Last updated: July 30, 2025
Introduction
LAMISIL (generic name: terbinafine) remains a cornerstone antifungal agent with widespread usage in the treatment of dermatophyte infections, including onychomycosis, tinea pedis, and tinea corporis. Its market positioning is shaped by evolving clinical guidelines, competitive landscape, patent status, and emerging therapies. An in-depth understanding of market dynamics and financial trajectories is key for stakeholders aiming to capitalize on LAMISIL’s growth opportunities or manage associated risks.
Market Overview
LAMISIL was introduced by Novartis in 1991 and has since been a leading oral and topical antifungal treatment. Its broad spectrum of activity against dermatophytes has secured its market share in dermatology practices worldwide. Despite competition from generic formulations and newer antifungal agents such as efinaconazole and tavaborole, LAMISIL maintains significant prominence due to its proven efficacy, favorable safety profile, and brand recognition.
In 2022, the global antifungal market was valued at approximately USD 11 billion, projected to grow at a CAGR of 4-6% through 2030, driven by increasing prevalence of fungal infections, rising awareness, and expanding aging populations (Source: MarketsandMarkets). LAMISIL's slice of this pie remains substantial, with sales driven by both prescription fills and off-label uses.
Market Dynamics
1. Competitive Landscape
Generic entry has exerted downward pressure on LAMISIL’s price point. Since patent expiration, numerous generics have entered markets across North America, Europe, and Asia, intensifying price competition. Data indicates that generic terbinafine accounts for over 80% of unit sales in mature markets such as the United States (FDA, 2022).
Emerging therapies offer additional competitive pressure. For instance, newly approved topical agents like efinaconazole (Jublia) and tavaborole (Kerydin) market themselves as alternative options, especially for onychomycosis. These drugs often boast improved formulations or reduced treatment durations but face market inertia due to physician familiarity with terbinafine.
2. Regulatory and Patent Trends
The expiration of key patents has broadened access to generic terbinafine, substantially impacting pricing and margins. However, some formulations or indications remain under patent protection, offering hybrid opportunities for brand retention.
Regulatory challenges, such as safety concerns or new guidelines citing side effects, influence prescribing patterns. Recent warnings about hepatotoxicity, although rare, have prompted clinicians to monitor liver function and consider alternative therapies in high-risk populations.
3. Clinical Practice and Prescribing Trends
Physicians' preferences are shaped by efficacy, safety profiles, and patient compliance. LAMISIL’s oral formulation offers convenience, yet topical versions are preferred in superficial infections to mitigate systemic side effects.
Increasing adoption of combination therapies and personalized treatment approaches also influences market dynamics. The rise of telemedicine accelerates prescribing, impacting supply chains and patient access.
4. Geographic Variations
Developed markets like North America and Europe represent a mature landscape with high penetration rates. Emerging markets, including parts of Asia and Latin America, are experiencing growth due to increasing awareness, urbanization, and expanding healthcare infrastructure. Market entry strategies and pricing are adapted accordingly, with significant growth potential noted in these regions.
Financial Trajectory and Market Projections
1. Revenue Trends
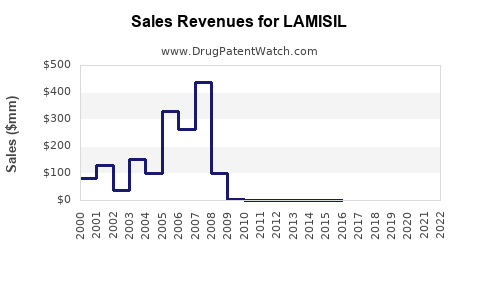
Post-2010, LAMISIL experienced peaks driven by strong sales in its branded form, peaking around USD 200 million annually in the U.S. (IQVIA, 2022). The patent expiration around 2014 led to a decline in branded sales, being displaced by generics, and subsequent stabilization at lower levels (~USD 80-100 million/year in the U.S. market).
