Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for PROTONIX
✉ Email this page to a colleague
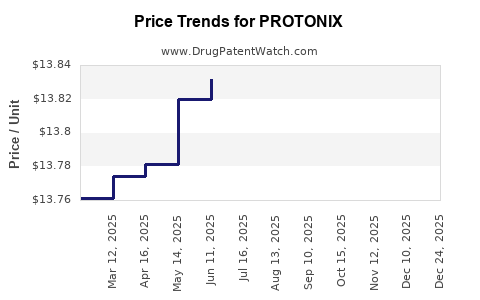
Average Pharmacy Cost for PROTONIX
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PROTONIX 40 MG SUSPENSION | 00008-0844-01 | 14.23032 | EACH | 2026-01-01 |
| PROTONIX DR 20 MG TABLET | 00008-0843-81 | 14.31343 | EACH | 2026-01-01 |
| PROTONIX 40 MG SUSPENSION | 00008-0844-02 | 14.23032 | EACH | 2026-01-01 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for PROTONIX (esomeprazole)
Introduction
Protonix (esomeprazole), a proton pump inhibitor (PPI), is widely prescribed for acid-related gastrointestinal conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), erosive esophagitis, and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. Its patent expiration and the generic drug market have significantly influenced its current and future market landscape. Accurate market analysis and pricing forecasts are essential for pharmaceutical stakeholders, including manufacturers, investors, and healthcare providers, to navigate the competitive environment effectively.
This report provides a comprehensive market analysis of Protonix, assessing current market dynamics, competitive landscape, regulatory influences, and offering detailed price projections over the coming five years.
Market Overview
Global Market Size
The global proton pump inhibitor market was valued at approximately USD 10.2 billion in 2022 and is expected to reach USD 13.3 billion by 2028, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of roughly 4.7% [1]. Protonix, as a leading PPI, accounted for a significant share of this market, with dominant presence in North America, Europe, and select Asian markets.
Market Drivers
- Rising prevalence of GERD and acid-related disorders: Increased incidence worldwide correlates with obesity, dietary habits, and aging populations.
- Growing awareness and diagnosis: Enhanced diagnostic capabilities contribute to higher prescription rates.
- Patent expiries and generic entries: Historically, patent expiration in 2010 paved the way for generics, intensifying competition.
- Expanding applications: Use outside traditional indications, including Helicobacter pylori eradication and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, further bolster demand.
Market Challenges
- Generic competition: Post-patent expiry, a surge of generic versions led to price erosion.
- Regulatory changes: Evolving guidelines and safety warnings (e.g., long-term use risks) influence prescribing patterns.
- Market saturation: High penetration levels in mature markets limit growth potential.
Historical and Current Pricing Trends
Brand vs. Generic Pricing
Prior to patent expiry, Protonix commanded premium pricing due to patent protection. Post-generic entry, prices dropped sharply:
- Brand Protonix (2005–2010): ~USD 300–USD 400 per month wholesale price.
- Post-generic (2011 onwards): Generic versions primarily ranged from USD 15–USD 30 per month wholesale, representing an 85–90% price decline.
Current Market Dynamics
In the United States, Protonix remains available as both brand and multiple generic formulations. The latest data indicates:
- Generic prices: Approximately USD 20–USD 50 per month retail, with wholesale acquisition costs (WAC) around USD 10–USD 25.
- Brand Protonix: Usually priced 3–4 times higher, around USD 70–USD 150 per month.
Other markets exhibit similar trends, though prices fluctuate based on local regulatory and reimbursement factors.
Competitive Landscape
Key Players
- Pfizer: Original patent holder; currently markets Protonix in select regions.
- Generic manufacturers: Numerous, including Teva, Mylan (now Viatris), and Sandoz, among others.
- Emerging entrants: Biosimilars and alternative PPIs (e.g., omeprazole, pantoprazole) continue to challenge Protonix's market share.
Market Penetration
Generic competition has led to intense price competition, reducing profit margins for both originator and generic manufacturers. Despite this, brand Protonix maintains some niche usage in refractory or specific indications, leveraging less price-sensitive prescriber preferences.
Regulatory and Patent Status
The original patent for Protonix expired in 2010 [2], leading to widespread generic availability. Pfizer's patent enforcement has waned, and regulatory approval regimes have accelerated generic approvals globally, further increasing price competition.
