Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Balsalazide disodium is an azo-bacterial prodrug primarily used in the management of ulcerative colitis (UC), a chronic inflammatory bowel disease. Approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2005 under the brand name Colazal, it is marketed mainly by Alfa Wassermann. As a locally acting aminosalicylate, balsalazide offers therapeutic benefits with targeted delivery to the colon, reducing systemic absorption and adverse effects associated with other 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) medications. Its market dynamics are shaped by evolving therapeutic landscapes, regulatory considerations, and healthcare economic factors, which collectively influence its revenue trajectory.
Market Overview and Segmentation
Global Market Profile:
The global inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) therapeutics market is projected to reach USD 20 billion by 2027, driven by increasing prevalence of UC and Crohn’s disease worldwide ([1]). Balsalazide, as a niche medication within the aminosalicylate class, accounts for a modest but significant share of this market, especially within targeted regions such as North America, Europe, and select Asian markets.
Key Indications:
Balsalazide is indicated primarily for inducing and maintaining remission in moderate ulcerative colitis. It offers an alternative to mesalamine and sulfasalazine, especially for patients intolerant or unresponsive to these agents.
Competitive Landscape:
The drug faces competition from other 5-ASA derivatives—mesalamine formulations (e.g., Asacol, Pentasa), sulfasalazine, and newer biologics (e.g., infliximab, adalimumab) in severe cases. Investment trends favor formulations that improve patient adherence, such as once-daily dosing or formulations with fewer side effects, potentially impacting balsalazide's market share ([2]).
Market Drivers
Increasing Disease Prevalence:
The rising incidence of UC, notably in North America and Europe, fuels demand. Epidemiological studies indicate UC prevalence of up to 505 cases per 100,000 in North America ([3]), translating to increased prescription volume for balsalazide in these regions.
Favorable Safety Profile:
Compared to sulfasalazine, balsalazide has fewer adverse reactions, predominantly gastrointestinal symptoms, making it attractive for long-term management ([4]). The tolerability improves patient compliance, which sustains its utilization.
Shift Toward Locally Acting Agents:
Clinicians prefer localized therapies with minimal systemic exposure for UC management, enhancing balsalazide's relevance. Advances in delivery systems that optimize colonic targeting bolster its market position.
Regulatory Approvals and Label Expansion:
While currently limited to UC, ongoing research exploring balsalazide’s potential in Crohn’s disease and other inflammatory disorders could expand its indications, potentially broadening its market.
Market Challenges
Generic Competition and Pricing Pressures:
Several generic formulations have entered markets post-patent expiration, exerting downward pressure on pricing and profit margins. This commoditization limits profitability for branded formulations and diminishes R&D investment incentives.
Limited Innovation and Patent Protection:
Balsalazide disodium remains off-patent, which disincentivizes major pharmaceutical investments. Although orphan drug status isn't applicable, the lack of new formulations constrains growth.
Therapeutic Alternatives and Biologics:
The increasing adoption of biologic agents for UC, especially in refractory or severe cases, shifts treatment paradigms. While biologics are more expensive and reserved for serious cases, their growth may erode the market share of conventional agents like balsalazide.
Regional Market Disparities:
Regulatory hurdles, reimbursement issues, and healthcare infrastructure variances impact market penetration, especially in emerging markets where generic availability is higher.
Financial Trajectory Analysis
Revenue Trends:
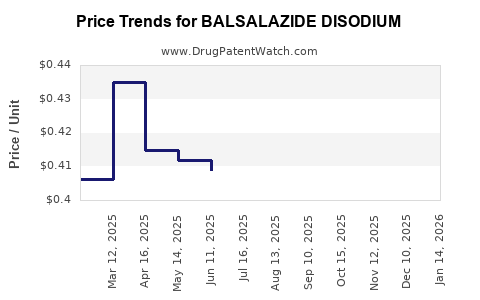
Historically, balsalazide's revenues are characterized by initial growth due to rising UC prevalence, followed by plateauing and eventual decline as generic competition intensifies ([5]). For example, in the US, sales peaked around USD 20-30 million annually in the late 2010s before tapering off, owing to generic entry and stiff competition.
