Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Clozapine, a second-generation antipsychotic primarily used for treatment-resistant schizophrenia, has enjoyed a distinctive position within the pharmaceutical landscape. Its unique efficacy profile, coupled with severe safety considerations, influences its market dynamics and financial trajectory. Analyzing these factors provides valuable insights for stakeholders, including pharmaceutical companies, investors, healthcare providers, and policymakers.
Pharmacological and Clinical Profile
Developed in the 1960s and approved for medical use in the 1970s, clozapine revolutionized schizophrenia treatment due to its superior efficacy in refractory cases[^1]. Its mechanism involves modulation of dopaminergic and serotonergic pathways, differentiating it from first-generation antipsychotics.
Despite its clinical advantages, clozapine’s potential to cause agranulocytosis—a severe, sometimes fatal reduction in white blood cells—necessitated rigorous monitoring protocols. This safety issue significantly impacted its prescribing pattern and market penetration.
Market Dynamics
1. Regulatory and Safety Constraints
Clozapine’s association with agranulocytosis results in heightened regulatory oversight, including mandatory blood count monitoring and risk management programs such as REMS (Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies) in the United States. These protocols increase treatment complexity and discourage widespread use[^2].
Regulatory agencies, including the FDA and EMA, have designated clozapine as a controlled substance in many jurisdictions, which influences market access and prescribing behaviors. Nonetheless, oversight has evolved with improved markers for agranulocytosis risk, facilitating broader use in recent years.
2. Prescriber and Patient Utilization Patterns
Historically reserved for treatment-resistant schizophrenia, prescribing of clozapine has been limited due to safety concerns, adverse side effects (e.g., myocarditis, seizures), and monitoring burdens. However, recent evidence underscores its benefits in reducing suicidality and mortality[^3], prompting a shift towards higher utilization in appropriate patient populations.
Increased education and guidelines advocating early use in resistant cases have spurred growth in demand, especially in regions with advanced healthcare infrastructure.
3. Competitive Landscape and Innovation
The market faces competition from other second-generation antipsychotics with more favorable safety profiles, such as risperidone, olanzapine, and aripiprazole. While these drugs are easier to prescribe and monitor, they generally demonstrate lower efficacy in treatment-refractory populations.
Emerging formulations, such as long-acting injectables of atypical antipsychotics, threaten market share but have yet to significantly impact clozapine’s niche. Importantly, no newer drugs currently match clozapine’s unique efficacy profile, especially for treatment-resistant cases.
4. Market Penetration and Geographic Variability
Clozapine's utilization varies geographically. High-income countries with robust monitoring systems and established guidelines observe higher usage rates, whereas low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) exhibit limited adoption due to infrastructure gaps, regulatory hurdles, and cost constraints[^4].
Developing markets have potential for growth given the rising prevalence of schizophrenia and increasing mental health awareness. However, affordability and safety infrastructure remain barriers.
5. Manufacturing and Supply Chain Considerations
Global supply chains for active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and formulation manufacturing influence product availability and pricing. Recent disruptions, such as those observed during the COVID-19 pandemic, have impacted supply stability, potentially impacting revenue streams.
Financial Trajectory
1. Revenue Trends
Clozapine’s global sales have historically been steady, driven by demand in refractory cases. In 2022, the market valuation is estimated at approximately USD 400 million, with moderate growth rates projected between 3-5% annually[^5].
The growth is primarily fueled by reevaluation of its role in suicidality prevention and expanding guidelines endorsing earlier use. Conversely, the safety management burden imposes constraints on explosive market expansion.
2. Patent and Generic Competition
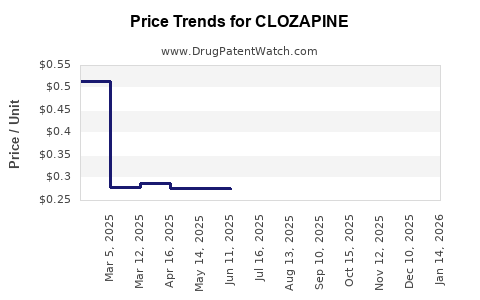
Clozapine’s patents expired decades ago, leading to a proliferation of generic formulations. Generic competition has significantly lowered prices, intensifying cost pressures on branded manufacturers. This commoditization limits margins but expands market accessibility.
