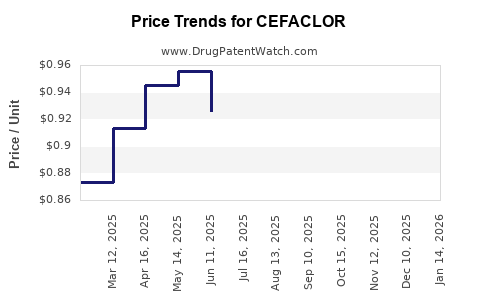
Last updated: July 28, 2025
Introduction
Cefaclor, a second-generation cephalosporin antibiotic, has maintained a significant role in the treatment of bacterial infections since its development. With a broad spectrum of activity against gram-positive and some gram-negative organisms, cefaclor is prescribed for conditions such as respiratory tract infections, skin infections, and urinary tract infections. This report examines the evolving market dynamics and financial outlook for cefaclor, considering factors like regulatory landscapes, competition, patent statuses, manufacturing trends, and clinical demand.
Market Overview
Globally, the cephalosporin antibiotics market was valued at approximately USD 12.5 billion in 2022, with therapeutic applications spanning various infectious diseases. Cefaclor, ranked among the prominent second-generation cephalosporins, held an estimated market share of 4-6%, driven largely by its efficacy, safety profile, and low resistance development in certain pathogens.
Key markets include North America, Europe, and select regions within Asia-Pacific, where rising bacterial infections and growing awareness about antibiotic use sustain demand. However, market growth faces challenges, notably antibiotic stewardship initiatives aimed at curbing overuse and resistance development, regulatory scrutiny, and competition from newer antibacterial agents.
Regulatory and Patent Dynamics
Patent Expirations and Generic Entry
Cefaclor was initially introduced in the 1980s, with key patents expiring around the early 2000s. The loss of exclusivity has led to widespread generic manufacturing, markedly reducing prices and impacting brand-name sales. Generic versions remain predominant in the market, diminishing manufacturers' control over pricing.
Regulatory Environment
Regulatory agencies like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) continue to assess antibiotics for efficacy and safety, influencing market access. The push for antibiotic stewardship has led to tighter regulations on indications and prescribing practices, indirectly affecting cefaclor utilization.
Approval and Off-Label Use
While cefaclor holds approved indications for specific bacterial infections, off-label prescribing persists in some regions, influenced by clinician preferences and local resistance patterns. Additionally, formulations such as extended-release and pediatric-friendly preparations enhance clinical appeal.
Competitive Landscape
Direct Competitors
Cefaclor faces competition primarily from other second-generation cephalosporins such as cefuroxime and cefoxitin, as well as from third-generation agents like ceftriaxone and ceftazidime which offer broader spectrum and better pharmacokinetic profiles.
Emerging Alternatives
The rise of oral fluoroquinolones and macrolides—though associated with resistance concerns—has affected demand for cefaclor in certain indications. Additionally, newer classes such as (\beta)-lactam/(\beta)-lactamase inhibitor combinations are increasingly preferred for resistant infections.
Innovation and Formulation Trends
Manufacturers are exploring novel formulations, including sustained-release variants and combination therapies, aiming to improve compliance and positioning within antimicrobial stewardship frameworks.
Market Drivers
- Growing Incidence of Bacterial Infections: Rising prevalence of respiratory and urinary tract infections sustains demand for oral cephalosporins.
- Clinician Preference for Oral Antibiotics: Cefaclor's oral bioavailability makes it favorable, especially in outpatient settings.
- Market Penetration in Developing Regions: Expanding healthcare infrastructure and prescribing practices boost use in Asia-Pacific and Latin America.
- Patent and Regulatory Environment: Generic prevalence ensures accessibility but constrains pricing power.
Market Restraints
- Antibiotic Resistance: The global increase in resistant strains, notably (\beta)-lactamase producing bacteria, restricts cefaclor efficacy and use.
- Regulatory Restrictions: Stewardship policies discourage unnecessary antibiotic prescriptions.
- Adverse Effect Profiles: Concerns about allergic reactions and gastrointestinal disturbances limit use in some populations.
- Competitive Alternatives: Entry of newer antibiotics with better resistance profiles diminishes cefaclor's appeal.
