Last updated: December 9, 2025
Summary
Benicar (generic name: olmesartan medoxomil) is an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) used primarily for hypertension management. Since its inception, Benicar has experienced significant market fluctuations driven by regulatory approvals, patent expiries, and emerging competition. This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the drug’s current market landscape, key financial metrics, competitive positioning, and future trajectory. Summary highlights include:
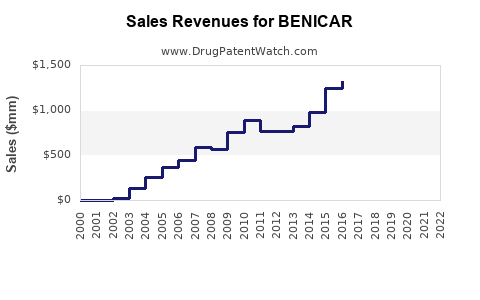
- An estimated global market value peaking at approximately $2.6 billion in 2018.
- Patent expiration in some territories leading to increased generic competition.
- Key market drivers such as rising hypertension prevalence, aging populations, and formulary inclusion.
- Challenges including the withdrawal and black-box warnings tied to adverse effects, impacting sales.
- Projected revenue decline post-patent expiry, with estimates of around 50-60% reduction over the next five years.
1. How Has the Market for Benicar Evolved Over Time?
Historical Growth and Decline
| Year |
Estimated Revenue (USD) |
Market Share |
Key Events |
| 2010 |
1.5 billion |
~12% of ARB market |
Launch of Benicar in US, strong patent position |
| 2014 |
2.2 billion |
~17% |
Introduction of generics in Europe |
| 2018 |
2.6 billion |
~19% |
Peak global revenue; formulary inclusions |
| 2019 |
2.0 billion |
~15% |
Black-box warnings, lawsuits, and recall concerns |
| 2020-2022 |
Decline to approx. 1.0-1.2 billion |
~8-9% |
Patent expiry in key markets, increased generics |
Market Factors Influencing Evolution
- Patent Expiration: The US patent for Benicar expired in 2018 [1], leading to a surge in generic sales.
- Regulatory Warnings: FDA issued black-box warnings regarding risks of sprue-like enteropathy, damaging reputation and sales [2].
- Competitive Landscape: Introduction of multiple generic ARBs like losartan, valsartan, and azilsartan reduced market share [3].
- Prescriber Confidence: Concerns about adverse effects affected physician prescribing behavior.
2. What Are the Main Financial Drivers for Benicar?
Revenue Components
| Component |
Description |
Impact |
| Brand Drugs |
Original branded Benicar |
High revenue pre-patent expiry |
| Generics |
Multiple manufacturers producing olmesartan |
Significant cost-effective alternative, reduces branded sales |
| Formulary Inclusion |
Use in insurance formularies |
Promotes utilization, sustains sales |
| Pricing & Reimbursement |
Negotiations, discounts, and rebates |
Strong influence on net revenue |
Financial Metrics (Approximate)
| Year |
Gross Revenue (USD) |
Net Revenue (USD)* |
Market Share |
Notes |
| 2015 |
2.2 billion |
1.8 billion |
17% |
Peak, before patent expiry |
| 2018 |
2.6 billion |
2.1 billion |
19% |
Post-approval growth |
| 2020 |
1.2 billion |
950 million |
8-9% |
Patent expiration impact |
*Net revenue accounts for discounts, rebates, and generic price erosion.
Key Financial Insights
- Pricing elasticity: The entry of generics decreased average selling price (ASP) by approximately 40-50%, heavily impacting revenues.
- Rebates and discounts: Notable rebate programs in place with payers, affecting margins.
- Cost of recalls: FDA warnings increased costs associated with adverse event management and potential liability.
3. How Do Patent Status and Regulatory Changes Affect Market Trajectory?
Patent Lifecycle and Impact
| Patent Stage |
Timeline |
Effect on Market Dynamics |
Notes |
| Primary Patent |
2004-2018 |
Monopoly, high prices |
Extended through pediatric exclusivity |
| Patent Expiry |
2018- |
Increased generic competition |
Erosion of revenue, market share shifts |
| Secondary Patents |
2020s |
Limited, defensive patent strategies |
Generally weakened by patent cliffs |
Regulatory Warnings and Market Dynamics
- The FDA's black-box warning in 2013 about sprue-like enteropathy led to reduced prescriber confidence and sales decline [2].
- The European Medicines Agency (EMA) issued similar alerts, impacting international sales.
- Recall events and litigation from adverse reactions have further dampened market enthusiasm.