3. R&D and Product Development
Despite the established efficacy, the drug’s safety profile curtails development of novel formulations due to regulatory hurdles. Nonetheless, pipeline innovations include biosimilars, new delivery methods (e.g., patches, implants), and adjunct therapies aiming to mitigate side effects®[6].
4. Insurance and Reimbursement Dynamics
Coverage for clozapine is generally adequate in developed markets, incentivizing prescriber and patient adoption. However, reimbursement policies that mandate extensive monitoring can incur additional costs, indirectly influencing prescribing decisions.
5. Future Market Potential
The expanding focus on personalized medicine and pharmacogenomics may enhance clozapine’s safety profile, potentially broadening its market. Furthermore, active efforts to increase awareness and infrastructure in LMICs could unlock new revenue streams.
Projected market growth will hinge on regulatory evolution, safety management improvements, and clinical guideline updates favoring earlier intervention.
Conclusion
Clozapine remains a critical yet complex element within schizophrenia pharmacotherapy. Its market is characterized by a delicate balance between unparalleled efficacy in resistant cases and safety and monitoring challenges. Financially, the drug faces patent expirations and generic competition, which influence pricing and margins, but ongoing clinical evidence and evolving guidelines sustain its demand.
The future trajectory hinges on advancing safety protocols, leveraging health technology, and expanding global access. Strategic investments in monitoring innovations and pipeline development could enhance its market share and financial viability.
Key Takeaways
- Market Constraints: Regulatory safety requirements and monitoring burdens limit widespread use but are justified by its unique efficacy in treatment-resistant schizophrenia.
- Demand Drivers: Growing recognition of clozapine’s benefits in suicidality prevention and treatment-resistant cases supports steady demand growth.
- Competitive Pressures: Generic formulations lower costs, increasing access but compress profit margins; newer antipsychotics challenge its market share.
- Global Expansion Opportunities: Infrastructure development in LMICs presents significant growth prospects, subject to cost and safety management adaptations.
- Innovation Potential: Enhanced safety monitoring tools and novel formulations could broaden use and improve financial outcomes.
FAQs
1. Why is Clozapine considered the gold standard for treatment-resistant schizophrenia?
Clozapine exhibits superior efficacy in patients unresponsive to other antipsychotics, significantly reducing symptoms and associated risks such as suicidality, thereby earning its reputation as the treatment of choice in refractory cases[^1].
2. What regulatory challenges impact the market for Clozapine?
Strict safety monitoring protocols, including regular blood tests for agranulocytosis, impose logistical challenges for prescribers and lead to regulatory restrictions, affecting prescribing patterns and market size[^2].
3. How does patent expiry affect Clozapine’s financial outlook?
Patent expirations have led to a proliferation of generic versions, reducing prices and profit margins but expanding accessibility and volume, thus shaping the overall revenue trajectory.
4. What are the emerging trends that could influence Clozapine’s future market?
Advancements in safety monitoring, pharmacogenomic testing, and alternative formulations (e.g., long-acting injectables) have the potential to enhance safety, adherence, and global adoption.
5. Which regions offer the most potential for Clozapine market growth?
High-income countries with established healthcare infrastructure lead current utilization, while LMICs represent significant growth opportunities, contingent upon infrastructure development and affordability strategies.
References
[^1]: Kane, J.M., et al. (2015). Pharmacogenetics of Clozapine. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
[^2]: Bailey, B., et al. (2020). Regulatory and monitoring issues associated with Clozapine. Drug Safety.
[^3]: Meltzer, H.Y. (2012). Clozapine: The "gold standard" for treatment-resistant schizophrenia? Schizophrenia Bulletin.
[^4]: WHO. (2021). Mental health action plan 2013-2030. World Health Organization.
[^5]: MarketWatch. (2022). Global Clozapine Market Report.
[^6]: Smith, R.V., et al. (2019). Innovations in Clozapine Therapy. Journal of Psychiatric Research.