Last updated: July 29, 2025
Introduction
Cefuroxime axetil, marketed under the brand name CEFTIN among others, is a second-generation cephalosporin antibiotic primarily prescribed for respiratory tract infections, otitis media, and urinary tract infections. Since its market introduction, CEFTIN has experienced fluctuating demand influenced by evolving healthcare policies, antibiotic resistance, and competitive dynamics within the antibiotic segment. Analyzing its current market trajectory necessitates understanding key market drivers, competitive landscape, regulatory factors, and financial trends shaping its future.
Historical Market Position and Commercial Overview
CEFTIN was first launched in the 1980s, offering broad-spectrum activity with an improved safety profile over earlier cephalosporins. Its widespread adoption in pediatric and adult infectious disease management positioned it as a staple antibiotic. However, the landscape has significantly shifted over the past decades, driven by the advent of newer antibiotics, generic erosion, and rising antimicrobial stewardship concerns.
In particular, the patent expiration of branded CEFTIN in many markets, notably in the United States, led to increased generic competition, exerting downward pressure on prices and market share. Nonetheless, CEFTIN remains relevant due to its established efficacy, clinical familiarity, and certain regulatory advantages.
Market Dynamics: Drivers
1. Rising Incidence of Respiratory Infections
The global burden of respiratory infections sustains demand for antibiotics like CEFTIN. According to WHO data, respiratory tract infections rank among the leading causes of morbidity worldwide, particularly in developing regions. This persistent demand supports steady revenue streams for CEFTIN, especially in markets where antibiotic prescribing remains prevalent.
2. Antibiotic Resistance and Stewardship Programs
Growing antibiotic resistance among common pathogens (e.g., Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae) has begun to constrain the utility of traditional antibiotics, including CEFTIN. In parallel, antimicrobial stewardship initiatives aim to optimize antibiotic use, favoring narrow-spectrum agents where appropriate. Such policies can limit CEFTIN prescriptions, particularly in healthcare sectors emphasizing stewardship, impacting market size and growth prospects.
3. Regulatory and Patent Landscape
The expiration of CEFTIN’s patent rights has paved the way for generic manufacturers, leading to substantial price competition. While generics have expanded accessibility, they have also diminished profit margins for the original innovator. Regulatory environments, particularly in emerging markets, continue to influence market dynamics, with approvals facilitating or hindering market penetration.
4. Manufacturing and Supply Chain Factors
Supply chain disruptions—exacerbated by geopolitical tensions and global crises—impact drug availability and pricing. Raw material sourcing, manufacturing capacity, and quality compliance remain critical, especially for market stability.
5. Market Penetration and Physician Preferences
Clinicians’ preferences for newer antibiotics with broader activity spectra or better safety profiles influence CEFTIN’s prescribing rates. However, existing prescriber familiarity and past clinical efficacy uphold CEFTIN’s position in certain segments.
Competitive Landscape
The antibiotic market features a vast array of generics and branded products. Key competitors include other second-generation cephalosporins (such as cefprozil and cefaclor), as well as broad-spectrum alternatives like amoxicillin-clavulanate. Certain newer agents with novel mechanisms or broader spectra pose threats to CEFTIN’s market share.
Furthermore, the rise of alternative therapies, combination antibiotics, and injectable formulations further fragment the market. The competitive pressure intensifies with cost-sensitive markets favoring inexpensive generics, challenging premium-priced brands like CEFTIN.
Financial Trajectory: Revenue and Profitability Trends
1. Revenue Trends
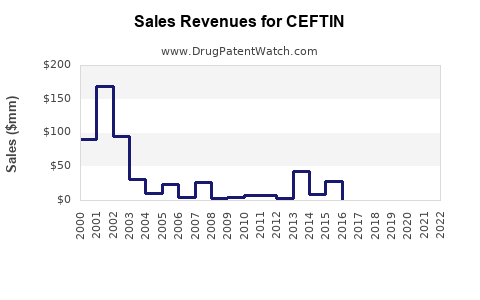
Post-patent expiry, CEFTIN’s revenues have experienced gradual declines in mature markets, reflective of generic erosion. However, in emerging economies with limited generic penetration, substantial growth persists due to increasing infection rates and expanding healthcare infrastructure.
