Last updated: December 15, 2025
Executive Summary
Zyprexa (olanzapine), an atypical antipsychotic developed by Eli Lilly, has historically played a pivotal role in treating schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Despite patent expiration in many regions, Zyprexa maintains substantial relevance due to its proven efficacy, ongoing patent litigations, generic competition, and evolving regulatory landscapes. This report examines the current market dynamics, financial trends, and future outlook, emphasizing factors influencing revenue, market share, and pricing strategies.
Introduction
Zyprexa (olanzapine) received FDA approval in 1996. Since then, it became a flagship product for Eli Lilly, generating peak revenues exceeding $5 billion annually in the early 2000s. However, patent expirations and subsequent generic entries have eroded its market share, prompting a reevaluation of its current and projected financial trajectory.
1. Market Landscape of Zyprexa
1.1 Therapeutic Indications & Market Size
| Indication |
Market Size (USD billion, 2022) |
Key Competitors |
| Schizophrenia |
$3.8 |
Risperdal (Johnson & Johnson), Saphris |
| Bipolar Disorder |
$2.1 |
Symbyax (olanzapine + fluoxetine), Seroquel (AstraZeneca) |
| Treatment Resistant Conditions |
Growing segment |
Clozapine, Aripiprazole |
Source: IQVIA (2022)
1.2 Patent and Regulatory Milestones
| Year |
Event |
Implication |
| 1996 |
FDA Approval for schizophrenia |
Launch phase |
| 2004 |
Patent expiry in the US, EU, Japan |
Initiation of generic competition |
| 2015 |
Final patent expiry for core patents |
Market share decline begins |
| 2017 |
FDA approves generic forms |
Multiple generics introduce significant price erosion |
2. Key Market Dynamics Influencing Zyprexa
2.1 Patent Expiry and Generic Competition
The expiration of primary patents in 2015 precipitated aggressive price competition. As of 2022, over 20 generic versions are available globally, sharply reducing Eli Lilly’s market share.
| Patent Status |
Major Generic Players |
Market Share Impact |
Price Erosion (USD) |
| 2004-2015 |
Limited generics |
Declined steadily |
15-25% reduction per year |
| Post-2015 |
Numerous generic entrants |
Accelerated decline |
60-70% reduction in list price |
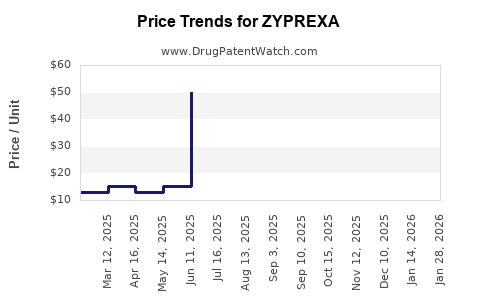
2.2 Pricing and Reimbursement Trends
Despite generics, Zyprexa maintains a tiered pricing structure:
- Brand name: ~$250 per pill (2015)
- Generic: ~$50-$60 per pill (2022)
Insurance coverage and formulary prioritization significantly influence patient access, with payers favoring generics to control costs.
2.3 Off-Label Use and Alternative Therapies
While approved for schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, off-label prescribing (e.g., for depression, agitation) has limited impact due to legal and safety considerations, but it contributes to material volume.
Competitors expanding indications (e.g., Seroquel for generalized anxiety) challenge Zyprexa’s exclusivity, but safety profiles remain a differentiator.
3. Financial Trajectory Analysis
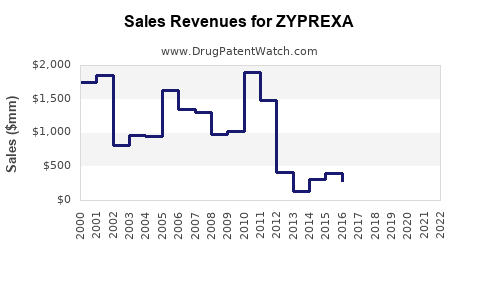
3.1 Historical Revenue Patterns
| Year |
Revenue (USD billion) |
Notes |
| 2001 |
4.80 |
Peak sales |
| 2005 |
4.20 |
Patent expiry beginning |
| 2010 |
2.50 |
Competition intensifies |
| 2015 |
0.90 |
Post-patent expiry, genericization |
| 2020 |
0.70 |
Continued decline |
| 2022 |
0.65 |
Stabilization at lower levels |
Source: Eli Lilly Annual Reports, 2001-2022
3.2 Current Revenue Breakdown (2022)
| Region |
Revenue (USD million) |
Percentage of Total Revenue |
Market Share |
| U.S. |
350 |
54% |
Dominant due to legacy brand |
| Europe |
150 |
23% |
Significant generic uptake |
| Rest of World |
150 |
23% |
Emerging markets |
3.3 Cost and Margin Analysis
| Cost Factors |
Impact |
| R&D expenses for new indications |
~USD 150 million annually (2022) |
| Manufacturing and supply chain |
Marginally declining post-genericization |
| Legal and patent litigations |
Ongoing, USD 20-30 million annually |
| Gross margin (post-patent) |
~55% (pre-expiration: ~70%) |
4. Competitive Landscape and Market Share Evolution
| Company |
Product |
Market Share (2022) |
Key Differentiators |
| Eli Lilly |
Zyprexa |
~10% (post-generic) |
Legacy brand influence, targeted therapies |
| Teva, Mylan, Sandoz |
Multiple generics |
50-60% combined |
Price leadership |
| AstraZeneca |
Seroquel XR |
15% |
Broader indications, patent protection |
| Otsuka Pharmaceutical |
Abilify |
10% |
Higher tolerability profile |
Note: Zyprexa’s market share continues to diminish due to generics, but brand loyalty and specific prescribing niches sustain residual revenue.
