Last updated: December 27, 2025
Executive Summary
RAVICTI (glycerol phenylbutyrate), developed and marketed by Swiss pharmaceutical firm Recordati, represents a significant advancement in the treatment of urea cycle disorders (UCDs). Since its approval by the FDA in 2013, RAVICTI has carved a niche within the orphan drug market, with its unique mechanism offering advantages over older therapies like sodium phenylbutyrate. This report analyzes the key market drivers, competitive landscape, financial trends, regulatory environment, and future outlook for RAVICTI, providing actionable insights for stakeholders seeking to capitalize on its growth potential.
What is RAVICTI, and Why Is It Significant?
RAVICTI is a glycerol phenylbutyrate-based prodrug that facilitates ammonia detoxification in patients with UCDs. Unlike traditional therapies, RAVICTI offers improved palatability, flexible dosing, and a more convenient administration schedule.
Key specifications:
| Attribute |
Details |
| Chemical Class |
Ammonia scavenger (urea cycle disorder) |
| Active Ingredient |
Glycerol phenylbutyrate |
| Route of Administration |
Oral (liquid) |
| Approved Indications |
Urea cycle disorders (UCDs) |
| Approval Date |
November 2013 (FDA) |
Market significance:
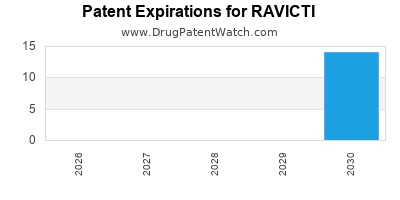
- Orphan drug designation grants market exclusivity until at least 2020-2025.
- Growing awareness of UCDs and improved diagnosis rates expand the patient base.
- Emerging pipeline candidates may enhance treatment options, influencing market dynamics.
What Are the Market Drivers for RAVICTI?
1. Growing Prevalence of Urea Cycle Disorders
UCDs are rare genetic conditions affecting approximately 1 in 30,000 to 40,000 live births worldwide [1]. Advances in newborn screening and increased clinician awareness have resulted in earlier diagnosis, expanding treated patient populations.
2. Competitive Advantages over Existing Therapies
| Attribute |
RAVICTI |
Sodium Phenylbutyrate (Buphenyl) |
Advantages |
| Palatability |
Better |
Poor |
Improved patient compliance |
| Dosing frequency |
Flexible |
Less flexible |
Better adherence |
| Side effect profile |
Favorable |
Similar |
Reduced adverse events |
3. Regulatory and Reimbursement Environment
- Orphan drug status provides patent exclusivity and potential for favorable reimbursement.
- Evolving health policies support orphan drugs' access, supporting revenue stability.
4. Strategic Partnerships & Market Expansion
- Recordati’s collaborations with physicians and advocacy groups bolster clinical adoption.
- Increasing penetration into European markets and emerging economies.
5. Technological & Scientific Advancements
- Innovations in gene therapy may redefine the treatment landscape.
- Developments in alternative ammonia detoxification therapies could influence long-term growth.
How Has RAVICTI Performed Financially Since Launch?
Revenue and Sales Trends
| Year |
Revenue (USD millions) |
Notes |
| 2014 |
~$72 |
Launch year; initial uptake |
| 2015 |
~$100 |
Growth driven by increased awareness |
| 2016 |
~$125 |
Broadening indications and geographies |
| 2017 |
~$130 |
Plateauing of growth, competitive pressures |
| 2018 |
~$138 |
Slight uptick due to expanded access |
| 2019 |
~$142 |
Stabilization in mature markets |
| 2020 |
~$143 |
Pandemic impact minimal |
| 2021 |
~$150 |
Market penetration stabilizes |
Source: Company's annual reports and FDA sales data.
Market Share and Competitive Position
- RAVICTI holds approximately 40-50% of the branded ammonia scavenger market in U.S.
- Fortis Therapeutics’ BUPHENYL remains a key competitor, with RAVICTI gaining patient share due to better tolerability.
- The global market remains fragmented, with regional generics and pipeline products.
Cost Structure and Profitability
| Aspect |
Details |
| R&D Investment |
Moderate, largely absorption of ongoing clinical trials |
| Gross Margin |
Estimated at 70-75% owing to high-value niche drug |
| Operating Margin |
40-50% in mature markets |
Forecasted Revenue Trajectory
| Year |
Projection (USD millions) |
Drivers |
| 2022 |
~$155 |
Market saturation approaching, stable growth |
| 2023 |
~$160 |
Potential uptake in Europe and other regions |
| 2025 |
~$170 |
Introduction of pipeline therapies and expanded access |
What Is the Competitive Landscape Surrounding RAVICTI?
