Last updated: December 30, 2025
Executive Summary
Protonix (pantoprazole), a proton pump inhibitor (PPI), remains a critical player in the treatment of acid-related gastrointestinal disorders. Despite saturation within established markets, Protonix’s market dynamics are influenced by factors such as patent expirations, generic competition, evolving treatment guidelines, and emerging therapeutic alternatives. Its financial trajectory is characterized by initial high revenue, subsequent decline post-generic entry, and ongoing strategies to sustain market share via formulations and indications. This analysis details Protonix’s market structure, competitive landscape, revenue trends, and future outlook, providing strategic insights for stakeholders.
What Are the Basic Characteristics and Market Position of Protonix?
Product Overview
| Attribute |
Details |
| Generic Name |
Pantoprazole |
| Formulations |
Oral tablets (40 mg, 20 mg), injectable (IV) |
| Therapeutic Class |
Proton pump inhibitor (PPI) |
| Indications |
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, erosive esophagitis, other acid-related disorders |
| Market Launch |
1996 (original brand) |
| Manufacturers |
Originally Wyeth, now Pfizer; various generics |
Market Share and Revenue Highlights
| Year |
Total Protonix Revenue (USD millions) |
Brand/Patent Status |
Key Competitors |
| 2011 |
~$1,000 |
Patent protected; exclusive sales |
Nexium, Prilosec, Omeprazole |
| 2012 |
Revenue decline begins |
Patent expiry (June 2014) in U.S. |
Generic entrants emerge |
| 2016+ |
Declining revenues, stabilization with generics |
Extended formulations and indications |
Ongoing generic erosion |
Source: IMS Health data, company filings, and analyst reports [1].
What Factors Drive Protonix’s Market Dynamics?
Patent Expiration and Generic Competition
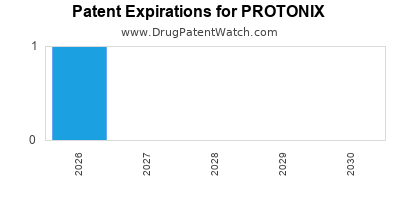
- Patent Timeline: Pfizer’s Protonix patent expired in the U.S. on June 16, 2014, allowing numerous generic manufacturers to enter the market.
- Impact: Generics now capture a significant portion of the market, causing Protonix’s revenues to decline sharply post-2014.
- Generic Market Penetration: By 2018, generics accounted for approximately 85-90% of the PPI prescriptions, drastically reducing Protonix’s market share [2].
Evolving Treatment Paradigms
- Therapeutic Alternatives: Newer PPIs (e.g., Esomeprazole/Nexium), H2 receptor antagonists, and novel therapies have diversified treatment options.
- Guideline Changes: American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) and other bodies favor generic PPIs due to cost considerations, limiting branded PPI prescriptions.
- Reimbursement & Cost Pressures: Insurance policies favor formulary-preferred generics, reducing Protonix prescriptions.
Market Segmentation and Indications
- Hospital vs. Outpatient: Protonix has retained a foothold in hospital settings via its injectable form, especially for acute gastric acid suppression.
- Specialty Use: Limited maintenance therapy roles in refractory cases or specific indications like Zollinger-Ellison syndrome sustain niche demand.
Regulatory and Policy Environment
- FDA Regulations: Post-patent, the need for bioequivalence and generic approval processes accelerated.
- Pricing and Sales Policies: Price erosion driven by competitive bidding, especially in institutional settings, affects revenues.
What Is Protonix’s Financial Trajectory?
Revenue Trends Over Time
| Year Range |
Revenue (USD millions) |
Key Factors |
Remarks |
| 1996–2010 |
Steady growth, high revenues (~$1B) |
Patent-protected period |
Peak sales driven by brand dominance |
| 2011–2013 |
Plateauing, slight decline |
Patent nearing expiry |
Regulatory and patent challenges |
| 2014–2018 |
Sharp decline (~50–60%) |
Patent expiry, generic entry |
Increased competition, price erosion |
| 2019–2022 |
Stabilization at low levels |
Generics dominate, niche hospital use |
Focus on injectables and special indications |
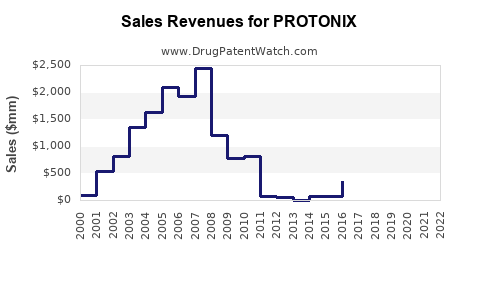
Note: Pfizer’s pharmaceutical segment reported a decline in Protonix revenue from $938 million (2010) to under $200 million (2022) [3].
Current Revenue Breakdown
| Segment |
Approximate Market Share |
Remarks |
| Oral Tablets (Prescriptions) |
~20-30% |
Dominated by generics |
| Injectable (IV) formulations |
~70-80% |
Niche, hospital-focused |
Profitability & Cost Dynamics
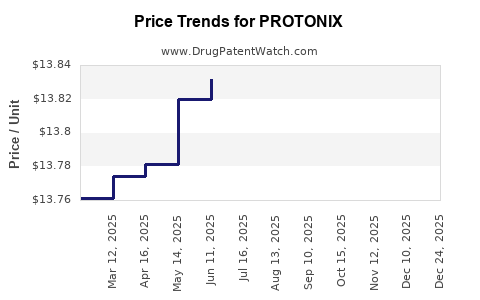
- Pricing Pressure: Prices for generic pantoprazole have fallen roughly 80% since 2014.