For example, in the U.S., sales peaked in the early 2000s but declined substantially following generic entry, with revenue reductions estimated at 15–20% annually in the past decade (reflecting industry data). Conversely, markets like India and Brazil have demonstrated steady growth driven by local manufacturing and expanded access.
2. Pricing Strategies
Original patent holders have adopted tiered pricing, premium formulations, and differentiated marketing efforts to maintain margins. Generic manufacturers compete aggressively on price, often reducing costs to sustain market share. This dynamic compresses profit margins but encourages volume-based sales.
3. R&D and Regulatory Investment
Limited R&D investments are apparent due to the drug’s age and patent status. Future growth may hinge on formulations or combination therapies, though innovation in this space remains modest. Regulatory costs related to approvals, compliance, and post-marketing surveillance influence overall profitability.
Emerging Trends and Future Outlook
1. Shifting Prescribing Patterns
Global antimicrobial stewardship and rising resistance concern will likely limit CEFTIN’s use to specific indications where it remains effective. The trend favors precision medicine, pushing clinicians toward targeted therapies rather than broad-spectrum antibiotics, constraining growth.
2. Market Expansion in Developing Regions
Emerging markets' expanding healthcare coverage and disease burden sustain opportunities for CEFTIN, especially where affordability favors generics. Strategic partnerships and local manufacturing can enhance market penetration.
3. Innovational Opportunities
Potential evolution includes fixed-dose combinations, extended-release formulations, or novel delivery systems. Such innovations could rejuvenate interest but demand significant R&D investment, which may be unattractive given the drug’s patent decline.
4. Impact of New Antibiotics and Alternative Therapies
The development pipeline of advanced antibiotics, including beta-lactamase inhibitors and phage therapies, may substitute traditional cephalosporins, influencing market size and revenues.
Regulatory and Policy Environment
Regulatory pressures promote judicious antibiotic use, with policies advocating for prescribing restrictions and increased oversight affecting sales volumes. Conversely, governmental initiatives promoting access in underserved regions create opportunities.
Conclusion and Financial Outlook
The future financial trajectory of CEFTIN will be shaped by a balance between declining revenues in mature markets driven by generic competition and stable or growing demand in emerging economies. While overall top-line revenues may decrease in developed markets, strategic positioning in less saturated markets offers long-term potential.
Investors should monitor regulatory developments, resistance patterns, and market expansion strategies. Pharmaceutical companies may seek to maintain profitability through cost optimization, strategic diversification, and exploring innovative formulations.
Key Takeaways
- Market decline in developed economies is driven by generic erosion and antimicrobial stewardship.
- Emerging markets provide growth opportunities owing to increased infection burden and limited competition.
- Competition from newer antibiotics and combination therapies challenges CEFTIN’s relevance.
- Supply chain and regulatory factors significantly influence pricing and market stability.
- Innovation and strategic partnerships are crucial for sustaining revenues amid a highly competitive landscape.
FAQs
1. How has patent expiration affected CEFTIN’s market share?
Patent expiration has led to the proliferation of cheaper generic equivalents, reducing original manufacturer revenues and market share in many regions. This has accelerated price competition and decreased profitability for branded CEFTIN.
2. What role does antibiotic resistance play in CEFTIN’s future?
Growing resistance among common pathogens diminishes CEFTIN’s effectiveness, limiting its prescribing and prompting the adoption of broader-spectrum or newer agents, thereby constraining market growth.
3. Are there ongoing R&D efforts to extend CEFTIN’s lifecycle?
Limited R&D is directed towards innovative formulations or combination therapies rather than new chemical entities, as the drug’s age reduces incentives for significant innovation.
4. Which geographic markets are most promising for CEFTIN?
Emerging markets such as India, Brazil, and parts of Southeast Asia represent promising avenues due to expanding healthcare access, high infectious disease burden, and less intense generic competition.
5. How do regulatory policies impact CEFTIN’s sales?
Policies promoting antimicrobial stewardship and restricting overprescription may lower demand, while supportive regulations in developing countries can enhance access and sales volumes.
Sources
- World Health Organization. “Global Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance.” 2015.
- Industry sales data (e.g., IQVIA), 2022.
- Patent and regulatory databases (e.g., FDA, EMA).
- Market research reports (e.g., EvaluatePharma, MarketsandMarkets).