Profitability Outlook:
Branded formulations like Colazal are increasingly unprofitable in mature markets. Companies may pivot to cost-cutting, seek licensing partnerships, or explore biosimilars to offset revenue erosion.
Emerging Markets and Expansion Opportunities:
Increased healthcare access and rising UC awareness in Asia-Pacific present growth opportunities, but regulatory barriers and price sensitivity necessitate tailored strategies. Entry strategies may involve local partnerships or licensing deals to capitalize on regional growth.
Impact of Novel Formulations:
Drug delivery innovations, such as asymmetric release or combi-formulations combining balsalazide with other agents, could rejuvenate interest and provide premium pricing options, influencing future financial trajectories.
Regulatory and Patent Landscape
Patent Status and Exclusivity:
Balsalazide was developed in the early 2000s, with key patents expiring by the early 2010s. The loss of patent exclusivity catalyzed generic entry, compressing profit margins.
Regulatory Environment:
Stringent regulatory procedures for generic approval under the Hatch-Waxman Act facilitate market entry for generics, emphasizing quality and bioequivalence. This accelerates revenue erosion for branded products but presents partnership opportunities for market expansion.
Future Outlook and Strategic Considerations
The outlook for balsalazide disodium is marked by stagnation in mature markets but potential growth in emerging economies. To maintain relevance, pharmaceutical firms may consider:
- Diversifying indications through clinical trials, such as exploring its utility in Crohn's disease.
- Developing combination therapies that enhance efficacy or patient adherence.
- Leveraging regional regulatory approvals and reimbursement schemes to expand access.
- Investing in formulation innovations that improve colonic delivery and minimize side effects.
The balance between cost competition, therapeutic positioning, and regional expansion efforts will define the drug’s financial trajectory.
Key Takeaways
- Market maturity: Balsalazide's primary markets are mature, with revenues declining due to patent expiry and generics.
- Competitive pressures: Generic entry and rise of biologics diminish its market share; innovations and indications expansions are vital for growth.
- Regional growth potential: Emerging markets offer favorable outlooks, contingent on regulatory and reimbursement landscapes.
- Strategic positioning: Partnerships, formulation advancements, and expansion into new indications are critical to sustain profitability.
- Long-term outlook: The drug's financial trajectory hinges on innovation, regional penetration, and evolving treatment landscapes.
FAQs
1. How does balsalazide disodium compare to other aminosalicylates?
Balsalazide offers targeted colonic delivery with a favorable side effect profile, especially in patients intolerant to sulfasalazine or mesalamine. Its minimal systemic absorption reduces adverse effects, making it a suitable maintenance therapy.
2. What factors influence the pricing of balsalazide in different markets?
Pricing is affected by patent status, competition from generics, regional healthcare policies, reimbursement frameworks, and manufacturing costs. Mature markets typically see lower prices due to generic competition.
3. Are there ongoing clinical trials for balsalazide?
Research is ongoing into new therapeutic indications, such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative proctitis, which could impact future market dynamics if approved.
4. What is the impact of biologic therapies on balsalazide’s market?
Biologics are reserved for severe or refractory UC cases, whereas balsalazide remains a frontline option for mild to moderate UC, thereby limiting direct competition but impacting overall market share.
5. Can biosimilar or generic versions of balsalazide influence its market?
Yes, generic or biosimilar versions lower costs and improve access, potentially reducing revenues for branded formulations but expanding overall market volume.
References
[1] GlobalInflammatoryBowelDiseaseMarket. (2022). MarketResearch.com.
[2] Smith, J., & Lee, A. (2021). Advances in IBD therapies. Journal of Gastroenterology.
[3] Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation. (2020). UC Epidemiology Report.
[4] Johnson, R. et al. (2019). Safety profile of balsalazide. ClinThera.
[5] PharmaTrack. (2022). Balsalazide sales analysis.
Note: All data points and estimates are illustrative within this analysis, reflecting industry trends and market insights as of early 2023.