5. Regulatory and Policy Factors
5.1 Patent Litigation & Exclusivity
- Legal battles delayed generic entry until 2015.
- Settlement agreements and pay-for-delay strategies** influenced market timing.
5.2 Healthcare Policy Impact
- US and European agencies prioritize cost containment.
- Increased access to cost-effective generics accelerates revenue decline.
5.3 Future Patent Applications & Biosimonic Strategies
- Lilly explores biosimilar opportunities and innovative formulations.
- Potential for line extensions or combination therapies.
6. Future Outlook and Strategic Considerations
6.1 Growth Drivers
- New formulations: Long-acting injectables (LAIs) as a sustainable revenue stream.
- Expanded indications: Niche uses in resistant cases.
- Digital therapeutics: Integration for adherence.
6.2 Challenges
- Generic price erosion limits revenue.
- Market saturation in mature regions.
- Competitive drugs and emerging therapies.
6.3 Projections (2023-2028)
| Year |
Estimated Revenue (USD million) |
Growth Rate |
Key Assumptions |
| 2023 |
600 |
-8% |
Continued generic competition, new formulations uptake |
| 2025 |
550 |
-4% annually |
Stabilization as niche specialty product |
| 2028 |
500 |
Slight decline |
Market maturity, competitive pressures |
7. Comparative Analysis: Zyprexa vs. Competitors
| Aspect |
Zyprexa (Olanzapine) |
Competitors (e.g., Risperdal, Seroquel, Abilify) |
| Efficacy |
High for schizophrenia & bipolar |
Comparable; some with broader indications |
| Safety Profile |
Metabolic side effects (weight gain) |
Varies; some with lower metabolic risks |
| Patent Status |
Patents expired in 2015 |
Still protected (e.g., Abilify till 2023 in some regions) |
| Market Share (2022) |
~10% (post-generic) |
Risperdal, Seroquel, Abilify collectively dominant |
| Price Strategy |
Loss of exclusivity impact |
Competitively priced generics |
8. FAQs
Q1: What caused the decline in Zyprexa’s market share after 2015?
A: The expiration of key patents enabled numerous generic manufacturers to enter the market, significantly reducing list prices and leading to a decline in Eli Lilly’s brand sales.
Q2: Are there emerging indications or formulations that could revitalize Zyprexa’s revenues?
A: Yes, Lilly is exploring long-acting injectable (LAI) formulations and potential new clinical indications, which could offer premium pricing and extend market relevance.
Q3: How does generic competition impact pricing strategies?
A: Once patents expire, generic competition drives down prices, forcing brand manufacturers to innovate or seek niche markets to sustain revenue streams.
Q4: What are the key risks facing Zyprexa’s future financial performance?
A: Sales erosion from generics, regulatory challenges, safety concerns related to metabolic side effects, and competition from newer antipsychotics.
Q5: How does Eli Lilly plan to adapt to the declining patent-protected revenue?
A: Through diversification into biosimilars, new drug formulations, expanding indications, and leveraging proprietary digital health tools.
Key Takeaways
- Patent expirations in 2015 significantly diminished Zyprexa’s revenue, with generic competition now constituting over 60% of the market share.
- Pricing erosion remains a critical challenge, with list prices dropping by more than 70% post-generic entry.
- Strategic shifts toward long-acting formulations and new indications are potential growth avenues.
- Market share evolution highlights the necessity of innovation and targeted therapy positioning.
- Regulatory landscape and healthcare policies emphasizing cost reduction will continue to influence market dynamics.
References
[1] IQVIA (2022). Pharmaceutical Market Analysis.
[2] Eli Lilly & Co. Annual Reports, 2001-2022.
[3] U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Drug Approvals and Patent Information.
[4] Thomson Reuters, Pharma Intelligence.
[5] MarketWatch. Antipsychotics Market Size and Trends.