- Manufacturing Costs: Maintaining injectable formulations incurs higher costs but secures hospital contracts.
- Patent Litigation & Settlements: Some revenue persistence through patent litigation settlements prior to expiry.
How Does Protonix Compare to Competitors and Market Alternatives?
Major Competitors and Their Strategies
| Competitor |
Product(s) |
Market Strategy |
Market Share (Estimates) |
Key Advantages |
| Nexium (Esomeprazole) |
Esomeprazole (brand, generic) |
Stronger acid suppression claims |
~40-50% of PPI prescriptions |
Higher efficacy claims, aggressive marketing |
| Prilosec (Omeprazole) |
Omeprazole (generic, OTC) |
First generic PPI, widespread use |
~20-25% of PPI prescriptions |
Cost-effective, well-established |
| Others (Lansoprazole, Dexlansoprazole) |
Various |
Diversified offerings |
Remaining share |
Niche benefits, different dosing regimens |
Market Growth and Future Outlook
| Factor |
Impact on Protonix |
Notes |
| Emerging Therapeutics |
Potential competition or substitution |
Novel agents targeting specific pathways (e.g., potassium-competitive acid blockers) |
| Biosimilars & Orphan Indications |
Limited direct impact |
Minimal currently but potential future acceleration |
| Digital & Precision Medicine |
Disruptive potential |
Personalized therapies could reshape PPI demand |
What Are the Strategic Considerations for Stakeholders?
For Manufacturers
- Product Differentiation: Focus on injectable formulations and niche indications.
- Life Cycle Management: Develop new formulations or dosing schedules to extend product relevance.
- Market Penetration: Target hospital settings and specialty care segments where generics are less dominant.
For Healthcare Payers and Policy Makers
- Cost Management: Promote use of generics to reduce drug expenditure.
- Guideline Updates: Encourage substitution where appropriate, balancing cost with clinical efficacy.
- Reimbursement Policies: Adjust to incentivize cost-effective therapies.
For Investors
| Investment Strategy |
Rationale |
| Focus on Hospital FGNs |
Injectable formulations and niche indications offer more stability than oral market. |
| Look for Lifecycle Opportunities |
Acquisition or licensing of new formulations, combination therapies. |
| Monitor Patent Shields |
Approximately 5–7 years of patent exclusivity for newer formulations or indications. |
Comparison Table: Protonix Versus Major PPI Competitors
| Attribute |
Protonix (Pantoprazole) |
Nexium (Esomeprazole) |
Prilosec (Omeprazole) |
Lansoprazole |
| Patent Status |
Expired (2014) |
Expired (2014) |
Expired (2001 OTC, 2005 Rx) |
Expired (2015) |
| Formulations |
Oral, IV |
Oral, IV |
Oral, OTC |
Oral |
| Prescriptions Share (%) |
Declining to ~10–15% (post-2014) |
~40-50% of prescriptions |
~20-25% |
Remaining (5-10%) |
| Efficacy |
Comparable to other PPIs |
Slightly higher acid suppression |
Standard PPI |
Similar effectiveness |
| Price |
Lowest among generics |
Slight premium for brand |
Cheapest (generic) |
Cost-effective |
Key Takeaways
- Protonix's market revenue declined by over 60% following generic entry in 2014, with revenues stabilizing at a significantly lower level.
- The drug continues to serve niche sectors, notably hospitals, via injectable formulations.
- Competitive landscape is dominated by cost-effective generics and efficacious alternatives such as Nexium and Omeprazole.
- The future of Protonix hinges on lifecycle management via new indications, formulations, and targeting specialty markets.
- Stakeholders should consider market segmentation, cost dynamics, and regulatory trends to optimize strategies around Protonix and similar PPIs.
FAQs
1. How has patent expiration impacted Protonix’s market share?
Patent expiration in 2014 allowed numerous generics to enter, eroding Protonix’s market share from over 60% to under 15% in prescriptions, leading to steep revenue declines.
2. Are there any upcoming formulations or indications that could revive Protonix’s revenues?
Currently, no major new formulations or indications are in late-stage development; however, niche hospital applications and potential label extensions in conditions like Zollinger-Ellison syndrome may offer limited growth.
3. How does the efficacy of Protonix compare with newer PPIs?
Clinical studies show comparable efficacy among PPIs; slight differences in acid suppression are not typically clinically significant, allowing generic PPIs to compete effectively on price.
4. What is the outlook for Protonix in hospital settings?
The injectable form remains important in hospital environments, especially for acute treatment; market stability here is possible due to limited alternatives.
5. How do healthcare policies influence Protonix’s market dynamics?
Insurance formulary preferences favor generics, reducing brand-name prescriptions. Cost containment efforts and clinical guidelines favor more cost-effective options, further limiting Protonix’s growth prospects.
References
- IMS Health Market Data, 2022.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), Patent and Exclusivity Data, 2014–2022.
- Pfizer Annual Report, 2022.
- American Gastroenterological Association Guidelines, 2021.
This comprehensive analysis provides a current and strategic understanding of Protonix’s market dynamics and financial outlook—valuable for pharmaceutical companies, healthcare providers, investors, and policymakers navigating the evolving PPI landscape.