QTERN Drug Patent Profile
✉ Email this page to a colleague
Which patents cover Qtern, and when can generic versions of Qtern launch?
Qtern is a drug marketed by Astrazeneca Ab and is included in two NDAs. There are eight patents protecting this drug and two Paragraph IV challenges.
This drug has three hundred and thirteen patent family members in forty-eight countries.
The generic ingredient in QTERN is dapagliflozin; metformin hydrochloride; saxagliptin hydrochloride. There are twenty-six drug master file entries for this compound. Additional details are available on the dapagliflozin; metformin hydrochloride; saxagliptin hydrochloride profile page.
DrugPatentWatch® Generic Entry Outlook for Qtern
Qtern was eligible for patent challenges on January 8, 2018.
By analyzing the patents and regulatory protections it appears that the earliest date
for generic entry will be June 16, 2030. This may change due to patent challenges or generic licensing.
There have been eighteen patent litigation cases involving the patents protecting this drug, indicating strong interest in generic launch. Recent data indicate that 63% of patent challenges are decided in favor of the generic patent challenger and that 54% of successful patent challengers promptly launch generic drugs.
Indicators of Generic Entry
AI Deep Research
Questions you can ask:
- What is the 5 year forecast for QTERN?
- What are the global sales for QTERN?
- What is Average Wholesale Price for QTERN?
Summary for QTERN
| International Patents: | 313 |
| US Patents: | 7 |
| Applicants: | 1 |
| NDAs: | 2 |
| Finished Product Suppliers / Packagers: | 1 |
| Raw Ingredient (Bulk) Api Vendors: | 1 |
| Patent Applications: | 10 |
| Drug Prices: | Drug price information for QTERN |
| Patent Litigation and PTAB cases: | See patent lawsuits and PTAB cases for QTERN |
| What excipients (inactive ingredients) are in QTERN? | QTERN excipients list |
| DailyMed Link: | QTERN at DailyMed |
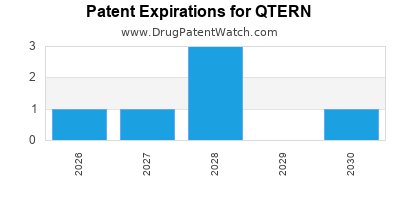
DrugPatentWatch® Estimated Loss of Exclusivity (LOE) Date for QTERN
Generic Entry Date for QTERN*:
Constraining patent/regulatory exclusivity:
NDA:
Dosage:
TABLET;ORAL |
*The generic entry opportunity date is the latter of the last compound-claiming patent and the last regulatory exclusivity protection. Many factors can influence early or later generic entry. This date is provided as a rough estimate of generic entry potential and should not be used as an independent source.
Pharmacology for QTERN
Paragraph IV (Patent) Challenges for QTERN
| Tradename | Dosage | Ingredient | Strength | NDA | ANDAs Submitted | Submissiondate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QTERN | Tablets | dapagliflozin; saxagliptin hydrochloride | 5 mg/5 mg | 209091 | 1 | 2020-07-29 |
| QTERN | Tablets | dapagliflozin; saxagliptin hydrochloride | 10 mg/5 mg | 209091 | 5 | 2018-01-08 |
US Patents and Regulatory Information for QTERN
QTERN is protected by seven US patents.
Based on analysis by DrugPatentWatch, the earliest date for a generic version of QTERN is ⤷ Get Started Free.
This potential generic entry date is based on patent 7,919,598.
Generics may enter earlier, or later, based on new patent filings, patent extensions, patent invalidation, early generic licensing, generic entry preferences, and other factors.
| Applicant | Tradename | Generic Name | Dosage | NDA | Approval Date | TE | Type | RLD | RS | Patent No. | Patent Expiration | Product | Substance | Delist Req. | Exclusivity Expiration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Astrazeneca Ab | QTERNMET XR | dapagliflozin; metformin hydrochloride; saxagliptin hydrochloride | TABLET, EXTENDED RELEASE;ORAL | 210874-003 | May 2, 2019 | DISCN | Yes | No | 8,716,251*PED | ⤷ Get Started Free | Y | ⤷ Get Started Free | |||
| Astrazeneca Ab | QTERNMET XR | dapagliflozin; metformin hydrochloride; saxagliptin hydrochloride | TABLET, EXTENDED RELEASE;ORAL | 210874-003 | May 2, 2019 | DISCN | Yes | No | 6,515,117*PED | ⤷ Get Started Free | Y | ⤷ Get Started Free | |||
| Astrazeneca Ab | QTERNMET XR | dapagliflozin; metformin hydrochloride; saxagliptin hydrochloride | TABLET, EXTENDED RELEASE;ORAL | 210874-004 | May 2, 2019 | DISCN | Yes | No | 8,628,799 | ⤷ Get Started Free | Y | ⤷ Get Started Free | |||
| >Applicant | >Tradename | >Generic Name | >Dosage | >NDA | >Approval Date | >TE | >Type | >RLD | >RS | >Patent No. | >Patent Expiration | >Product | >Substance | >Delist Req. | >Exclusivity Expiration |
Expired US Patents for QTERN
| Applicant | Tradename | Generic Name | Dosage | NDA | Approval Date | Patent No. | Patent Expiration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Astrazeneca Ab | QTERN | dapagliflozin; saxagliptin hydrochloride | TABLET;ORAL | 209091-001 | Feb 27, 2017 | 8,628,799 | ⤷ Get Started Free |
| Astrazeneca Ab | QTERN | dapagliflozin; saxagliptin hydrochloride | TABLET;ORAL | 209091-002 | May 2, 2019 | 6,414,126 | ⤷ Get Started Free |
| Astrazeneca Ab | QTERN | dapagliflozin; saxagliptin hydrochloride | TABLET;ORAL | 209091-002 | May 2, 2019 | RE44186 | ⤷ Get Started Free |
| >Applicant | >Tradename | >Generic Name | >Dosage | >NDA | >Approval Date | >Patent No. | >Patent Expiration |
International Patents for QTERN
When does loss-of-exclusivity occur for QTERN?
