RIVASTIGMINE Drug Patent Profile
✉ Email this page to a colleague
Which patents cover Rivastigmine, and when can generic versions of Rivastigmine launch?
Rivastigmine is a drug marketed by Alvogen, Amneal Pharms, Breckenridge, Mylan Technologies, Yichang Humanwell, Zydus Pharms, Alembic Pharms Ltd, Apotex Inc, Aurobindo Pharma, Cadila Pharms Ltd, Chartwell Rx, Dr Reddys Labs Inc, Macleods Pharms Ltd, Orbion Pharms, Sun Pharm, and Watson Labs. and is included in sixteen NDAs.
The generic ingredient in RIVASTIGMINE is rivastigmine tartrate. There are thirty-two drug master file entries for this compound. Twelve suppliers are listed for this compound. Additional details are available on the rivastigmine tartrate profile page.
DrugPatentWatch® Litigation and Generic Entry Outlook for Rivastigmine
A generic version of RIVASTIGMINE was approved as rivastigmine tartrate by DR REDDYS LABS INC on October 31st, 2007.
AI Deep Research
Questions you can ask:
- What is the 5 year forecast for RIVASTIGMINE?
- What are the global sales for RIVASTIGMINE?
- What is Average Wholesale Price for RIVASTIGMINE?
Summary for RIVASTIGMINE
| US Patents: | 0 |
| Applicants: | 16 |
| NDAs: | 16 |
| Finished Product Suppliers / Packagers: | 7 |
| Raw Ingredient (Bulk) Api Vendors: | 64 |
| Clinical Trials: | 106 |
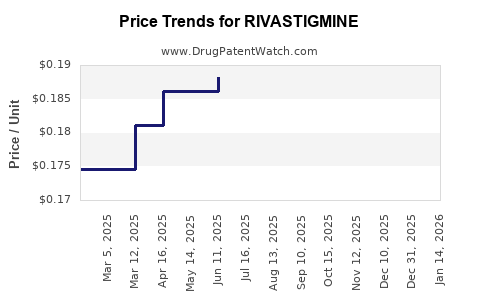
| Drug Prices: | Drug price information for RIVASTIGMINE |
| Patent Litigation and PTAB cases: | See patent lawsuits and PTAB cases for RIVASTIGMINE |
| What excipients (inactive ingredients) are in RIVASTIGMINE? | RIVASTIGMINE excipients list |
| DailyMed Link: | RIVASTIGMINE at DailyMed |
Recent Clinical Trials for RIVASTIGMINE
Identify potential brand extensions & 505(b)(2) entrants
| Sponsor | Phase |
|---|---|
| Washington University School of Medicine | PHASE2 |
| American Academy of Clinical Toxicology | PHASE2 |
| Herlev Hospital | PHASE2 |
Pharmacology for RIVASTIGMINE
| Drug Class | Cholinesterase Inhibitor |
| Mechanism of Action | Cholinesterase Inhibitors |
Medical Subject Heading (MeSH) Categories for RIVASTIGMINE
Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) Classes for RIVASTIGMINE
Paragraph IV (Patent) Challenges for RIVASTIGMINE
| Tradename | Dosage | Ingredient | Strength | NDA | ANDAs Submitted | Submissiondate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EXELON | Transdermal System Extended-release | rivastigmine | 13.3 mg/24 hr | 022083 | 1 | 2013-01-22 |
| EXELON | Transdermal System Extended-release | rivastigmine | 4.6 mg/24 hr and 9.5 mg/24 hr | 022083 | 1 | 2011-04-27 |
US Patents and Regulatory Information for RIVASTIGMINE
EU/EMA Drug Approvals for RIVASTIGMINE
| Company | Drugname | Inn | Product Number / Indication | Status | Generic | Biosimilar | Orphan | Marketing Authorisation | Marketing Refusal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actavis Group PTC ehf | Rivastigmine Actavis | rivastigmine | EMEA/H/C/002036Symptomatic treatment of mild to moderately severe Alzheimer's dementia.Symptomatic treatment of mild to moderately severe dementia in patients with idiopathic Parkinson's disease. | Authorised | yes | no | no | 2011-06-16 | |
| Krka, d.d., Novo mesto | Nimvastid | rivastigmine | EMEA/H/C/001029Symptomatic treatment of mild to moderately severe Alzheimer's dementia., , Symptomatic treatment of mild to moderately severe dementia in patients with idiopathic Parkinson's disease., | Authorised | yes | no | no | 2009-05-11 | |
| 1 A Pharma GmbH | Rivastigmine 1 A Pharma | rivastigmine | EMEA/H/C/001181Symptomatic treatment of mild to moderately severe Alzheimer's dementia.Symptomatic treatment of mild to moderately severe dementia in patients with idiopathic Parkinson's disease. | Authorised | no | no | no | 2009-12-11 | |
| Novartis Europharm Limited | Exelon | rivastigmine | EMEA/H/C/000169Symptomatic treatment of mild to moderately severe Alzheimer's dementia.Symptomatic treatment of mild to moderately severe dementia in patients with idiopathic Parkinson's disease. | Authorised | no | no | no | 1998-05-11 | |
| Novartis Europharm Limited | Prometax | rivastigmine | EMEA/H/C/000255Symptomatic treatment of mild to moderately severe Alzheimer's dementia.Symptomatic treatment of mild to moderately severe dementia in patients with idiopathic Parkinson's disease. | Authorised | no | no | no | 1998-12-03 | |
| Sandoz GmbH | Rivastigmine Sandoz | rivastigmine | EMEA/H/C/001183Symptomatic treatment of mild to moderately severe Alzheimer's dementia.Symptomatic treatment of mild to moderately severe dementia in patients with idiopathic Parkinson's disease. | Authorised | no | no | no | 2009-12-10 | |
| Hexal AG | Rivastigmine Hexal | rivastigmine | EMEA/H/C/001182Symptomatic treatment of mild to moderately severe Alzheimer's dementia.Symptomatic treatment of mild to moderately severe dementia in patients with idiopathic Parkinson's disease. | Authorised | no | no | no | 2009-12-11 | |
| >Company | >Drugname | >Inn | >Product Number / Indication | >Status | >Generic | >Biosimilar | >Orphan | >Marketing Authorisation | >Marketing Refusal |
Market Dynamics and Financial Trajectory for Rivastigmine
More… ↓