Global sales, adjusted for regional variations and generic competition, are expected to flatten but remain significant due to ongoing demand in specific markets and indications.
2. Impact of Patent Expiry and Generics
The advent of generics has compressed profit margins but expanded access and volume. Projected revenue declines have been partly offset by new formulations and formulations for niche indications (e.g., pediatric use), which command premium pricing.
Future forecasts suggest a gradual decline in branded revenues, with steady sales from generics, barring new formulations or indications.
3. Future Growth Opportunities
Emerging trends such as longer-duration formulations, better patient adherence, and combination therapies could revive growth. Novel delivery systems like liposomal or nanoparticle formulations may command higher prices (MarketWatch, 2022).
Moreover, rising prevalence of fungal infections in diabetic and immunocompromised populations will sustain demand. Investment in clinical research exploring terbinafine's off-label applications, including onychomycosis in elderly populations, could further extend revenue streams.
4. Risks and Uncertainties
Market uncertainties include potential regulatory restrictions, adverse safety perceptions, and competition from newer agents with superior efficacy profiles. Additionally, geopolitical factors affecting supply chains and healthcare policies influence profitability.
Key Market Drivers and Challenges
| Market Drivers |
Market Challenges |
| Rising fungal infections prevalence |
Evolving regulatory environment |
| Cost-effectiveness of generics |
Competition from novel antifungal agents |
| Increasing adoption in emerging markets |
Safety warnings impacting physician prescribing behaviors |
| Development of advanced formulations |
Patent and exclusivity expirations |
| Growing awareness and diagnostic capabilities |
Price erosion from generic saturation |
Strategic Outlook
For pharmaceutical companies and investors, strategic considerations should include prioritizing pipeline innovation, exploring new formulations, and expanding into emerging markets. Augmenting regulatory strategies to extend patent protections or secure exclusivities can mitigate revenue erosion.
Partnerships and licensing agreements for combination therapies or novel delivery platforms could unlock additional value. Moreover, focusing on patient-centric formulations that enhance adherence may bolster market penetration.
Key Takeaways
- The LAMISIL market is characterized by mature dominance in developed regions, with a growing footprint in emerging markets.
- Patent expiry has shifted revenue streams toward generics, pressuring profit margins but expanding access.
- Innovation in formulations and indications remains critical to counteract generic competition and sustain growth.
- Safety concerns, regulatory changes, and competitive advances are key risks to monitor.
- Strategic positioning through pipeline development and geographic expansion can unlock future revenue potential.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How has patent expiration affected LAMISIL’s market share?
Patent expiration led to increased generic entry, reducing branded sales significantly and intensifying price competition. However, it also expanded market access due to lower prices, maintaining overall demand.
2. Are there new formulations of LAMISIL on the horizon?
Research into novel delivery systems, such as liposomal terbinafine or topical gels with improved pharmacokinetics, is ongoing to enhance efficacy and patient compliance.
3. What are the primary therapeutic competitors to LAMISIL?
Emerging topical antifungals like efinaconazole (Jublia) and tavaborole (Kerydin) serve as primary alternatives, especially for onychomycosis, often with shorter treatment durations.
4. How do safety considerations influence LAMISIL’s market?
While generally well-tolerated, rare reports of hepatotoxicity and drug interactions necessitate ongoing monitoring, which can influence prescribing behaviors and regulatory guidance.
5. What is the outlook for LAMISIL’s financial performance?
Revenue is expected to stabilize, with potential growth driven by new formulations, indications, and geographic expansion, counteracting declines from generic competition.
References
[1] MarketsandMarkets. "Antifungal Drugs Market by Type, Route of Administration, Distribution Channel, and Region – Global Forecast to 2030." 2022.
[2] IQVIA. "Pharmaceutical Market Data." 2022.
[3] FDA. "Drug Safety Communication: Hepatotoxicity concerns with topical and oral terbinafine." 2022.
[4] MarketWatch. "Emerging Trends in Antifungal Drug Delivery." 2022.