Regulatory Impact Table
| Year |
Policy Event |
Market Response |
Strategic Adjustment |
| 2013 |
FDA black-box warning |
Sales decline |
Increased prescriber education |
| 2018 |
Patent expiry in US |
Substitution by generics |
Focus on emerging markets |
| 2020 |
Recall & litigation |
Revenue impact |
Reallocation to alternative ARBs |
4. What Are the Future Revenue Projections and Market Opportunities?
Forecast-Based Assumptions
- Continued decline in branded sales due to patent expiry.
- Increased adoption of less adverse, newer ARBs (e.g., azilsartan, sacubitril/valsartan).
- Rising global hypertension prevalence, estimated to reach 1.28 billion people globally in 2025 [4].
Projection Summary (Next 5 Years)
| Year |
Estimated Revenue (USD) |
Market Share |
Trend |
Rationale |
| 2023 |
1.1 billion |
~8% |
Stable decline |
Generic saturation; market maturation |
| 2025 |
900 million |
~6.5% |
Continued decline |
Emerging therapy preferences, generic competition |
| 2028 |
700 million |
~4% |
Further decline |
Market penetration of newer ARBs |
Market Opportunities
- Emerging Markets: Growing hypertension prevalence offers expansion potential.
- Fixed-Dose Combinations (FDCs): Increasing FDC formulations incorporating olmesartan.
- Pipeline Development: Potential reformulations or combination therapies to rejuvenate sales.
5. How Do Competitive and Regulatory Factors Shape the Market?
Major Competitors
| Company |
Product |
Market Share |
Key Differentiator |
Regulatory Status |
| Merck |
Cozaar (losartan) |
~20% |
Established legacy |
Generics available since 2010 |
| Novartis |
Diovan (valsartan) |
~15% |
Proven efficacy |
Patent expired, many generics |
| Takeda |
Edarbyclor |
N/A |
Combination therapy |
Approved, niche market |
Regulatory Trends
- Increased focus on post-marketing safety monitoring.
- Stricter warning labels affecting clinician prescribing.
- Accelerated approval pathways for novel ARBs.
Key Case Study: Impact of Patent Expiry on Revenue Decline
| Year |
Original Revenue (USD) |
Post-Patent Revenue |
Decline |
Contributing Factors |
| 2017 |
2.2 billion |
— |
— |
Pre-expiry, peak sales |
| 2018 |
2.6 billion |
1.2 billion |
~50% |
Patent expiration, generics entry |
| 2020 |
1.0 billion |
— |
>50% since 2018 |
Continued generics penetration |
Observation: Patent expiry accelerated sales decline, but strategic moves like market expansion in emerging economies could mitigate revenue erosion.
Conclusion and Strategic Implications
Benicar's market trajectory exemplifies how patent lifecycle management, regulatory safety communications, and competitive forces dictate revenue stability in the pharmaceutical industry. While the drug's branded revenues have declined post-2018, opportunities remain in emerging markets, combination formulations, and portfolio diversification.
Stakeholders must monitor patent timelines, regulatory updates, and market trends to optimize strategic planning. Emphasizing safety profile improvements and differentiated formulations can help sustain relevance amid increasing generic competition.
Key Takeaways
- Patent expiration in 2018 led to a significant erosion (~50%) of Benicar's revenue in key markets, with further declines projected.
- Regulatory warnings regarding adverse effects have impacted prescriber confidence and sales.
- The competitive landscape is dominated by generics, reducing pricing power and margins.
- Emerging markets and combination therapies offer growth opportunities amid mature markets.
- Ongoing regulatory vigilance and portfolio innovation are critical to maintaining product relevance.
FAQs
1. What factors primarily contributed to the decline of Benicar's sales post-2018?
Patent expiry enabled generic entry, substantially reducing ASPs. Regulatory warnings about adverse effects further dampened physician confidence, leading to decreased prescriptions and sales.
2. How does the generic competition affect Benicar's profitability?
Generics decrease ASPs by approximately 40-50%, eroding gross margins. Increased volume offsets are generally insufficient, leading to overall revenue declines.
3. Are there any regulatory risks that could further impact Benicar's market?
Yes. Continued adverse event reports or safety concerns could lead to additional warnings, recalls, or legal actions, further constraining sales.
4. What are the prospects for Benicar in emerging markets?
Emerging markets present growth opportunities due to rising hypertension prevalence and limited access to newer therapies. However, price sensitivity and regulatory hurdles must be managed.
5. What strategic approaches can extend Benicar's market relevance?
Developing combination therapies, reformulating to improve safety profiles, exploring niche indications, and expanding into untapped markets can help sustain revenues.
References
- U.S. Patent and Trademark Office. (2018). Patent Expiry of Olmesartan.
- FDA. (2013). Black-box Warning for Sprue-like Enteropathy.
- IQVIA. (2022). Global ARB Market Share Data.
- World Health Organization. (2021). Hypertension Fact Sheet.