POSACONAZOLE - Generic Drug Details
✉ Email this page to a colleague
What are the generic drug sources for posaconazole and what is the scope of freedom to operate?
Posaconazole
is the generic ingredient in three branded drugs marketed by Msd Merck Co, Merck Sharp Dohme, Aspiro, Eugia Pharma, Fresenius Kabi Usa, Gland, Mylan Labs Ltd, Ph Health, Schering, Hikma, Actavis Labs Fl Inc, Aet Pharma, Amneal, Aurobindo Pharma, Biocon Pharma, Dr Reddys, Hetero Labs Ltd Iii, I 3 Pharms, MSN, Qilu Pharm Hainan, Sinotherapeutics Inc, Specgx Llc, and Westminster Pharms, and is included in twenty-four NDAs. There are six patents protecting this compound and three Paragraph IV challenges. Additional information is available in the individual branded drug profile pages.Posaconazole has eighty-one patent family members in twenty-four countries.
There are twenty-one drug master file entries for posaconazole. Twenty-nine suppliers are listed for this compound. There is one tentative approval for this compound.
Summary for POSACONAZOLE
| International Patents: | 81 |
| US Patents: | 6 |
| Tradenames: | 3 |
| Applicants: | 23 |
| NDAs: | 24 |
| Drug Master File Entries: | 21 |
| Finished Product Suppliers / Packagers: | 29 |
| Raw Ingredient (Bulk) Api Vendors: | 81 |
| Clinical Trials: | 93 |
| Patent Applications: | 5,262 |
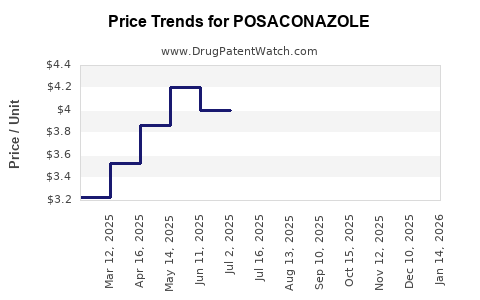
| Drug Prices: | Drug price trends for POSACONAZOLE |
| Patent Litigation and PTAB cases: | See patent lawsuits and PTAB cases for POSACONAZOLE |
| What excipients (inactive ingredients) are in POSACONAZOLE? | POSACONAZOLE excipients list |
| DailyMed Link: | POSACONAZOLE at DailyMed |
Recent Clinical Trials for POSACONAZOLE
Identify potential brand extensions & 505(b)(2) entrants
| Sponsor | Phase |
|---|---|
| AstraZeneca | PHASE1 |
| Tongji Hospital | NA |
| Ruijin Hospital North Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine | NA |
Generic filers with tentative approvals for POSACONAZOLE
| Applicant | Application No. | Strength | Dosage Form |
| ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 18MG | INJECTION;SOLUTION |
The 'tentative' approval signifies that the product meets all FDA standards for marketing, and, but for the patents / regulatory protections, it would approved.
