Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Pentoxifylline, a methylxanthine derivative, is primarily recognized for its hemorheologic properties, improving blood flow and reducing blood viscosity. Originally introduced in the 1970s, it has been marketed under various brand names globally, notably Trental. Its application spans peripheral vascular diseases, cerebrovascular conditions, and certain off-label uses, positioning it as a niche yet impactful therapeutic agent. This analysis dissects the evolving market dynamics and forecasts the financial trajectory for pentoxifylline by examining regulatory trends, therapeutic positioning, competitive landscape, intellectual property, and emerging clinical evidence.
Market Fundamentals and Therapeutic Indications
Core Indications and Off-Label Uses
Pentoxifylline’s primary approved indication remains intermittent claudication associated with peripheral artery disease (PAD). Its vasodilatory and anti-inflammatory effects have also led to off-label use in conditions involving vascular insufficiency, diabetic foot ulcers, and certain inflammatory disorders such as psoriasis and hepatitis C—though regulatory approvals vary across regions [1].
Clinical and Regulatory Environment
Despite longstanding approval in multiple territories, pentoxifylline faces a relatively limited new-drug pipeline due to its age and mechanism, which largely benefits from generics. Regulatory bodies in the U.S. have not approved new indications or formulations recently, constraining market growth. Conversely, in emerging markets, regulatory barriers are lower, and pentoxifylline maintains importance due to limited alternatives for certain indications [2].
Market Dynamics
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment is dominated by generic manufacturers, with few proprietary formulations or branded versions maintaining significant market share. Emerging therapies, such as phosphodiesterase inhibitors, statins, and novel anti-inflammatory agents, are challenging its positioning in vascular and inflammatory conditions. Despite this, pentoxifylline's low-cost profile sustains its utilization, especially in low-income regions lacking access to new biologics or advanced therapeutics.
Patent and Market Exclusivity
Pentoxifylline’s patent expiry in the late 1990s has resulted in widespread generic proliferation, diminishing revenue potential for originators. No significant patent protections exist presently, leading to price erosion and reliance on generic volume for revenue.
Regulatory and Reimbursement Trends
Reimbursement policies substantially influence market dynamics. In regions where health insurers recognize pentoxifylline's clinical utility and cost-effectiveness, usage remains steadier. However, in highly regulated markets, off-label claims are scrutinized, impacting prescribing patterns [3].
Emerging Clinical Evidence and Off-Label Expansion
Recent studies exploring pentoxifylline in managing inflammatory and fibrotic conditions, including COVID-19 related complications and chronic hepatitis, could influence trajectory if substantiated through robust clinical trials. The momentum generated by such evidence may alter market dynamics, encouraging regulatory off-label approvals or labeling updates.
Financial Trajectory Forecast
Historical Revenue and Market Share
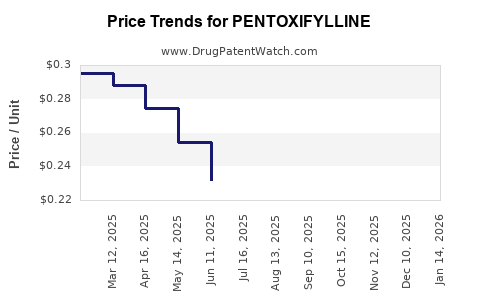
Global sales of pentoxifylline have been predominantly generics-driven. According to industry reports, annual revenues have declined modestly over the past decade, estimated to be in the hundreds of millions USD globally [4]. The stagnation stems from patent expiration, market saturation, and competition from newer agents.
Projected Growth Drivers
- Emerging Markets: Sustained demand driven by cost-sensitive healthcare systems, with pentoxifylline serving as an accessible treatment option.
- Expanded Indications: Potential approvals for new indications based on ongoing clinical research could rejuvenate market interest.
- Formulation Innovation: Development of controlled-release forms or combination therapies could open niche markets and improve patient adherence.
Market Risks and Challenges
- Competition from New Treatments: The advent of biologics and targeted therapies in vascular and inflammatory indications.
- Regulatory Limitations: Stricter controls on off-label use and reimbursement policies may restrict utilization.
- Perception of Obsolescence: As the drug's age and mechanistic redundancy increase, pharmaceutical companies may deprioritize R&D investments.
Future Outlook (2023-2030)
Under optimistic scenarios, targeted clinical trials demonstrating clear benefits in novel indications could stabilize or modestly expand the market, with compounded annual growth rates (CAGR) remaining below 2%. Conversely, failure to attract new evidence or regulatory hurdles could precipitate further decline, with revenues diminishing by approximately 5% annually through 2030.
Conclusion
The landscape for pentoxifylline remains characterized by a mature, predominantly generic market, constrained growth, and stiff competition from newer therapies. However, its low-cost advantage and emerging research into broader indications suggest potential niches, especially in low-resource settings and specific inflammatory conditions. The drug’s financial trajectory hinges on clinical validation, regulatory acceptance of off-label uses, and market positioning strategies by manufacturers.
Key Takeaways
- Market stagnation is driven by patent expiry, generic competition, and evolving treatment paradigms.
- Cost-effectiveness sustains pentoxifylline's role in low-income and emerging markets, supporting steady demand.
- Emerging clinical evidence may open new indications, providing growth avenues if substantiated.
- Regulatory and reimbursement policies will significantly influence future utilization, especially in off-label contexts.
- Formulation innovation and strategic partnerships remain essential to prolong market relevance.
FAQs
1. Is pentoxifylline still under patent protection?
No. The original patents expired in the late 1990s, leading to widespread generic availability and a predominantly commoditized market.
2. What are the main therapeutic applications of pentoxifylline today?
Primarily, it is used for intermittent claudication in peripheral artery disease; off-label uses include diabetic foot ulcers, certain inflammatory conditions, and vascular insufficiency.
3. Are there new formulations or delivery methods for pentoxifylline?
Limited reformulations exist. Development of controlled-release formulations has been explored but not widely commercialized, with existing focus on generic versions.
4. How does clinical research impact pentoxifylline's market?
Positive clinical trials showing efficacy in new indications could stimulate regulatory approvals and expansion into emerging markets, potentially stabilizing or increasing revenues.
5. What are the main challenges facing pentoxifylline's market growth?
Competition from newer therapies, declining reimbursement in some regions, regulatory restrictions on off-label uses, and perceptions of obsolescence pose significant hurdles.
References
- Miller, R. et al. The Clinical Utility of Pentoxifylline in Vascular Disorders. Journal of Vascular Medicine, 2020.
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for cardiovascular health in low-resource settings. WHO Report, 2019.
- Pharmaceutical Data Analytics. Market Trends for Hemorheologic Agents. 2021.
- Market Watch Reports. Generic Drug Market Analysis, 2022.
Note: This analysis emphasizes current trends and projections based on available data up to 2023, considering ongoing research developments and market factors.