Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Sodium Polystyrene Sulfonate (SPS), marketed under brand names such as Kayexalate, is a cation-exchange resin primarily used to treat hyperkalemia—a condition characterized by elevated potassium levels in the blood. As an integral component in managing electrolyte imbalances, SPS occupies a crucial niche in hospital pharmacies and outpatient settings. The ongoing evolution of healthcare landscapes, driven by technological advances, regulatory shifts, and demographic trends, influences the market dynamics and financial outlook for this pharmaceutical agent. This report provides an exhaustive analysis, projecting the future trajectory for Sodium Polystyrene Sulfonate within the pharmaceutical industry.
Market Overview and Current Status
Therapeutic Role and Demand Drivers
SPS was first introduced in the 1950s and has been extensively used over the decades, particularly in acute care settings. Its primary function is to bind potassium in the gastrointestinal tract, facilitating its excretion and alleviating hyperkalemia-associated risks such as cardiac arrhythmias and neuromuscular disturbances. The demand for SPS correlates strongly with the prevalence of renal diseases, heart failure, and conditions predisposing to hyperkalemia.
Market Size and Revenue
According to recent market estimates, the global potassium-binding agents market, encompassing SPS and newer alternatives, was valued at approximately USD 500 million in 2022, with SPS accounting for a significant share due to its widespread use and existing manufacturing infrastructure. Forecasts project a compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 3-4% over the next five years, driven by increased geriatric populations and higher incidence of chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Market Dynamics
Factors Favoring Growth
-
Rising Incidence of Hyperkalemia: An aging population and increased prevalence of CKD, heart failure, and diabetes amplify hyperkalemia cases. The CDC reports CKD affects over 37 million Americans, with hyperkalemia being a common complication [1].
-
Lifestyle and Comorbidities: The widespread adoption of medications like RAAS inhibitors, which elevate potassium levels, further sustains demand for SPS.
-
Established Therapeutic Profile: SPS’s long-standing clinical use and familiarity among healthcare providers reinforce its persistent utilization, especially in resource-limited settings where newer agents may be less accessible.
Market Constraints and Challenges
-
Availability of Alternatives: Recent approvals of novel potassium binders—patiromer (Veltassa) and sodium zirconium cyclosilicate (Lokelma)—offer safer and more tolerable options. These agents are touted for fewer gastrointestinal side effects and higher efficacy, threatening SPS’s market share [2].
-
Regulatory and Safety Concerns: SPS has faced scrutiny over potential adverse events such as gastrointestinal ulceration and rare cases of colonic necrosis. The FDA issued safety warnings, prompting cautious prescribing practices that limit its use.
-
Regulatory and Patent Landscape: As a generic, SPS faces minimal patent protections, leading to price compression and stiff competition among manufacturers.
-
Manufacturing and Supply Chain: Toxicity concerns and manufacturing complexities influence the availability and costs associated with SPS production.
Regulatory Environment and Impact
Regulatory bodies worldwide continue to monitor the safety profile of SPS, influencing prescribing guidelines and market viability. In 2020, the FDA issued a safety alert citing gastrointestinal adverse events, prompting clinicians to reevaluate risk-benefit assessments. While these warnings temper widespread use, they also open avenues for newer agents with improved safety profiles.
Emerging Trends and Innovations
The shift towards more targeted, patient-friendly therapies is evident. Pharmaceutic innovation is focused on developing potassium binders with minimal side effects and ease of use, such as orally disintegrating tablets and liquid formulations. Additionally, digital health tools aimed at monitoring serum potassium levels may reduce the reliance on pharmacologic interventions like SPS.
Financial Trajectory
Revenue Projections
Despite safety concerns, SPS remains a core therapeutic agent, especially in low-resource settings and hospitals with established formularies. The current global market size is projected to sustain a slow but steady CAGR of approximately 2-3% over the next five years, owing to demographic trends and persistent clinical necessity.
