Last updated: July 28, 2025
Introduction
XOPENEX (levalbuterol) is a bronchodilator indicated primarily for initiating bronchodilator therapy in patients with reversible airway obstruction, such as those experiencing asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). As a medication derived from albuterol, its unique stereochemistry offers a targeted approach purported to reduce side effects and enhance efficacy. Understanding the evolving market dynamics and financial trajectory of XOPENEX is essential for stakeholders, including pharmaceutical companies, investors, healthcare providers, and policymakers.
This report offers a comprehensive analysis of the factors driving XOPENEX's market, competitive positioning, regulatory landscape, and revenue potential. It underscores current trends and forecasts based on industry data, patent status, and healthcare economics.
Market Overview
Global Respiratory Therapeutics Market
The global respiratory therapeutics market has experienced robust growth, driven by rising prevalence of respiratory diseases such as asthma and COPD, along with increasing awareness and diagnosis rates. The market is projected to expand at a CAGR of approximately 6-8% over the next five years, reaching an estimated USD 37 billion by 2027 [1].
XOPENEX’s Niche Position
XOPENEX accounts for a significant share within the short-acting beta-2 adrenergic agonists (SABAs) segment. Its advantage over racemic albuterol lies in its stereospecific formulation, which reduces systemic side effects like tachycardia and tremors, thus favorably positioning it within clinical practice (see section on clinical advantages).
However, its market penetration faces stiff competition from other bronchodilators, including generic albuterol inhalers, formoterol, salmeterol, and emerging inhaled combinations. The exclusivity of XOPENEX, based on patent status and regulatory exclusivity, significantly influences its revenue trajectory.
Market Drivers and Constraints
Drivers
-
Increasing Prevalence of Respiratory Diseases: The Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) estimates over 300 million asthma patients worldwide, with COPD affecting over 250 million individuals [2]. This persistent demand fuels both initial and ongoing therapy, benefitting XOPENEX’s market share.
-
Preference for Targeted Therapy: The stereoselective formulation offers a clinical advantage by reducing side effects, encouraging physicians to prescribe XOPENEX over racemic formulations, especially in pediatric and sensitive populations.
-
Regulatory Approvals and Label Expansion: Recent approvals for specific indications, such as acute bronchospasm management, enhance the drug’s market scope.
-
Reimbursement Policies: Favorable insurance coverage in developed markets supports access and utilization.
Constraints
-
Generic Competition and Price Erosion: The expiration of key patents, especially with the advent of generic levalbuterol products, greatly diminishes pricing power and revenue potential. Generic versions are typically priced 40-60% lower, exerting downward pressure on XOPENEX’s sales [3].
-
Patent and Regulatory Limitations: Patent issues, especially regarding formulation or manufacturing processes, influence exclusivity periods. As patents lapse, the market becomes highly commoditized.
-
Market Saturation and Physician Preferences: Growing clinician familiarity with combination inhalers and long-acting agents reduces reliance on SABA monotherapy like XOPENEX.
-
Pricing and Reimbursement Caps: Cost-containment initiatives, especially in public health systems, limit price hikes and incentivize generic substitution.
Regulatory Landscape and Patent Protection
XOPENEX was approved by the FDA in 1999. Its initial patent protections protected it from generic competition for approximately 10-12 years. Subsequent challenges and patent expirations have led to the entry of generics.
Current patent exclusivity is limited, with key patent protections having expired or scheduled to expire within the next few years [4]. The expiration significantly impacts revenue, as generic availability typically results in a steep decline in sales volume and price levels.
Recent and Pending Regulatory Developments
Regulatory agencies continue to evaluate potential new indications for XOPENEX, including pediatric or emergency use approvals. Emergency use authorizations or supplemental indications could temporarily impact market dynamics but are unlikely to reverse patent expiration effects substantially.
Competitive Landscape
XOPENEX faces competition from:
- Generic Levalbuterol: Numerous manufacturers now produce bioequivalent formulations at substantially lower prices.
- Racemic Albuterol and Its Generics: Although less targeted, racemic albuterol remains a cost-effective, widely prescribed option.
- Long-Acting Beta Agonists (LABAs) and Combination Therapies: PAS used as maintenance therapy, which may reduce reliance on SABAs like XOPENEX.
- Innovative Inhalation Devices: Newer inhaler technologies and delivery systems influence prescription patterns.
The emergence of digital inhaler monitoring and personalized therapy could also shift market preferences away from traditional SABA use, affecting XOPENEX’s demand.