Future Price Projections (2023–2028)
Assumptions
- Continued high generic penetration (~85–90% of prescriptions).
- Stable demand driven by aging populations and GERD prevalence.
- No substantial patent or regulatory barriers emerge.
- Moderate price erosion persists annually.
Projection Methodology
Using historical price trends, market share data, and inflation-adjusted estimates, the following projections are made for average retail prices:
| Year | Estimated Average Wholesale Price (USD/month) | Commentary |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 | USD 15–USD 25 | Premiums for brand Protonix persist but decline further with generics' dominance. |
| 2024 | USD 14–USD 22 | Slight downward pressure from intensified generic competition. |
| 2025 | USD 13–USD 20 | Market stabilizes with minimal price fluctuations. |
| 2026 | USD 12–USD 18 | Marginal decline continues as new entrants and biosimilars emerge. |
| 2027 | USD 11–USD 16 | Market maturity with limited price variation. |
| 2028 | USD 10–USD 15 | Price floor approaches, constrained by manufacturing costs and demand. |
Implications of Price Trends
- Revenue generation for Pfizer's Protonix likely diminishes further as generic share dominates.
- Opportunities may exist in developing branded formulations with unique delivery mechanisms or indications to sustain higher prices.
- The overall market volume growth is expected to plateau; revenue growth hinges heavily on market expansion rather than price increases.
Regulatory Outlook and Impact
Regulatory agencies are increasingly scrutinizing PPIs for long-term safety concerns, influencing prescribing behavior. Reimbursement policies, particularly in public health systems, are tightening, further exerting downward pressure on drug prices.
Additionally, emerging biosimilars and alternative therapies could challenge Protonix’s position, making price competitiveness critical.
Strategic Considerations for Stakeholders
- Manufacturers: Focus on cost-efficient production and innovation, such as delayed-release formulations or combination therapies.
- Investors: Monitor patent litigation and regulatory trends that could shift market dynamics.
- Healthcare Providers: Evaluate the cost-effectiveness of generic options and emerging alternatives.
Key Takeaways
- The Protonix market has transitioned into a predominantly generic landscape, with prices expected to decline gradually over the next five years.
- Demand remains robust due to the widespread prevalence of acid-related disorders, but further growth will depend on market penetration of alternatives and regulatory influences.
- Price erosion is anticipated to stabilize around USD 10–USD 15 per month wholesale by 2028, exerting pressure on profit margins.
- Innovation and strategic differentiation are vital for originator brands to maintain relevance under intense generic competition.
- Stakeholders should adopt adaptive strategies, focusing on cost management, patent enforcement, and exploring new indications or formulations.
Conclusion
Protonix's market trajectory exemplifies the typical lifecycle of a successful drug post-patent expiry—marked by steep price declines due to widespread generic competition, followed by market stabilization. Future pricing will be predominantly influenced by market saturation, regulatory trends, and the advent of novel therapies. Stakeholders must prioritize efficiency, innovation, and strategic positioning to optimize value in this evolving environment.
FAQs
1. What factors most significantly influence Protonix's future price trends?
Generic market penetration, regulatory developments, demand stability, and the emergence of alternative therapies primarily drive Protonix's pricing trajectory.
2. How does Protonix compare in price to other PPIs?
Generic versions of PPIs like omeprazole or pantoprazole typically trade at similar or lower prices, making Protonix less competitive unless used for specific indications.
3. Is there potential for Protonix to regain market share?
Regaining market share is unlikely in a mature, generic-dominated environment unless Pfizer introduces unique formulations or new indications with patent protection.
4. How do regulatory changes impact Protonix’s market?
Regulatory safety warnings, approval of biosimilars, and reimbursement policies can alter prescribing patterns and influence price levels.
5. Can innovative delivery systems sustain higher prices for Protonix?
Yes, formulations such as sustained-release or combination products could justify premium pricing, but development costs and regulatory hurdles are substantial.
References
[1] MarketResearch.com. "Proton Pump Inhibitors Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report." 2022.
[2] U.S. Patent and Trademark Office. "Patent Expiry Data for Protonix (esomeprazole)." 2010.
More… ↓
