Last updated: July 28, 2025
Introduction
TOBREX, an ophthalmic antibiotic containing tobramycin, plays a critical role in treating bacterial eye infections, notably conjunctivitis, keratitis, and blepharitis. Its efficacy against a broad spectrum of Gram-negative and Gram-positive pathogens underscores its longstanding market presence. This article analyzes the current market dynamics and financial trajectory of TOBREX, considering patent statuses, regulatory landscapes, competitive forces, and evolving demand patterns within the ophthalmic pharmaceutical sector.
Regulatory and Patent Landscape
Patent Expiry and Market Implications
TOBREX's primary patent protections have long expired, rendering it a generic medicine for over a decade (post-2000s). The expiration of patent exclusivity significantly increased market competition, leading to a decline in exclusive sales revenues. Generic manufacturers have proliferated, offering lower-cost alternatives that eroded brand loyalty and margin premiums initially associated with TOBREX.
Regulatory Approvals and Labeling
The drug's approval timeline, regulated by authorities like the FDA in the U.S. and EMA in Europe, ensures consistent standards but also introduces hurdles for new formulations or delivery systems. Recent advances are focusing on novel drug delivery mechanisms—such as sustained-release implants—that may require new regulatory pathways, potentially creating opportunities for lifecycle extension.
Market Dynamics
Demand Drivers
Prevalence of Bacterial Eye Infections
The global burden of bacterial conjunctivitis and keratitis sustains steady demand for effective antibiotics like TOBREX. Rising incidence in developing regions correlates with increased urbanization, environmental factors, and limited access to healthcare, amplifying the need for affordable, effective treatments.
Awareness and Antibiotic Stewardship
Growing emphasis on antibiotic stewardship seeks to optimize prescription patterns, potentially restricting overuse but also fueling demand for trusted, tried-and-true agents. TOBREX's established efficacy makes it a preferred choice among ophthalmologists, particularly in regions with limited access to newer, costly therapies.
Competitive Landscape
Generic Proliferation
Generic competitors have saturated the market, offering tobramycin formulations at substantially reduced prices. Companies such as Sandoz, Teva, and others have introduced various ophthalmic tobramycin solutions, impacting brand sales. Their widespread availability limits the growth prospects of branded TOBREX.
Emerging Alternatives and Innovations
New drug delivery systems—such as liposomal formulations, nanoparticle carriers, and sustained-release implants—are in development. While these aim to enhance efficacy and compliance, their high development costs and regulatory hurdles delay near-term impact.
Brand Versus Generic Dynamics
Branded TOBREX maintains a niche for patients with specific sensitivities or previous positive responses, but the overall market shift favors generics. Pricing strategies tend to be aggressive, constrained by biosimilar and generic competition, pressuring profit margins for the original manufacturer.
Market Expansion Opportunities
Geographic Penetration
Emerging markets in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa exhibit unmet demand due to inadequate healthcare infrastructure and affordability barriers. Efforts to penetrate these regions could offset declines in saturated markets. Local partnerships and licensing could facilitate this expansion.
New Formulations and Indications
Developing improved formulations—such as preservative-free drops, combination therapies, or sustained-release implants—may rejuvenate interest. Label expansions for other ocular bacterial infections broaden market horizons but require significant R&D investment and regulatory approval.
Financial Trajectory
Revenue Trends
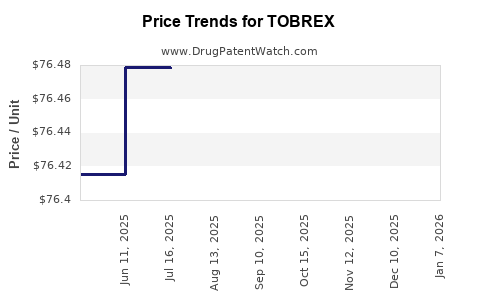
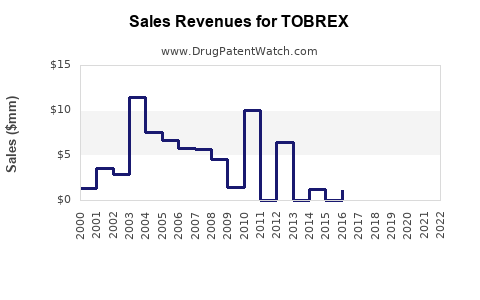
The revenue from TOBREX has experienced a gradual decline over the past decade, primarily driven by generic competition post-patent expiry. For instance, in the U.S., branded sales have reportedly fallen by approximately 20-30% since the early 2010s, aligning with increased generic availability and price erosion (source: industry reports).