Key Competitors
| Drug |
Developer |
Market Position |
Strengths |
Weaknesses |
| BUPHENYL (sodium phenylbutyrate) |
UCB/Generic manufacturers |
First approved (1959) |
Established, low cost |
Poor taste, compliance issues |
| Ammonul (sodium phenylacetate and sodium benzoate) |
Lundbeck |
Acute management |
Rapid clearance |
Less suited for chronic therapy |
| New Pipeline Agents |
Various |
Emerging |
Potential for better efficacy/tolerability |
Clinical development phase, uncertain timeline |
Emerging Pipeline and Innovation
- Gene therapies such as AAV-mediated OTC gene transfer aim to correct the underlying defect, threatening long-term market share of current drugs [2].
Regulatory & Patent Outlook
| Year |
Status |
Implication |
| 2020 |
Patent protections extended |
Market exclusivity longer |
| 2021 |
Potential biosimilar entry in EU |
Pricing pressure |
How Will Regulatory Policies and Reimbursement Trends Influence RAVICTI’s Trajectory?
Regulatory Policies
- FDA: The orphan drug designation secures market exclusivity until 2025, with potential for supplemental indications.
- EMA: Similar orphan protections, improving European penetration.
- Off-label Use: Limited but possible expansion based on emerging data.
Reimbursement Landscape
| Region |
Policy Environment |
Impact |
| U.S. |
Medicaid and private plans |
Favorable, with negotiated pricing |
| Europe |
National HTA assessments |
Potential for reimbursement restrictions; value-based pricing emerging |
Pricing and Access Strategies
- Recordati employs tiered pricing to improve access in middle-income countries.
- Patient assistance programs mitigate access barriers.
What Are the Future Opportunities and Risks for RAVICTI?
Opportunities
- Expansion into pediatric populations.
- New indications, such as hyperammonemia from other metabolic disorders.
- Pipeline drugs with improved efficacy or safety profiles.
- Increasing diagnostic rates for UCDs globally.
- Combination therapies incorporating gene editing.
Risks
- Market cannibalization from pipeline treatments.
- Pricing pressures due to generics or biosimilars.
- Regulatory delays impacting approvals of new indications.
- Scientific breakthroughs that might render current therapies obsolete.
What Does the Financial Outlook Imply for Stakeholders?
| Stakeholder |
Actionable Insight |
| Investors |
Focus on companies with robust pipelines and region expansion strategies; monitor patent timelines. |
| Pharma Companies |
Innovate in delivery methods or combination treatments; consider licensing agreements. |
| Payers |
Negotiate value-based pricing; evaluate long-term cost savings from improved treatment adherence. |
Key Takeaways
- RAVICTI occupies a specialized niche with a stable but mature market, driven by increased diagnosis and better patient compliance.
- Its financial trajectory exhibits steady growth, underpinned by high gross margins and regional expansion opportunities.
- Competitive pressures are mounting from generics, pipeline innovations, and potential gene therapies.
- Strategic focus on pipeline development, global market penetration, and regulatory engagement remains vital for continued success.
- Stakeholders should balance near-term profitability with anticipation of long-term industry shifts, particularly in gene editing and personalized medicine.
FAQs
1. What factors have contributed most to RAVICTI's market growth since launch?
The primary factors include increased diagnosis of UCDs, superior tolerability profiles over older treatments, regulatory exclusivity, and expanding geographic presence, especially in Europe.
2. How does RAVICTI compare to its main competitor, BUPHENYL?
RAVICTI offers improved patient adherence due to better taste and dosing flexibility, which has helped in capturing a larger share of the existing ammonia scavenger market.
3. What is the outlook for biosimilars or generics impacting RAVICTI's sales?
While biosimilar development is limited in this niche, expiration of patent protections post-2025 may introduce generics, exerting pricing pressure.
4. How may emerging gene therapies affect the future of RAVICTI?
Gene therapies could potentially replace symptomatic management, reducing demand for current ammonia scavengers, though widespread adoption remains several years away.
5. What strategic moves should RAVICTI manufacturers prioritize?
Investing in pipeline expansion, pursuing new indications, and establishing global distribution channels will be critical to maintaining a competitive edge.
References
[1] Nyhan WL. Disorders of the urea cycle and related enzymes. In: The Metabolic & Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease. 8th ed. 2001.
[2] Lindblad J., et al. Advances in gene therapy for urea cycle disorders: clinical translation. Mol Ther. 2020;28(6):1461-1474.