Pharmacology for POSACONAZOLE
| Drug Class | Azole Antifungal |
Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) Classes for POSACONAZOLE
Paragraph IV (Patent) Challenges for POSACONAZOLE
| Tradename | Dosage | Ingredient | Strength | NDA | ANDAs Submitted | Submissiondate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOXAFIL | Injection | posaconazole | 18 mg/mL, 16.7 mL vials | 205596 | 1 | 2015-11-24 |
| NOXAFIL | Delayed-release Tablets | posaconazole | 100 mg | 205053 | 1 | 2014-06-16 |
| NOXAFIL | Oral Suspension | posaconazole | 40 mg/mL | 022003 | 1 | 2011-02-28 |
US Patents and Regulatory Information for POSACONAZOLE
| Applicant | Tradename | Generic Name | Dosage | NDA | Approval Date | TE | Type | RLD | RS | Patent No. | Patent Expiration | Product | Substance | Delist Req. | Exclusivity Expiration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aspiro | POSACONAZOLE | posaconazole | SOLUTION;INTRAVENOUS | 219057-001 | Dec 23, 2024 | AP | RX | No | No | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | |||
| Ph Health | POSACONAZOLE | posaconazole | SOLUTION;INTRAVENOUS | 208768-001 | May 25, 2022 | AP | RX | No | No | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | |||
| Schering | NOXAFIL | posaconazole | SUSPENSION;ORAL | 022003-001 | Sep 15, 2006 | AB | RX | Yes | Yes | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | |||
| Eugia Pharma | POSACONAZOLE | posaconazole | SOLUTION;INTRAVENOUS | 214842-001 | Dec 26, 2023 | AP | RX | No | No | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | |||
| Merck Sharp Dohme | NOXAFIL | posaconazole | TABLET, DELAYED RELEASE;ORAL | 205053-001 | Nov 25, 2013 | DISCN | Yes | No | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | ||||
| >Applicant | >Tradename | >Generic Name | >Dosage | >NDA | >Approval Date | >TE | >Type | >RLD | >RS | >Patent No. | >Patent Expiration | >Product | >Substance | >Delist Req. | >Exclusivity Expiration |
Expired US Patents for POSACONAZOLE
| Applicant | Tradename | Generic Name | Dosage | NDA | Approval Date | Patent No. | Patent Expiration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schering | NOXAFIL | posaconazole | SUSPENSION;ORAL | 022003-001 | Sep 15, 2006 | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free |
| Merck Sharp Dohme | NOXAFIL | posaconazole | SOLUTION;INTRAVENOUS | 205596-001 | Mar 13, 2014 | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free |
| Schering | NOXAFIL | posaconazole | SUSPENSION;ORAL | 022003-001 | Sep 15, 2006 | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free |
| Merck Sharp Dohme | NOXAFIL | posaconazole | TABLET, DELAYED RELEASE;ORAL | 205053-001 | Nov 25, 2013 | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free |
| Schering | NOXAFIL | posaconazole | SUSPENSION;ORAL | 022003-001 | Sep 15, 2006 | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free |
| >Applicant | >Tradename | >Generic Name | >Dosage | >NDA | >Approval Date | >Patent No. | >Patent Expiration |
EU/EMA Drug Approvals for POSACONAZOLE
| Company | Drugname | Inn | Product Number / Indication | Status | Generic | Biosimilar | Orphan | Marketing Authorisation | Marketing Refusal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Merck Sharp and Dohme B.V | Noxafil | posaconazole | EMEA/H/C/000610Noxafil gastro-resistant tablets are indicated for use in the treatment of the following fungal infections in adults (see sections 4.2 and 5.1):- Invasive aspergillosisNoxafil gastro-resistant tablets are indicated for use in the treatment of the following fungal infections in paediatric patients from 2 years of age weighing more than 40 kg and adults (see sections 4.2 and 5.1):- Invasive aspergillosis in patients with disease that is refractory to amphotericin B or itraconazole or in patients who are intolerant of these medicinal products;- Fusariosis in patients with disease that is refractory to amphotericin B or in patients who are intolerant of amphotericin B;- Chromoblastomycosis and mycetoma in patients with disease that is refractory to itraconazole or in patients who are intolerant of itraconazole;- Coccidioidomycosis in patients with disease that is refractory to amphotericin B, itraconazole or fluconazole or in patients who are intolerant of these medicinal products.Refractoriness is defined as progression of infection or failure to improve after a minimum of 7 days of prior therapeutic doses of effective antifungal therapy.Noxafil gastro-resistant tablets are also indicated for prophylaxis of invasive fungal infections in the following paediatric patients from 2 years of age weighing more than 40 kg and adults (see sections 4.2 and 5.1):- Patients receiving remission-induction chemotherapy for acute myelogenous leukaemia (AML) or myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) expected to result in prolonged