Financial Trajectory
Revenue Trends
Post-patent expiry, cefaclor's revenue has declined steadily, with generic sales dominating. In mature markets like the U.S. and Europe, annual sales are estimated to be in the hundreds of millions USD, experiencing year-on-year declines of approximately 3-5%.
Market Growth Projections
Despite declining sales in developed regions, emerging markets show incremental growth fueled by increasing infection rates and healthcare coverage. The global cefaclor market is projected to decline modestly at a CAGR of around 1-2% over the next five years, primarily influenced by generic competition and resistance concerns.
Profitability Outlook
Profit margins for cefaclor are under pressure, with generic manufacturing driving prices down. Innovator companies are likely to prioritize pipeline drugs or biosimilars, reducing investments in cefaclor-specific R&D.
Investment Considerations
Pharmaceutical companies may consider strategic patenting of novel formulations or combination therapies involving cefaclor to sustain revenue streams. However, the overarching trend favors newer agents with more robust resistance profiles.
Future Outlook
Antimicrobial stewardship initiatives and resistance dynamics will continue to shape the cefaclor market. While existing demand persists, especially in regions with limited access to newer antibiotics, long-term growth prospects remain constrained. Focus on clinical innovations, such as improved formulations or combination therapies, could extend the product lifecycle marginally.
Emerging technologies, including rapid diagnostics and targeted therapy, could also redefine usage patterns, potentially limiting cefaclor’s market share further.
Key Market Trends and Opportunities
- Development of Extended-Release Formulations: Enhancing compliance and reducing dosing frequency.
- Combination Therapies: Combining cefaclor with (\beta)-lactamase inhibitors could overcome resistance issues.
- Regional Market Expansion: Strategic focus on Asia-Pacific and Latin America where demand is growing.
- Second-Generation Cephalosporin Niches: Targeting specific indications with minimal competition.
Challenges and Risks
- Antibiotic Resistance: Rapidly evolving resistance patterns threaten efficacy and market viability.
- Regulatory Constraints: Increasing restrictions on antibiotic prescribing could reduce volume.
- Market Saturation: Existing generic competition caps growth potential.
Conclusion
Cefaclor's market dynamics are characterized by mature, declining revenues amidst intensifying competition and resistance issues. While it remains a valuable therapeutic agent, its financial trajectory is expected to be subdued in the coming years, barring significant innovation or strategic repositioning. Manufacturers and investors should weigh innovations in formulation, regional expansion, and combination therapies to sustain interest in cefaclor's portfolio.
Key Takeaways
- Market Maturity: Post-patent expiration, cefaclor faces generic saturation, leading to price erosion and profit margin compression.
- Competitive Pressures: Emerging resistant strains and newer antibiotics limit cefaclor’s future growth potential.
- Regional Opportunities: Developing markets present growth opportunities due to rising infectious disease prevalence.
- Innovation Focus: Formulation enhancements and combination therapies can extend lifecycle and market relevance.
- Regulatory and Stewardship Impact: Strict policies on antibiotic use could further restrict cefaclor’s utilization, emphasizing the importance of targeted, sustainable prescribing.
FAQs
1. How has patent expiry affected cefaclor's market?
Patent expiration led to widespread generic manufacturing, significantly reducing prices and market control for original developers. Consequently, revenues declined, and market dynamics shifted toward price competition among generics.
2. What are the primary factors constraining cefaclor’s growth?
Rising antibiotic resistance, regulatory restrictions, and competition from newer agents limit cefaclor’s expanding use and profitability.
3. Are there ongoing innovations to revitalize cefaclor's market?
Yes. Strategies include developing extended-release formulations, combination therapies with (\beta)-lactamase inhibitors, and regional market expansion efforts.
4. Which regions offer the most growth potential for cefaclor?
Emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America present the most promising growth opportunities due to increasing infectious disease burden and evolving healthcare infrastructure.
5. How does antibiotic resistance influence cefaclor’s future?
Resistance reduces cefaclor’s efficacy, restricting its clinical indications, and elevates the importance of newer, more resistant-proof drugs, thereby limiting cefaclor’s long-term market viability.
References
- Grand View Research. "Cephalosporins Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis." 2022.
- World Health Organization. "Antimicrobial Resistance Global Report." 2022.
- IQVIA. "Global Antibiotics Market Trends." 2022.
- FDA. "Guidance for Industry: Antibiotic Stewardship." 2021.
- MarketWatch. "Generic Drugs Market Overview." 2022.