Based on analysis by DrugPatentWatch, the following patents block generic entry in the countries listed below:
Argentina
Patent: 1730
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Australia
Patent: 07265246
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Brazil
Patent: 0713544
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 2017015106
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 2017021516
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Canada
Patent: 53344
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 24318
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 85797
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Chile
Patent: 07001915
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
China
Patent: 1479287
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 3145773
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Colombia
Patent: 60299
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Croatia
Patent: 0141007
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Cyprus
Patent: 15738
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Denmark
Patent: 69374
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Eurasian Patent Organization
Patent: 8229
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 0428
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 8259
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 5999
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 0900066
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 1171333
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 1490902
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 1791254
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 2091391
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
European Patent Office
Patent: 69374
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 57918
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 45466
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 63807
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Hong Kong
Patent: 27359
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Israel
Patent: 5882
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 4180
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 4181
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 4182
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Japan
Patent: 13889
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 66651
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 37187
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 09545525
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 13209394
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 15071636
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 16172758
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 17222681
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 19059779
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Malaysia
Patent: 8566
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 3930
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Mexico
Patent: 9143
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 7155
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 08015377
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
New Zealand
Patent: 4346
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 9190
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 9195
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 9202
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Norway
Patent: 6828
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 7770
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 085169
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 221233
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Peru
Patent: 080349
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 120776
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Philippines
Patent: 012500168
Patent: CRYSTALLINE SOLVATES AND COMPLEXES OF (IS)-1,5-ANHYDRO-L-C-(3-((PHENYL)METHYL)PHENYL)-D-GLUCITOL DERIVATIVES WITH AMINO ACIDS AS SGLT2 INHIBITORS FOR THE TREATMENT OF DIABETES
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Poland
Patent: 69374
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Portugal
Patent: 69374
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Serbia
Patent: 638
Patent: KRISTALNI SOLVATI DERIVATA (1S)-1,5-ANHIDRO-1-C-(3-((FENIL) METIL) FENIL)-D-GLUCITOLA SA ALKOHOLIMA KAO INHIBITORI SGLT2 ZA TRETMAN DIJABETESA (CRYSTALLINE SOLVATES OF (1S)-1,5-ANHYDRO-1-C-(3-((PHENYL) METHYL) PHENYL)-D-GLUCITOL DERIVATIVES WITH ALCOHOLS AS SGLT2 INHIBITORS FOR THE TREATMENT OF DIABETES)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Singapore
Patent: 2741
Patent: CRYSTALLINE SOLVATES AND COMPLEXES OF (1S) -1, 5-ANHYDRO-1-C- (3- ( (PHENYL) METHYL) PHENYL) -D-GLUCITOL DERIVATIVES WITH AMINO ACIDS AS SGLT2 INHIBITORS FOR THE TREATMENT OF DIABETES
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 201402181S
Patent: CRYSTALLINE SOLVATES AND COMPLEXES OF (1S) -1, 5-ANHYDRO-1-C- (3- ( (PHENYL) METHYL) PHENYL) -D-GLUCITOL DERIVATIVES WITH AMINO ACIDS AS SGLT2 INHIBITORS FOR THE TREATMENT OF DIABETES
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Slovenia
