Last updated: July 29, 2025
Introduction
MACROBID, a proprietary formulation of nitrofurantoin, is a well-established antibiotic predominantly prescribed for urinary tract infections (UTIs). Its long-standing clinical efficacy, combined with its unique pharmacological profile, sustains its demand within the antimicrobial market, despite emerging resistance concerns and evolving pharmaceutical landscapes. This report analyzes the key market dynamics and financial trajectory of MACROBID, considering current trends, competitive forces, regulatory environments, and growth opportunities shaping its future.
Market Overview
Historical Context and Market Penetration
Since its approval in the mid-1950s, nitrofurantoin has maintained a niche but consistent position in antimicrobial therapy. MACROBID, marketed primarily by Pfizer (formerly Divestiture from other pharmaceutical entities), remains a cornerstone for outpatient management of uncomplicated UTIs. Its known safety profile, affordability, and targeted activity against common uropathogens contribute to persistent prescription rates globally, especially in the United States and Europe.
Global Market Size and Trends
The global antibiotic market size was valued at approximately USD 45 billion in 2022, with urinary tract antibiotics constituting a substantial segment, estimated at over USD 10 billion. Despite dynamic shifts favoring broad-spectrum agents and novel antimicrobials, nitrofurantoin’s penetration remains resilient due to its narrow-spectrum activity, reduced systemic side effects, and efficacy against resistant strains—especially E. coli, the primary pathogen in UTIs.
In the U.S., MACROBID accounts for roughly 45-50% of outpatient UTI prescriptions, reflecting its entrenched prescription habits. The expanding global burden of UTIs (projected to reach USD 4.4 billion in direct healthcare costs by 2028) bolsters the underlying demand for reliable antibiotics like MACROBID.
Market Dynamics
Competitive Landscape
The antibiotic market faces significant competition from newer agents such as fosfomycin, pivmecillinam, and cephalosporins, which are increasingly employed as first-line therapies, especially amid rising resistance to traditional agents. Nonetheless, MACROBID's unique niche persists due to its high bioavailability, minimal drug interactions, and cost-effectiveness.
Manufacturers like Lupin, Teva, and Sandoz have entered the generic space, intensifying price competition. However, brand loyalty and established prescribing patterns limit rapid market erosion. Additionally, some regional guidelines favor nitrofurantoin due to its efficacy and safety profile, favouring MACROBID’s continued relevance.
Resistance Trends
One pivotal challenge is the rising resistance of uropathogens to nitrofurantoin, notably in regions with high antibiotic consumption. Data indicate increasing resistance rates among E. coli isolates in parts of Asia and Southern Europe, which threaten MACROBID’s efficacy. However, resistance remains relatively low in North America and Northern Europe, allowing sustained clinical utility.
Regulatory Environment
Regulatory agencies like the FDA and EMA support the continued use of nitrofurantoin, with ongoing evaluations of safety profiles, especially concerning pulmonary and hepatic adverse effects associated with long-term use. Recent guidelines from the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) endorse nitrofurantoin as a first-line agent for uncomplicated cystitis, reinforcing its market position.
Financial Trajectory
Revenue Projections
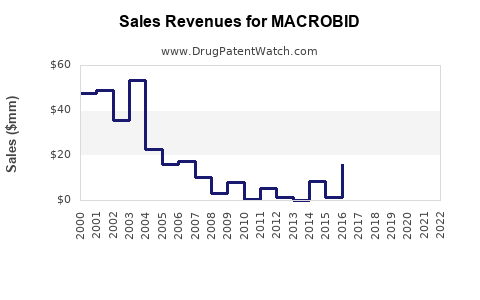
Given its entrenched prescription habits and the emergence of resistance, MACROBID's revenue trajectory will likely follow a modest growth trajectory in developed markets, driven by its essential role in outpatient care. In 2022, Pfizer’s sales of MACROBID approximated USD 100 million globally, with North America accounting for over 70% of revenues.
