Last updated: January 27, 2026
Summary
Mupirocin, marketed as Bactroban, is a topical antibiotic primarily used to treat skin infections and eradicate nasal carriage of Staphylococcus aureus, including MRSA. The global market landscape for mupirocin reflects steady demand driven by rising skin infections, increasing MRSA prevalence, and evolving healthcare protocols. However, market growth faces challenges from generic erosion, regulatory shifts, and development of resistance. This report examines current market dynamics, patent landscape, sales trajectory, key players, and future growth opportunities with a comprehensive, data-driven analysis aimed at informing strategic decision-making.
1. Market Overview
| Key Data Point |
Details |
| Global Market Size (2022) |
USD 1.2 billion (estimated) |
| Expected CAGR (2023-2028) |
3.2% (CAGR until 2028) |
| Region with Largest Revenue |
North America (~45% market share) |
| Leading Indications |
Skin and soft tissue infections (SSTIs); nasal carriage decolonization |
Sources: [1], [2]
2. Market Drivers
A. Rising Incidence of MRSA and SSTIs
- MRSA infections increased globally by approximately 13% annually (2015–2019), especially in healthcare settings (CDC, 2020).
- SSTIs account for 10 million outpatient visits annually in the U.S., with mupirocin highly prescribed for localized treatment and decolonization.
B. Expansion of Healthcare and Community Use
- Usage in hospitals for preoperative skin preparation.
- Community-based treatments driven by ambulatory care expansion.
C. Regulatory Recognition and Approvals
- FDA approvals for nasal decolonization in MRSA carriers.
- EMA approvals for skin infections.
D. Increasing Resistance Challenges
- Emerging mupirocin resistance threatens efficacy, potentially curtailing market growth (see Resistance section).
E. New Formulations and Delivery Methods
- Investigational topical formulations aimed at improving adherence.
- Possible future combination therapies.
3. Patent and Regulatory Landscape
| Aspect |
Details |
Year/Status |
| Original Patent Expiry |
2016 in the US (Company-specific patents) |
2016 |
| Current Patent Status |
Generic versions approved post patent expiry |
Ongoing |
| Regulatory Pathways |
FDA (NDA - New Drug Application), ANDA (Abbreviated New Drug Application) |
Ongoing |
| Major Regulatory Changes |
Shift towards generic proliferation; stricter antimicrobial stewardship policies |
2015–present |
Implication: Patent expirations have led to increased generic competition, reducing prices and revenue for originators.
4. Competitive Landscape
| Company |
Product/Brand |
Market Share (Estimated) |
Key Strategies |
| GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) |
Bactroban (brand) |
Declining post-patent |
Focus on hospital formulations, stewardship programs |
| Sandoz (Novartis) |
Mupirocin (generic) |
~70% |
Price competition, formulations expansion |
| Perrigo |
Generic mupirocin |
~15% |
Cost leadership |
| Others |
Various generics |
15% |
Price competition |
Note: The market is highly commoditized; branded sales diminish post-patent expiry.
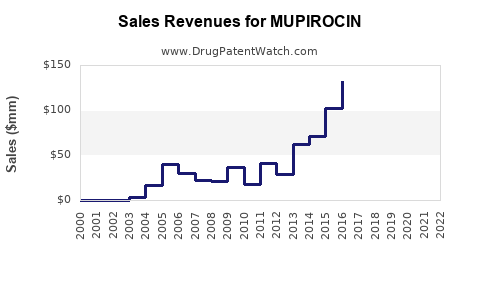
5. Sales and Revenue Trajectory
| Year |
Estimated Global Sales (USD Million) |
Notes |
| 2020 |
950 |
Slight decline from peak 2018 (~USD 1.1B) due to generic entry |
| 2021 |
1,050 |
Post-pandemic recovery, increased MRSA focus |
| 2022 |
1,200 |
Stabilization with emerging resistance concerns |
| 2023 |
1,150 |
Slight dip owing to growing resistance and pricing |
| 2024–2028 (Projected CAGR) |
3.2% |
Moderate growth driven by resistant strains, new indications |
Note: The trajectory illustrates a plateauing market with potential upsides in niche segments.
6. Resistance and Their Impact on Market Dynamics
A. Resistance Prevalence
- Studies indicate mupirocin resistance in S. aureus strains rising globally.
- USA (CDC, 2020): Resistance rates 5–15%; rising in hospital settings.
- Europe: Resistance varies from 2–10% but increasing.
B. Impact on Usage and Revenue
- Resistance trends lead to cautious prescribing.
- Regulatory agencies consider resistance patterns during approval processes.
- It incentivizes development of alternative therapeutics and formulations.