neutropenia and who are at high risk of developing invasive fungal infections;- Hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) recipients who are undergoing high-dose immunosuppressive therapy for graft versus host disease and who are at high risk of developing invasive fungal infections.Please refer to the Summary of Product Characteristics of Noxafil oral suspension for use in oropharyngeal candidiasis. Noxafil concentrate for solution for infusion is indicated for use in the treatment of the following fungal infections in adults (see sections 4.2 and 5.1):- Invasive aspergillosisNoxafil concentrate for solution for infusion is indicated for use in the treatment of the following fungal infections in adult and paediatric patients from 2 years of age (see sections 4.2 and 5.1):- Invasive aspergillosis in patients with disease that is refractory to amphotericin B or itraconazole or in patients who are intolerant of these medicinal products;- Fusariosis in patients with disease that is refractory to amphotericin B or in patients who are intolerant of amphotericin B;- Chromoblastomycosis and mycetoma in patients with disease that is refractory to itraconazole or in patients who are intolerant of itraconazole;- Coccidioidomycosis in patients with disease that is refractory to amphotericin B, itraconazole or fluconazole or in patients who are intolerant of these medicinal products.Refractoriness is defined as progression of infection or failure to improve after a minimum of 7 days of prior therapeutic doses of effective antifungal therapy.Noxafil concentrate for solution for infusion is also indicated for prophylaxis of invasive fungal infections in the following adult and paediatric patients from 2 years of age (see sections 4.2 and 5.1):- Patients receiving remission-induction chemotherapy for acute myelogenous leukaemia (AML) or myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) expected to result in prolonged neutropenia and who are at high risk of developing invasive fungal infections;- Hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) recipients who are undergoing high-dose immunosuppressive therapy for graft versus host disease (GVHD) and who are at high risk of developing invasive fungal infections.Please refer to the Summary of Product Characteristics of Noxafil oral suspension for use in oropharyngeal candidiasis. Noxafil gastro resistant powder and solvent for oral suspension is indicated for use in the treatment of the following fungal infections in paediatric patients from 2 years of age (see sections 4.2 and 5.1):- Invasive aspergillosis in patients with disease that is refractory to amphotericin B or itraconazole or in patients who are intolerant of these medicinal products;- Fusariosis in patients with disease that is refractory to amphotericin B or in patients who are intolerant of amphotericin B;- Chromoblastomycosis and mycetoma in patients with disease that is refractory to itraconazole or in patients who are intolerant of itraconazole;- Coccidioidomycosis in patients with disease that is refractory to amphotericin B, itraconazole or fluconazole or in patients who are intolerant of these medicinal products.Refractoriness is defined as progression of infection or failure to improve after a minimum of 7 days of prior therapeutic doses of effective antifungal therapy.Noxafil gastro-resistant powder and solvent for oral suspension is indicated for prophylaxis of invasive fungal infections in the following paediatric patients from 2 years of age:- Patients receiving remission-induction chemotherapy for acute myelogenous leukaemia (AML) or myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) expected to result in prolonged neutropenia and who are at high risk of developing invasive fungal infections;- Haematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) recipients who are undergoing high-dose immunosuppressive therapy for graft versus host disease and who are at high risk of developing invasive fungal infections.Please refer to the Summary of Product Characteristics of Noxafil concentrate for solution for infusion and the gastro-resistant tablets for use in primary treatment of invasive aspergillosis.Please refer to the Summary of Product Characteristics of Noxafil oral suspension for use in oropharyngeal candidiasis. Noxafil oral suspension is indicated for use in the treatment of the following fungal infections in adults (see section 5.1):- Invasive aspergillosis in patients with disease that is refractory to amphotericin B or itraconazole or in patients who are intolerant of these medicinal products;- Fusariosis in patients with disease that is refractory to amphotericin B or in patients who are intolerant of amphotericin B;- Chromoblastomycosis and mycetoma in patients with disease that is refractory to itraconazole or in patients who are