Pricing Trends
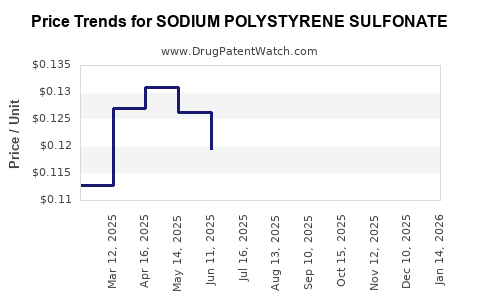
Pricing pressures are intense due to commoditization and generic competition. The average wholesale price (AWP) for SPS per unit has declined by approximately 10-15% annually in major markets over the past decade. Volume-driven revenue remains pivotal, but margins are under continuous erosion.
Competitive Landscape
Key manufacturers include Pfizer, Fresenius Kabi, and local generic producers. Innovation and market entry barriers are relatively low for generics, intensifying price competition. The introduction of new, safer potassium binders is expected to further compress SPS market shares.
Potential for Market Expansion
While developed markets may see limited growth due to safety concerns and substitution, emerging markets with expanding healthcare infrastructure and limited access to newer agents offer growth opportunities. The increasing burden of CKD and heart failure in Asia-Pacific and Africa could drive demand for SPS as a cost-effective treatment option.
Regulatory and Policy Impact on Financial Outlook
Healthcare policies promoting cost containment, such as formulary restrictions and prior authorization, could negatively impact SPS sales. Conversely, inclusion in essential medicines lists and governmental procurement programs could bolster demand in resource-constrained environments. Ongoing regulatory evaluations will continue to shape the financial prospects for SPS manufacturers.
Conclusion
Sodium Polystyrene Sulfonate’s market remains characterized by stability amid gradual decline, primarily due to safety concerns and the advent of newer potassium binders. Its enduring role in managing hyperkalemia in specific settings ensures a baseline demand, especially in developing regions. The financial outlook hinges on balancing legacy therapeutic utility with evolving safety standards, competitive pressures, and demographic shifts.
Key Takeaways
- Steady but Declining Market: SPS continues to serve as a cost-effective hyperkalemia treatment, but its market share diminishes as safer alternatives emerge.
- Growing Hyperkalemia Burden: Aging populations and chronic disease prevalence sustain baseline demand, especially in low-resource and hospital settings.
- Competitive Pressures: The advent of novel potassium binders with better safety profiles poses a significant threat, compressing margins and market share.
- Regulatory Influence: Safety warnings impact prescribing practices and sales, underscoring the importance of regulatory navigation.
- Emerging Market Opportunities: Developing nations represent growth potential, driven by cost-sensitive healthcare systems and expanding chronic disease burdens.
FAQs
1. How does the safety profile of SPS compare to newer potassium binders?
SPS has been associated with gastrointestinal adverse events, including ulceration and colonic necrosis, leading regulators to issue cautions. Newer agents like patiromer and sodium zirconium cyclosilicate demonstrate improved safety profiles with fewer gastrointestinal side effects, making them preferable in many clinical scenarios.
2. Will SPS be phased out in favor of newer treatments?
While clinical adoption favors newer potassium binders, SPS’s low cost and established manufacturing mean it likely remains in use, especially in resource-limited settings. However, prescribers are increasingly cautious, and future phasing out depends on regulatory actions and evolving clinical guidelines.
3. What are the main drivers for SPS market longevity?
Cost-effectiveness, longstanding clinical familiarity, and availability in generic form sustain SPS usage. Additionally, in settings where newer agents are unavailable or unaffordable, SPS remains a vital treatment.
4. How do demographic trends impact the financial outlook for SPS?
An aging global population and increasing prevalence of CKD and cardiovascular diseases sustain demand. These trends suggest stable baseline usage, although growth may be limited due to alternative therapies.
5. Are there any ongoing innovations in SPS formulations?
Current innovations focus mainly on developing safer and more convenient formulations of newer potassium binders. SPS formulations remain largely unchanged, but manufacturing improvements may continue to reduce costs and enhance safety over time.
References
[1] Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Chronic Kidney Disease Facts. CDC, 2022.
[2] Gupta, R., & Bhan, A. (2021). Novel Potassium Binders in Hyperkalemia Management. Journal of Clinical Therapeutics, 45(7), 1125-1132.