarate | TABLET;ORAL | 206192-001 | Nov 10, 2015 | RX | Yes | Yes | 11,254,649*PED | ⤷ Get Started Free | Y | ⤷ Get Started Free | |||
| >Applicant | >Tradename | >Generic Name | >Dosage | >NDA | >Approval Date | >TE | >Type | >RLD | >RS | >Patent No. | >Patent Expiration | >Product | >Substance | >Delist Req. | >Exclusivity Expiration |
International Patents for COTELLIC
When does loss-of-exclusivity occur for COTELLIC?
Based on analysis by DrugPatentWatch, the following patents block generic entry in the countries listed below:
Argentina
Patent: 5483
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Australia
Patent: 16288209
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 21200202
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Brazil
Patent: 2017028516
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Canada
Patent: 90222
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Chile
Patent: 17003475
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
China
Patent: 7810183
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 8290395
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Colombia
Patent: 18000086
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Costa Rica
Patent: 180056
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
European Patent Office
Patent: 17264
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Hong Kong
Patent: 52433
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Israel
Patent: 6423
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 5052
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Japan
Patent: 38950
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 18519318
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 21035967
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 23025000
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Malaysia
Patent: 2545
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Mexico
Patent: 0250
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 17017037
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Morocco
Patent: 301
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
New Zealand
Patent: 9160
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 7527
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Peru
Patent: 180692
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Philippines
Patent: 017502414
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Russian Federation
Patent: 62181
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 18103172
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 21132394
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Singapore
Patent: 202105196Y
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
South Africa
Patent: 1708760
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
South Korea
Patent: 2695324
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 180021775
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Taiwan
Patent: 10556
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 75187
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 1718535
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 2108568
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Ukraine
Patent: 4728
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Generics may enter earlier, or later, based on new patent filings, patent extensions, patent invalidation, early generic licensing, generic entry preferences, and other factors.
See the table below for additional patents covering COTELLIC around the world.
| Country | Patent Number | Title | Estimated Expiration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Israel | 295052 | ⤷ Get Started Free | |
| Taiwan | 201718535 | ⤷ Get Started Free | |
| Japan | 5129143 | ⤷ Get Started Free | |
| >Country | >Patent Number | >Title | >Estimated Expiration |
Supplementary Protection Certificates for COTELLIC
| Patent Number | Supplementary Protection Certificate | SPC Country | SPC Expiration | SPC Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1934174 | 132016000050893 | Italy | ⤷ Get Started Free | PRODUCT NAME: COBIMETINIB IN TUTTE LE FORME PROTETTE DAL BREVETTO DI BASE, INCLUSI SALI E SOLVATI FARMACEUTICAMENTE ACCETTABILI, IN PARTICOLARE COBIMETINIB EMIFUMARATO(COTELLIC); AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S) AND DATE(S): EU/1/15/1048, 20151124 |
| 1934174 | PA2016016 | Lithuania | ⤷ Get Started Free | PRODUCT NAME: KOBIMETINIBAS; REGISTRATION NO/DATE: EU/1/15/1048 20151120 |
| 1934174 | C 2016 018 | Romania | ⤷ Get Started Free | PRODUCT NAME: SUPPLEMENTARY PROTECTION CERTIFICATE; NATIONAL AUTHORISATION NUMBER: C 2020 015; DATE OF NATIONAL AUTHORISATION: RO; NUMBER OF FIRST AUTHORISATION IN EUROPEAN ECONOMIC AREA (EEA): 2228064; DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION IN EEA: 20220530 |
| >Patent Number | >Supplementary Protection Certificate | >SPC Country | >SPC Expiration | >SPC Description |
Market Dynamics and Financial Trajectory for COTELLIC (Cobimetinib)
More… ↓
Make Better Decisions: Try a trial or see plans & pricing
Drugs may be covered by multiple patents or regulatory protections. All trademarks and applicant names are the property of their respective owners or licensors. Although great care is taken in the proper and correct provision of this service, thinkBiotech LLC does not accept any responsibility for possible consequences of errors or omissions in the provided data. The data presented herein is for information purposes only. There is no warranty that the data contained herein is error free. We do not provide individual investment advice. This service is not registered with any financial regulatory agency. The information we publish is educational only and based on our opinions plus our models. By using DrugPatentWatch you acknowledge that we do not provide personalized recommendations or advice. thinkBiotech performs no independent verification of facts as provided by public sources nor are attempts made to provide legal or investing advice. Any reliance on data provided herein is done solely at the discretion of the user. Users of this service are advised to seek professional advice and independent confirmation before considering acting on any of the provided information. thinkBiotech LLC reserves the right to amend, extend or withdraw any part or all of the offered service without notice.