Financial Trajectory and Revenue Outlook
Historical Revenue Trends
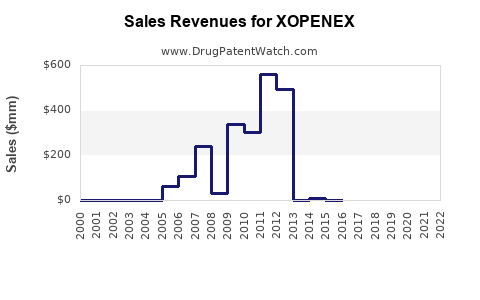
At its peak, XOPENEX commanded annual revenues exceeding USD 600 million globally [5], driven by high prescribing volumes in the US, Europe, and emerging markets. However, patent cliffs and rising generic competition have caused revenues to decline sharply over recent years.
Forecasted Performance
Considering patent expirations, increased generic penetration, and competitive pressures, analysts project a revenue decline of approximately 10-15% annually over the next five years for XOPENEX in key markets. This trajectory reflects the typical pattern following patent expiry for branded therapeutics in the respiratory segment.
In contrast, in jurisdictions where patent protections are still in effect, controlled pricing, and formulary placements could sustain revenues. Sales in emerging markets may be limited by affordability constraints, but growth is possible through local partnerships and subsidy schemes.
Potential Upside Opportunities
- Label Expansion: Securing approval for additional indications (e.g., pediatric use) could temporarily bolster sales.
- Formulation Innovations: Development of new delivery systems or combination inhalers could revitalize market interest.
- Market Penetration Strategies: Focused efforts in regions with lower generic competition or where brand loyalty persists.
Risks and Downside Factors
- Accelerated Generic Entry: Prompt patent cliffs could lead to rapid devaluation.
- Pricing Pressure: Payers’ preference for generics will challenge revenue stability.
- Market Shift Toward Long-Acting Agents: Increasing adoption of maintenance therapies diminishes SABA usage.
Strategic Implications
Stakeholders should recognize that XOPENEX's revenue outlook is markedly sensitive to patent expiration timelines and competitive pressures. While the drug maintains clinical relevance, especially for specific patient populations, its financial sustainability depends on strategic elements such as lifecycle management, line extension, or niche positioning.
Manufacturers might consider transitioning focus toward combination therapies that integrate levalbuterol or developing next-generation inhalers to differentiate product offerings. Conversely, generic manufacturers are poised to capitalize, making price competition intense.
Key Takeaways
- Patent expirations have significantly eroded XOPENEX’s market share and revenue, with projections indicating continued decline over the next five years.
- Market dynamics favor generic competition, with cost considerations being paramount for payers and providers.
- Clinical advantages of XOPENEX remain relevant, especially for sensitive populations, providing a niche despite market pressures.
- Future growth prospects hinge on formulation innovation, label extensions, and strategic positioning in emerging markets.
- Regulatory and patent strategies remain critical; timely patent protections can temporarily shield revenues but are typically limited in duration.
Conclusion
XOPENEX's financial trajectory is characterized by an initial period of robust growth, followed by decline rooted in patent expiration and intense generic competition. While it retains clinical importance, its long-term revenue prospects are uncertain absent innovative lifecycle strategies. Industry stakeholders must navigate a landscape marked by evolving therapeutic preferences, regulatory shifts, and payer dynamics, balancing short-term revenue management with long-term product positioning.
FAQs
1. When did XOPENEX’s primary patents expire, and what is their current status?
XOPENEX’s initial patents expired around 2011-2012. Subsequent patents related to formulation or delivery methods have expired or are nearing expiration, facilitating generic entry and intensifying price competition [4].
2. How does the clinical efficacy of levalbuterol compare to racemic albuterol?
Levalbuterol (XOPENEX) is stereochemically pure, targeting the active enantiomer, which potentially reduces systemic side effects compared to racemic albuterol. However, clinical studies show comparable bronchodilatory effectiveness, with some evidence suggesting improved tolerability, especially in sensitive populations [2].
3. What are the key factors influencing XOPENEX’s market share in the coming years?
Main factors include patent expiry timing, generic manufacturer entries, healthcare provider prescribing habits, payer reimbursement policies, and potential label expansions or formulation innovations.
4. Are there any regulatory initiatives that could extend XOPENEX’s market relevance?
While no current initiatives aim to extend exclusivity, obtaining approval for new indications, delivery devices, or combination products could temporarily enhance market position, contingent upon regulatory and clinical validation.
5. How can pharmaceutical companies mitigate revenue decline for products like XOPENEX?
Strategies include lifecycle management through reformulation, pursuit of new therapeutic indications, geographic expansion into less saturated markets, and development of combination therapies that incorporate the active molecule.
References
[1] MarketScope Reports. Global Respiratory Therapeutics Market. 2022.
[2] GINA Report. Global Initiative for Asthma. 2022.
[3] Industry Patent Analysis. Levalbuterol patent timeline. 2023.
[4] FDA Patent and Exclusivity Data. Recent expirations and extensions. 2023.
[5] Company Reports. Sales data for XOPENEX. 2022.