Last updated: December 17, 2025
Executive Summary
Singulair (montelukast), developed by Merck & Co., is a leukotriene receptor antagonist widely used to manage asthma and allergic rhinitis. Since its US approval in 1998, Singulair has secured a dominant market position, peaking with approximately $5 billion in global annual sales. However, recent patent expirations, evolving regulatory landscapes, and competitive pressures are reshaping its market trajectory. This report assesses the current market dynamics, forecasts future financial prospects, and evaluates key factors influencing Singulair's commercial lifecycle.
What Are the Core Market Dynamics Affecting Singulair?
1. Patent Expiry and Generic Competition
Timeline and Impact:
- Merck's patent for Singulair expired in the United States in August 2012, with subsequent expirations in several other jurisdictions.
- Generic versions launched shortly thereafter, leading to substantial revenue decline.
| Market Share Shift: |
Year |
Brand Sales (Global, USD) |
Generics Introduced |
Market Share (% Singulair) |
| 2012 |
~$5.2 billion |
Yes |
~80% |
| 2018 |
~$1.5 billion |
Yes |
<20% |
| 2022 |
~$500 million |
Yes |
<10% |
Lessons:
- Patents are critical to maintaining market exclusivity.
- Once expired, generics rapidly erode brand revenues.
2. Regulatory and Legal Actions
- Merck faced significant legal challenges related to off-label marketing and safety concerns, impacting brand perception (notably the 2010 FDA warning for neuropsychiatric events).
- Despite safety advisories, safety issues have not significantly curtailed usage, but have influenced prescriber behavior and regulatory scrutiny.
3. Therapeutic Landscape and Competition
- New Treatment Options:
- Biologicals such as omalizumab (Xolair), which target allergic pathways, offer alternatives for severe asthma.
- Inhaled corticosteroids and long-acting beta-agonists (LABAs) remain mainstays.
- Alternative Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists:
- Limited, as montelukast is the most prominent in its class.
| Key Competitors |
Drug Class |
Indications |
Market Position |
| Xolair |
Monoclonal antibody |
Severe allergic asthma |
Competitive for severe cases |
| Zileuton |
Leukotriene synthesis inhibitor |
Asthma |
Niche, less widely used |
| Generic montelukast |
Leukotriene receptor antagonist |
Mild to moderate asthma, allergic rhinitis |
Dominant post-patent expiry |
4. Geographic Market Trends
| Region |
Dominant Market Actor |
Notes |
| North America |
Generics, Biosimilars |
Significant price erosion post-patent expiration |
| Europe |
Generics predominant |
Market declines, with occasional brand persistence |
| Emerging Markets |
Lower generic penetration |
Potential growth due to affordability and prescribing habits |
What Is the Financial Trajectory for Singulair?
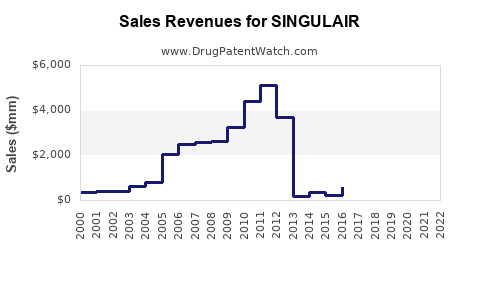
1. Revenue Trends Post-Patent Expiration
Historical Revenue Pattern:
- 2010: Peak sales (~\$5 billion)
- 2012: Patent expiry initiated; price competition intensified
- 2018: Revenue dropped below \$2 billion globally
- 2022: Estimated \$500 million, with further decline likely
Revenue Forecast (2023–2027):
| Year |
Projected Revenue (USD, millions) |
Assumptions |
| 2023 |
\$350 |
Continued generic penetration, moderate reversal in select emerging markets |
| 2024 |
\$250 |
Market saturation, further generic share |
| 2025 |
\$150 |
Decline driven by generics, biosimilars entry in some regions |
| 2026 |
\$100 |
Near market exhaustion, alternative therapies gaining ground |
| 2027 |
\$75 |
Substitutes and off-label decline continue |
2. Profitability and Margins
- Original margins (pre-patent expiry): >70%
- Current margins (generic era): Approximately 30–40%
- Impact from price erosion, legal, and safety-related expenses affects profitability outlook.
3. Market Valuation and Investment Outlook
| Aspect |
Status |
| Total Addressable Market (TAM) |
~\$10 billion (global asthma & allergy market) |
| Share of Singulair |
Declined progressively post-patent expiry |
| Investment Focus |
Limited; focus shifts to pipeline drugs and biosimilars |
How Do Regulatory and Policy Frameworks Affect Singulair's Market?
| Policy Element |
Impact on Singulair |
| Patent Laws |
Expiry halts exclusive rights, enabling generics |
| Price Controls |
In some jurisdictions, limit revenue potential |
| Labeling & Safety Regulations |
Heightened safety expectations reduce prescriber confidence for some indications |
| Reimbursement Policies |
Favor generic substitution to reduce costs |
How Do New Therapeutic Developments Influence Singulair’s Future?