intolerant of itraconazole;- Coccidioidomycosis in patients with disease that is refractory to amphotericin B, itraconazole or fluconazole or in patients who are intolerant of these medicinal products;- Oropharyngeal candidiasis: as first-line therapy in patients who have severe disease or are immunocompromised, in whom response to topical therapy is expected to be poor.Refractoriness is defined as progression of infection or failure to improve after a minimum of 7 days of prior therapeutic doses of effective antifungal therapy.Noxafil oral suspension is also indicated for prophylaxis of invasive fungal infections in the following patients:- Patients receiving remission-induction chemotherapy for acute myelogenous leukaemia (AML) or myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) expected to result in prolonged neutropenia and who are at high risk of developing invasive fungal infections;- Hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) recipients who are undergoing high-dose immunosuppressive therapy for graft versus host disease and who are at high risk of developing invasive fungal infections.Please refer to the Summary of Product Characteristics of Noxafil concentrate for solution for infusion and the gastro-resistant tablets for use in primary treatment of invasive aspergillosis. | Authorised | no | no | no | 2005-10-25 | |
| Accord Healthcare S.L.U. | Posaconazole AHCL | posaconazole | EMEA/H/C/005028Posaconazole AHCL oral suspension is indicated for use in the treatment of the following fungal infections in adults:Invasive aspergillosis in patients with disease that is refractory to amphotericin B or itraconazole or in patients who are intolerant of these medicinal products;Fusariosis in patients with disease that is refractory to amphotericin B or in patients who are intolerant of amphotericin B;Chromoblastomycosis and mycetoma in patients with disease that is refractory to itraconazole or in patients who are intolerant of itraconazole;Coccidioidomycosis in patients with disease that is refractory to amphotericin B, itraconazole or fluconazole or in patients who are intolerant of these medicinal products.Oropharyngeal candidiasis: as first-line therapy in patients who have severe disease or are immunocompromised, in whom response to topical therapy is expected to be poor.Refractoriness is defined as progression of infection or failure to improve after a minimum of 7 days of prior therapeutic doses of effective antifungal therapy.Posaconazole AHCL oral suspension is also indicated for prophylaxis of invasive fungal infections in the following patients:Patients receiving remission-induction chemotherapy for acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) or myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) expected to result in prolonged neutropenia and who are at high risk of developing invasive fungal infections;Hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) recipients who are undergoing high-dose immunosuppressive therapy for graft versus host disease and who are at high risk of developing invasive fungal infections. | Authorised | yes | no | no | 2019-07-25 | |
| Accord Healthcare S.L.U. | Posaconazole Accord | posaconazole | EMEA/H/C/005005Posaconazole Accord is indicated for use in the treatment of the following fungal infections in adults:Invasive aspergillosis;Fusariosis in patients with disease that is refractory to amphotericin B or in patients who are intolerant of amphotericin B;Chromoblastomycosis and mycetoma in patients with disease that is refractory to itraconazole or in patients who are intolerant of itraconazole;Coccidioidomycosis in patients with disease that is refractory to amphotericin B, itraconazole or fluconazole or in patients who are intolerant of these medicinal products.Refractoriness is defined as progression of infection or failure to improve after a minimum of 7 days of prior therapeutic doses of effective antifungal therapy.Posaconazole Accord is also indicated for prophylaxis of invasive fungal infections in the following patients: Patients receiving remission-induction chemotherapy for acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) or myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) expected to result in prolonged neutropenia and who are at high risk of developing invasive fungal infections;Hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) recipients who are undergoing high-dose immunosuppressive therapy for graft versus host disease and who are at high risk of developing invasive fungal infections. | Authorised | yes | no | no | 2019-07-25 | |