Patent: 69374
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
South Africa
Patent: 0810475
Patent: CRYSTALLINE SOLVATES AND COMPLEXES OF (IS)-1,5-ANHYDRO-L-C-(3-((PHENYL)METHYL)PHENYL)-D-GLUCITOL DERIVATIVES WITH AMINO ACIDS AS SGLT2 INHIBITORS FOR THE TREATMENT OF DIABETES
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
South Korea
Patent: 1493102
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 090023643
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Spain
Patent: 21665
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 59862
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 69130
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Taiwan
Patent: 21245
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 66876
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 19528
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 0811127
Patent: Crystal structures of SGLT2 inhibitors and processes for preparing same
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 1406743
Patent: Crystal structures of SGLT2 inhibitors and processes for preparing same
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 1509927
Patent: Crystal structures of SGLT2 inhibitors and processes for preparing same
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 1546054
Patent: Crystal structures of SGLT2 inhibitors and processes for preparing same
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Ukraine
Patent: 765
Patent: КРИСТАЛЛИЧЕСКИЕ СОЛЬВАТЫ И КОМПЛЕКСЫ ПРОИЗВОДНЫХ (IS)-1,5-АНГИДРО-L-C-(3-((ФЕНИЛ)МЕТИЛ)ФЕНИЛ)-D-ГЛЮЦИТОЛА С АМИНОКИСЛОТАМИ КАК ИНГИБИТОРЫ БЕЛКА SGLT2, ПРИГОДНЫЕ В ЛЕЧЕНИИ ДИАБЕТА;КРИСТАЛІЧНІ СОЛЬВАТИ І КОМПЛЕКСИ ПОХІДНИХ (IS)-1,5-АНГІДРО-L-C-(3-((ФЕНІЛ)МЕТИЛ)ФЕНІЛ)-D-ГЛЮЦИТОЛУ З АМІНОКИСЛОТАМИ ЯК ІНГІБІТОРИ БІЛКА SGLT2, ПРИДАТНІ У ЛІКУВАННІ ДІАБЕТУ (CRYSTALLINE SOLVATES AND COMPLEXES OF (IS) -1, 5-ANHYDRO-L-C- (3- ((PHENYL) METHYL) PHENYL) -D-GLUCITOL DERIVATIVES WITH AMINO ACIDS AS SGLT2 INHIBITORS FOR THE TREATMENT OF DIABETES)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Generics may enter earlier, or later, based on new patent filings, patent extensions, patent invalidation, early generic licensing, generic entry preferences, and other factors.
See the table below for additional patents covering QTERN around the world.
| Country | Patent Number | Title | Estimated Expiration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Luxembourg | 92182 | ⤷ Get Started Free | |
| Taiwan | I466876 | ⤷ Get Started Free | |
| China | 1896088 | C-aryl glucoside sglt2 inhibitors | ⤷ Get Started Free |
| >Country | >Patent Number | >Title | >Estimated Expiration |
Supplementary Protection Certificates for QTERN
| Patent Number | Supplementary Protection Certificate | SPC Country | SPC Expiration | SPC Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1261586 | 10C0010 | France | ⤷ Get Started Free | PRODUCT NAME: SAXAGLIPTINE ET SES SELS PHARMACEUTIQUEMENT ACCEPTABLES, Y COMPRIS LE CHLORHYDRATE DE SAXAGLIPTINE; NAT. REGISTRATION NO/DATE: EU/1/09/545/001 20091001; FIRST REGISTRATION: EU/1/09/454/001 20091001 |
| 1506211 | C 2014 029 | Romania | ⤷ Get Started Free | PRODUCT NAME: COMBINATIE DE DAPAGLIFLOZIN SAU O SARE ACCEPTABILAFARMACEUTIC A ACESTUIA SI METFORMINA SAU O SARE ACCEPTABILA FARMACEUTIC A ACESTEIA; NATIONAL AUTHORISATION NUMBER: EU/1/13/900; DATE OF NATIONAL AUTHORISATION: 20140116; NUMBER OF FIRST AUTHORISATION IN EUROPEAN ECONOMIC AREA (EEA): EU/1/13/900; DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION IN EEA: 20140116 |
| 1261586 | 1290013-0 | Sweden | ⤷ Get Started Free | PRODUCT NAME: SAXAGLIPTIN/METFORMIN; REG. NO/DATE: EU/1/11/731/001 20111124 |
| >Patent Number | >Supplementary Protection Certificate | >SPC Country | >SPC Expiration | >SPC Description |
Market Dynamics and Financial Trajectory for QTERN (Saxagliptin and Dapagliflozin)
More… ↓
Make Better Decisions: Try a trial or see plans & pricing
Drugs may be covered by multiple patents or regulatory protections. All trademarks and applicant names are the property of their respective owners or licensors. Although great care is taken in the proper and correct provision of this service, thinkBiotech LLC does not accept any responsibility for possible consequences of errors or omissions in the provided data. The data presented herein is for information purposes only. There is no warranty that the data contained herein is error free. We do not provide individual investment advice. This service is not registered with any financial regulatory agency. The information we publish is educational only and based on our opinions plus our models. By using DrugPatentWatch you acknowledge that we do not provide personalized recommendations or advice. thinkBiotech performs no independent verification of facts as provided by public sources nor are attempts made to provide legal or investing advice. Any reliance on data provided herein is done solely at the discretion of the user. Users of this service are advised to seek professional advice and independent confirmation before considering acting on any of the provided information. thinkBiotech LLC reserves the right to amend, extend or withdraw any part or all of the offered service without notice.