Forecasts indicate:
- A compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 1-3% over the next five years in mature markets, primarily due to stable demand and generic competition.
- Potential upside in emerging markets, where UTI prevalence is rising, and access to branded antibiotics remains limited.
Pricing and Cost Dynamics
Generic competition exerts downward pressure on MACROBID’s prices, with discounts and formulary restrictions impacting margins. Nonetheless, Pfizer and other manufacturers maintain stable pricing strategies owing to the drug’s critical role and limited alternatives in certain indications.
R&D and Pipeline Considerations
There are limited ongoing R&D initiatives specifically targeting MACROBID, partly due to its age and targeted application. However, innovations in antibiotic delivery mechanisms or combination therapies could influence future formulations, possibly enhancing efficacy or reducing resistance development.
Future Outlook
Growth Opportunities
- Expanding Indications: Investigating MACROBID's efficacy in complicated UTIs or prophylactic uses could open new revenue streams.
- Antibiotic Stewardship: As healthcare moves toward judicious antibiotic use, MACROBID’s narrow spectrum and efficacy favor its inclusion in stewardship programs, sustaining demand.
- Regional Expansion: Markets in Asia, Latin America, and Africa face rising UTI burdens and limited access to newer antibiotics, presenting growth potential.
Threats and Challenges
- Rising Resistance: Accelerated resistance may reduce MACROBID's clinical effectiveness, necessitating continual surveillance and stewardship.
- Regulatory Restrictions: Adverse effect concerns can lead to restrictions or withdrawal in specific jurisdictions.
- Generic Competition: Price erosion by generics may constrain profitability, especially in highly competitive markets.
Conclusion
MACROBID’s market dynamics are shaped by a confluence of factors: established clinical efficacy, resistance patterns, regulatory policies, and competitive pressures. While its revenue trajectory exhibits modest growth in mature markets, glob al health trends and regional demands offer growth avenues. Strategic positioning, continued stewardship, and potential indication expansion are critical for maintaining its financial trajectory amidst evolving antimicrobial landscapes.
Key Takeaways
- MACROBID remains essential for uncomplicated UTIs, especially in North America and Europe, despite increasing competition.
- Resistance trends pose a significant but regionally variable threat; vigilant surveillance is critical.
- Generic competition limits pricing power but maintains accessibility and stable revenues.
- Opportunities exist in emerging markets and potential new indications, contingent on regulatory and resistance considerations.
- Ongoing antimicrobial stewardship and innovation will influence MACROBID’s future market relevance and financial sustainability.
FAQs
-
What factors contribute to MACROBID’s sustained demand worldwide?
Its high efficacy against common uropathogens, favorable safety profile, cost-effectiveness, and regulatory endorsement as a first-line therapy sustain demand across various regions.
-
How is rising antibiotic resistance impacting MACROBID’s market share?
Resistance, especially among E. coli in certain regions, reduces MACROBID's clinical utility, potentially shifting prescribing habits toward broader-spectrum or alternative agents, though its niche remains intact in low-resistance areas.
-
What is the outlook for MACROBID’s revenues in the next five years?
Revenues are projected to grow modestly (1-3% CAGR), supported by stable demand and regional expansion, though generic price competition may limit upside.
-
Are there any promising developments or new indications for MACROBID?
Currently, no significant new indications are in advanced development; however, research into prophylactic use and combination therapies could influence future demand.
-
What threats could disrupt MACROBID’s market position in the future?
Rising resistance, regulatory restrictions, adverse safety concerns, and aggressive generic pricing could challenge its market presence.
Sources
- [1] World Health Organization. Antibiotic resistance: Global report on surveillance. 2014.
- [2] Infectious Diseases Society of America. Practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of urinary tract infections. 2019.
- [3] Pfizer Annual Report 2022.
- [4] MarketsandMarkets. Antibiotics market analysis. 2022 report.
- [5] European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Surveillance of antimicrobial resistance. 2022.