| Schering-Plough Europe | Posaconazole SP | posaconazole | EMEA/H/C/000611Posaconazole SP is indicated for use in the treatment of the following fungal infections in adults (see section 5.1):- Invasive aspergillosis in patients with disease that is refractory to amphotericin B or itraconazole or in patients who are intolerant of these medicinal products;- Fusariosis in patients with disease that is refractory to amphotericin B or in patients who are intolerant of amphotericin B;- Chromoblastomycosis and mycetoma in patients with disease that is refractory to itraconazole or in patients who are intolerant of itraconazole;- Coccidioidomycosis in patients with disease that is refractory to amphotericin B, itraconazole or fluconazole or in patients who are intolerant of these medicinal products;- Oropharyngeal candidiasis: as first-line therapy in patients who have severe disease or are immunocompromised, in whom response to topical therapy is expected to be poor.Refractoriness is defined as progression of infection or failure to improve after a minimum of 7 days of prior therapeutic doses of effective antifungal therapy.Posaconazole SP is also indicated for prophylaxis of invasive fungal infections in the following patients:- Patients receiving remission-induction chemotherapy for acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) or myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) expected to result in prolonged neutropenia and who areat high risk of developing invasive fungal infections;- Hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) recipients who are undergoing high-dose immunosuppressive therapy for graft versus host disease and who are at high risk of developing invasive fungal infections. | Withdrawn | no | no | no | 2005-10-25 | |
| >Company | >Drugname | >Inn | >Product Number / Indication | >Status | >Generic | >Biosimilar | >Orphan | >Marketing Authorisation | >Marketing Refusal |
International Patents for POSACONAZOLE
| Country | Patent Number | Title | Estimated Expiration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eurasian Patent Organization | 031355 | ⤷ Get Started Free | |
| Mexico | 346901 | FORMULACIONES DE SOLUCION INTRAVENOSA DE POSACONAZOL ESTABILIZADAS MEDIANTE BETA-CICLODEXTRINA SUSTITUIDA. (POSACONAZOLE INTRAVENOUS SOLUTION FORMULATIONS STABILIZED BY SUBSTITUTED BETA-CYCLODEXTRIN.) | ⤷ Get Started Free |
| Russian Federation | 2747757 | КОМПОЗИЦИИ АЛКИЛИРОВАННОГО ЦИКЛОДЕКСТРИНА И СПОСОБЫ ИХ ПОЛУЧЕНИЯ И ПРИМЕНЕНИЯ (COMPOSITIONS OF ALKYLATED CYCLODEXTRIN AND METHODS OF THEIR PREPARATION AND APPLICATION) | ⤷ Get Started Free |
| Denmark | 3391890 | ⤷ Get Started Free | |
| European Patent Office | 2588116 | FORMULATIONS D'UNE SOLUTION INTRAVEINEUSE DE POSACONAZOLE STABILISÉES PAR UNE CYCLODEXTRINE BÊTA SUBSTITUÉE (POSACONAZOLE INTRAVENOUS SOLUTION FORMULATIONS STABILIZED BY SUBSTITUTED BETA-CYCLODEXTRIN) | ⤷ Get Started Free |
| >Country | >Patent Number | >Title | >Estimated Expiration |
Supplementary Protection Certificates for POSACONAZOLE
| Patent Number | Supplementary Protection Certificate | SPC Country | SPC Expiration | SPC Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0736030 | SPC/GB06/007 | United Kingdom | ⤷ Get Started Free | PRODUCT NAME: POSACONAZOLE, OPTIONALLY IN THE FORM OF AN ESTER OR PHARMACEUTICALLY ACCEPTABLE SALT.; REGISTERED: UK EU/1/05/320/001 20051025; UK EU/1/05/321/001 20051025 |
| 0736030 | 06C0009 | France | ⤷ Get Started Free | PRODUCT NAME: POSACONAZOLE; REGISTRATION NO/DATE: EU/1/05/320/001 20051025 |
| >Patent Number | >Supplementary Protection Certificate | >SPC Country | >SPC Expiration | >SPC Description |
Market Dynamics and Financial Trajectory for Posaconazole
More… ↓
Make Better Decisions: Try a trial or see plans & pricing
Drugs may be covered by multiple patents or regulatory protections. All trademarks and applicant names are the property of their respective owners or licensors. Although great care is taken in the proper and correct provision of this service, thinkBiotech LLC does not accept any responsibility for possible consequences of errors or omissions in the provided data. The data presented herein is for information purposes only. There is no warranty that the data contained herein is error free. We do not provide individual investment advice. This service is not registered with any financial regulatory agency. The information we publish is educational only and based on our opinions plus our models. By using DrugPatentWatch you acknowledge that we do not provide personalized recommendations or advice. thinkBiotech performs no independent verification of facts as provided by public sources nor are attempts made to provide legal or investing advice. Any reliance on data provided herein is done solely at the discretion of the user. Users of this service are advised to seek professional advice and independent confirmation before considering acting on any of the provided information. thinkBiotech LLC reserves the right to amend, extend or withdraw any part or all of the offered service without notice.