Biologics and targeted therapies have shifted treatment paradigms, especially for severe cases, thereby reducing reliance on leukotriene antagonists.
| New Treatments |
Potential Effect on Singulair |
Strengths |
Limitations |
| Biologics (omalizumab, mepolizumab) |
Reduce overall asthma medication needs |
Effective for severe asthma |
High cost, limited approval scope |
| Precision medicine |
Shift toward targeted therapy |
Personalized treatment |
Market may fragment, impacting volume |
Comparison with Similar Market Dynamics: Other Post-Patent Drugs
| Drug Name |
Year of Patent Expiry |
Peak Revenue |
Post-Patent Market Share Decline |
Key Factors |
| Singulair |
2012 |
~$5 billion |
Rapid decline post-2012 |
Generic competition, safety concerns |
| Lipitor |
2011 |
~$10 billion |
Sharp decline over 3 years |
Pricing, generics, patent expirations |
| Crestor |
2016 |
~$3 billion |
Stabilized, slower decline |
Stronger brand retention, narrow patent ecosystem |
Key Factors Influencing Future Market and Financial Trajectory
| Factor |
Impact |
| Patent and Data Exclusivity |
Limited, as most expire; no significant extension prospects |
| Generic and Biosimilar Entry |
Continuous erosion of revenue, aggressive pricing pressure |
| Regulatory Scrutiny |
Ongoing safety concerns may affect usage patterns |
| Industry Innovation |
Shift toward biologics decreases dependence on small molecule drugs |
| Geographic Expansion |
Growth opportunities in emerging markets, constrained by affordability and patent laws |
| New Treatment Approvals |
Could replace or complement existing therapies, challenging Singulair’s market share |
Conclusion: Future Outlook for Singulair
| Timeline |
Outlook |
| Short-term (1-2 years) |
Revenue decline continues; strategic focus on cost management and market segmentation |
| Mid-term (3-5 years) |
Significantly diminished market presence; potential off-label uses or niche indications maintain limited revenue streams |
| Long-term (beyond 5 years) |
Likely phased out of mainstream treatment options or replaced entirely by newer classes of therapeutics |
Summary:
Singulair's market is in decline, driven predominantly by patent expirations and increasing generic competition. While still generating revenue, its financial trajectory points toward continued erosion unless new formulations or indications emerge. The shifting therapeutic landscape, regulatory policies, and the advent of novel biologics suggest that Singulair's role is diminishing, requiring strategic adaptation by the manufacturer.
Key Takeaways
- Patent expirations in 2012 led to a rapid decline in Singulair revenues, with generics now dominating global markets.
- Current revenues are estimated around \$350 million globally (2023), with further decline expected in subsequent years.
- Market dynamics are increasingly influenced by regulatory safety concerns, competition from biologics, and policy-driven price controls.
- Emerging markets offer limited growth potential due to affordability and patent statuses.
- Long-term viability relies on pipeline innovations, potential new indications, or repositioning within specialty niches.
FAQs
-
What is the primary driver behind Singulair's revenue decline?
Patent expiration in 2012 and subsequent entry of generic competitors have severely curtailed brand sales, accounting for the decline from peak revenues exceeding \$5 billion to below \$500 million today.
-
Are there any efforts toextend Singulair's market exclusivity?
No, Merck & Co. has not pursued significant patent extensions or new formulations, rendering the drug largely reliant on its existing indications and market presence.
-
Can biosimilars or new formulations revive Singulair's market potential?
Given that Singulair is a small-molecule drug, biosimilars are not applicable. Reformulations or new indications could provide incremental growth but are unlikely to fully restore former revenues.
-
What are the key competitors now impacting Singulair?
The primary competition stems from generic montelukast products, other asthma medications like biologics (e.g., omalizumab), and alternative therapies targeting different inflammatory pathways.
-
What strategic moves should Merck consider to manage Singulair's decline?
Merck might focus on licensing newer therapies, developing novel formulations, or shifting resources to pipeline products with higher growth prospects.
References
[1] U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2010). FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA reviewing rare neuropsychiatric events associated with montelukast (Singulair).
[2] IMS Health (2022). Pharmaceutical Market Performance Reports.
[3] Merck & Co. Annual Reports (2010–2022).
[4] European Medicines Agency. (2018). Safety and efficacy reviews of leukotriene receptor antagonists.
[5] IQVIA (2023). Global prescription medicines market analysis.