However, in regions where healthcare systems remain predominantly prescription-based and brand-preserving, such as parts of Europe and Asia, TOBREX retains a steady revenue stream. Additionally, sales of compounded formulations in hospital settings sustain some income.
Profitability and Market Margins
Gross margins on TOBREX have compressed due to intense price competition. Laboratory and regulatory costs associated with developing new formulations or acquiring licenses for newer delivery systems could affect overall profitability. However, economies of scale with generic manufacturing plants help mitigate some margin pressures.
Forecasting and Strategic Outlook
Short-term (1–3 years): Revenue decline is projected to continue, barring strategic innovation or market diversion. Focus remains on maintaining existing market share in core regions.
Medium-term (3–5 years): Introduction of novel formulations or combination therapies could stabilize revenues, especially if supported by regulatory approvals and strategic partnerships.
Long-term (5+ years): The landscape could shift further towards biologics and targeted therapies for ocular infections, with small-molecule antibiotics like TOBREX being phased out or relegated to niche markets unless lifecycle extension strategies succeed.
Market Trends Influencing Future Financial Outcomes
- Emergence of Biosimilars and Generic Competition: As patents expire, biosimilars may disrupt the market further, intensifying price compression.
- Advances in Drug Delivery Technologies: Sustained-release implants and targeted delivery could command premium pricing, offsetting volume declines.
- Regulatory Changes and Policy Shifts: Governments emphasizing antimicrobial stewardship might restrict over-the-counter sales, impacting demand.
- COVID-19 and Global Health Trends: Enhanced focus on ocular hygiene and infection control could temporarily boost demand; however, pandemic-related supply chain disruptions pose risks.
Strategic Recommendations
- Innovation and Lifecycle Extension: Investment in innovative delivery systems or combination therapies could revive revenue streams.
- Geographic Diversification: Expanding into underserved markets with tailored pricing and distribution models enhances growth prospects.
- Collaborations and Licensing: Partnering with innovative biotech entities to develop next-generation ocular antibiotics can offset competitive decline.
- Cost Optimization: Streamlining manufacturing and distribution processes maintains profitability amid declining revenues.
Key Takeaways
- Patent expiries and aggressive generic competition have significantly diminished TOBREX's market exclusivity, pressuring revenues and margins.
- Demand remains stable in certain regions due to high prevalence of bacterial ocular infections and limited access to alternative therapies, creating localized growth opportunities.
- Emerging drug delivery technologies and combination therapies present potential for market rejuvenation but require substantial investment and regulatory approval.
- Market expansion into emerging economies and strategic partnerships can offset declines in mature markets.
- Long-term viability depends on innovation, geographic expansion, and adapting to evolving regulatory and antimicrobial stewardship policies.
FAQs
Q1: How significant is the impact of patent expiration on TOBREX's market share?
A1: The patent expiration led to increased generic competition, which drastically reduced brand-specific sales by approximately 20-30% over the past decade, with the market shifting toward lower-cost alternatives.
Q2: Are there any recent innovations that could revitalize TOBREX’s market?
A2: Yes. Developing sustained-release formulations, preservative-free drops, and combination therapies are under exploration to enhance efficacy and patient compliance, potentially offering a competitive edge.
Q3: Which regions offer the most growth potential for TOBREX?
A3: Emerging markets such as India, Southeast Asia, and Latin America hold significant growth potential due to increasing incidence of bacterial eye infections and limited access to advanced antibiotics.
Q4: What risks threaten the long-term financial sustainability of TOBREX?
A4: Major risks include further patent expiries, aggressive generic and biosimilar entries, regulatory restrictions on antibiotics, and rapid technological advancements favoring new drug delivery systems.
Q5: How should stakeholders approach the future of TOBREX?
A5: Stakeholders should focus on lifecycle management through innovation, geographic diversification, strategic partnerships, and optimizing manufacturing efficiencies to maintain competitiveness.
References
[1] Industry Reports on Ophthalmic Antibiotics Market, 2022.
[2] U.S. FDA Drug Approvals Database.
[3] Market Analysis: Global Ophthalmic Antibiotics, 2021.
[4] Patent Status and Generic Market Trends, 2022.
[5] Advances in Ocular Drug Delivery Systems, 2023.