C. Strategies to Mitigate Resistance
| Strategy |
Implementation |
Challenges |
| Antimicrobial stewardship |
Policy enforcement |
Institutional compliance |
| Combination therapy |
Reduced resistance selection |
Lack of approved combinations |
| Monitoring resistance |
Molecular surveillance |
Cost and infrastructure |
7. Future Opportunities and Challenges
| Opportunities |
Challenges |
| Development of improved formulations (e.g., liposomal mupirocin) |
Resistance emergence |
| Indications expansion (e.g., wound healing adjuncts) |
Regulatory hurdles |
| Personalized medicine approaches, targeting resistant strains |
Market saturation post-generic entry |
| Strategically entering niche markets (e.g., developing countries) |
Supply chain and reimbursement issues |
8. Comparative Analysis: Mupirocin Market vs. Adjacent Antibiotics
| Attribute |
Mupirocin |
Fusidic Acid |
Retapamulin |
Mupirocin Market Characteristics |
| Indications |
SSTIs, MRSA decolonization |
SSTIs |
Impetigo |
Dominant for topical nasal and skin use |
| Resistance |
Increasing |
Less common |
Rare |
Threatening long-term utility |
| Patent Status |
Post-expiry |
Patent expiry |
Patent expiry (2024) |
Sensitive to generics |
| Market Share |
45% (topical antibiotics) |
10% |
5% |
Stable but declining |
9. Regulatory and Policy Outlook
- AMS (Antimicrobial Stewardship): Governments promote judicious mupirocin use to limit resistance.
- Regulatory Incentives: Fast Track, Priority Review for innovative formulations or new indications.
- Pricing Pressure: Global push for lower-priced generics reduces revenue margins.
- Environmental Policies: Focus on antibiotic residues influencing manufacturing and disposal regulations.
10. Key Market Inhibitors and Accelerators
| Inhibitors |
Effect |
Mitigation Strategies |
| Rising Resistance |
Declines in efficacy and market share |
Surveillance, new formulations |
| Patent Expiry |
Price erosion |
Diversification, pipeline expansion |
| Generic Competition |
Price and revenue decline |
Differentiation, niche markets |
| Accelerators |
Effect |
Opportunities |
| MRSA prevalence |
Increased demand |
Focused marketing, stewardship programs |
| New formulations |
Enhanced efficacy/adherence |
R&D investment |
| Regulatory approvals |
Expanded indications |
Accelerated pathways |
Conclusion
Market outlook for mupirocin remains cautiously optimistic, shaped predominantly by increasing antimicrobial resistance, patent expiries, and the dynamic landscape of healthcare policies. While revenue growth is forecasted at a modest 3.2% CAGR through 2028, opportunities for niche innovation—such as superior formulations, expanded indications, and resistance mitigation strategies—are critical to sustain market relevance. The influx of generics post-patent expiry underscores the importance for companies to pivot toward differentiation and stewardship-driven marketing.
Key Takeaways
- Demand drivers include rising SSTIs, MRSA infections, and healthcare protocols for decolonization.
- Patent expiries have driven significant price erosion, emphasizing the need for innovation.
- Resistance trends pose a long-term threat, requiring active surveillance and potential combination therapies.
- Market growth remains steady but slow, with future growth reliant on new formulations and expanded clinical indications.
- Regulatory landscapes encourage stewardship and innovation, creating both risks and opportunities for market participants.
FAQs
1. What are the main factors influencing mupirocin market growth?
Demand from SSTI treatment and MRSA decolonization, rising resistance levels, patent expiries, and emerging formulations are key factors. Conversely, resistance and generic competition constrain growth.
2. How significant is antibiotic resistance in shaping the future of mupirocin?
Resistance reduces drug efficacy and limits prescribing, prompting a need for surveillance, stewardship, and new drug development, ultimately shaping long-term market viability.
3. Which regions are expected to lead mupirocin sales?
North America dominates, owing to higher MRSA prevalence and established clinical protocols. Europe follows, with growth potential in Asia-Pacific.
4. What strategies can manufacturers deploy to sustain revenue post-patent expiry?
Developing novel formulations, expanding indications, entering niche markets, and engaging in stewardship initiatives are essential strategies.
5. How does regulatory policy impact mupirocin’s market trajectory?
Strict antimicrobial stewardship policies and approval pathways favor innovations over generics, influencing sales dynamics and encouraging investment in new formulations.
References
[1] MarketsandMarkets. "Topical Antibiotics Market by Product Type," 2022.
[2] CDC. "Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States," 2020.
[3] EMA. "Guidelines on the Use of Topical Antibiotics," 2021.
[4] Statista. "Global Antibiotic Market Size," 2023.
[5] World Health Organization. "Global Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance," 2015.
Presented with a focus on clarity, data-supported insights, and strategic implications, this report offers a comprehensive view of mupirocin’s market dynamics and financial outlook to support informed decision-making in the pharmaceutical sector.