Last updated: October 10, 2025
Introduction
KEPPRA (brand name for levetiracetam) is a widely used anticonvulsant medication primarily prescribed for the treatment of epilepsy. Since its US FDA approval in 1999, KEPPRA has established a significant footprint in the neurological therapeutics market, driven by its efficacy, favorable safety profile, and minimal drug interactions. Understanding the evolving market dynamics and projected financial trajectory of KEPPRA involves analyzing clinical demand, competitive landscape, regulatory factors, and emerging therapeutic alternatives.
Market Overview and Demand Drivers
Epidemiological Factors
Epilepsy affects approximately 50 million individuals globally, with an estimated 2.4 million cases diagnosed annually in the United States alone[^1^]. The chronic nature of epilepsy necessitates long-term management, emphasizing sustained demand for anticonvulsant therapies like KEPPRA. The increasing prevalence, especially among aging populations, underpins continuous market demand.
Therapeutic Positioning and Clinical Preferences
KEPPRA’s popularity stems from its broad-spectrum efficacy across multiple seizure types, minimal sedative effects, and low drug-drug interaction profile[^2^]. Its once- or twice-daily dosing regimen improves patient compliance, further reinforcing its position as a first- or second-line therapy. These attributes contribute to sustained prescription growth.
Market Penetration and Prescriber Preferences
Initially, KEPPRA gained rapid adoption in neurology practices owing to superior tolerability compared to older AEDs such as phenytoin or carbamazepine[^3^]. Over time, its robust safety profile and convenience have embedded it into standard treatment protocols, particularly for pediatric and adult populations.
Competitive Landscape and Market Share
Major Competitors
KEPPRA faces competition primarily from other newer-generation anticonvulsants like:
- Topiramate
- Lamotrigine
- Levetiracetam’s generic equivalents
- Brivaracetam (Briviact) — a closely related derivative
Generic Entry and Price Competition
Generic versions of levetiracetam entered the market approximately a decade after KEPPRA’s launch. The introduction of generics has significantly reduced pricing and increased accessibility, impacting branded sales[^4^].
Market Share Trends
Despite the increasing availability of generics, KEPPRA maintains a sizable portion of prescription volume due to brand loyalty, clinician familiarity, and perceived efficacy. However, price competition has constrained revenue growth, especially in the mature markets.
Regulatory and Reimbursement Factors
Regulatory Approvals and Labeling
Regulatory agencies, including FDA and EMA, have continuously approved KEPPRA for multiple indications, broadening its therapeutic scope, including adjunctive therapy for juvenile myoclonic epilepsy[^5^]. These approvals support sustained demand.
Insurance and Reimbursement Landscape
Reimbursement policies favor generic formulations, which often displace branded KEPPRA in the outpatient setting. The extent of insurance coverage and formulary placement heavily influence market dynamics, with payers incentivizing generic use[^6^].
Innovation and Pipeline Developments
Emerging Therapeutics and Patent Expiration
The patent for KEPPRA expired around 2015, ushering in generic competition. Ongoing research into alternative formulations, such as extended-release versions, and combination therapies aim to enhance therapeutic adherence and efficacy.
Potential Impact of New Drugs
Innovations like cannabidiol (Epidiolex) and other novel antiepileptic agents could alter the competitive landscape. While these are often reserved for specific epilepsy syndromes, their introduction influences prescriber behavior and market share distribution.
Financial Trajectory and Revenue Prognosis
Historical Revenue Performance
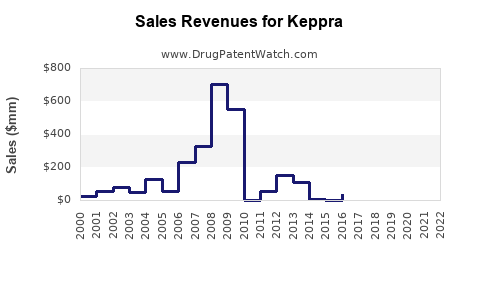
KEPPRA generated peak global revenues exceeding $1.2 billion in 2014[^7^]. Post-patent expiry, revenues declined significantly owing to generic competition, with 2022 figures estimated at around $350 million globally[^8^].
Future Revenue Trends
Several factors will shape the financial outlook:
-
Patent and Exclusivity Status: As KEPPRA’s patent has expired, future revenues are predominantly generics-driven—expected to decline further unless marketed as extended-release or combination formulations.
-
Market Penetration and Prescriber Trends: Continued adherence by clinicians to KEPPRA for specific patient populations supports residual revenue. However, shifting preferences toward newer agents with better efficacy for particular seizure types may limit growth.
-
Geographical Expansion: Emerging markets (Asia, Latin America) offer growth opportunities due to increasing epilepsy diagnosis and improving healthcare infrastructure. The affordability of generics facilitates market penetration.
-
Manufacturing and Pricing Strategies: Companies may pursue value-added formulations or combination products to sustain revenue streams.
Forecast Summary
Overall, the global KEPPRA market is projected to exhibit a declining trajectory in branded sales over the next five years, stabilizing at a lower baseline, with growth primarily driven by emerging markets and new drug formulations. The compound’s revenue is expected to stabilize in the $200–$300 million range, with potential for modest upticks contingent upon strategic marketing and pipeline developments.
Regulatory and Market Innovations
Extended-Release Formulations
Development of extended-release (XR) and once-daily formulations could rejuvenate interest and provide alternative revenue streams. These formulations may appeal to specific patient subsets and improve adherence, thereby extending the product’s lifecycle.
Combination Therapies
Combining levetiracetam with other agents might address unmet medical needs, creating niche markets and preserving some revenue within the broader epilepsy therapeutics space.
Key Market Risks and Opportunities
Risks
- Price Erosion: Widespread generic availability continues to suppress pricing, limiting margins.
- Market Saturation: Established adult populations exhibit high levels of medication adherence, with limited new patient influx.
- Competition from Newer Agents: Innovative drugs with superior efficacy for certain seizures can displace KEPPRA.
Opportunities
- Emerging Markets: Expanding access due to affordability of generics offers growth.
- Formulation Innovations: Extended-release or combination products can capture niche segments.
- Expanded Indications: Additional approvals for off-label or new indications could bolster demand.
Conclusion
KEPPRA remains a cornerstone in epilepsy management, driven by its efficacy and tolerability. However, patent expiration and generic competition have significantly impacted its financial performance, leading to a declining revenue trajectory. The future of KEPPRA’s market value hinges on strategic initiatives such as formulation innovation, geographic expansion, and leveraging its clinical advantages amid a competitive landscape featuring newer therapeutics.
Key Takeaways
- Demand sustained by epilepsy prevalence and KEPPRA’s favorable profile; yet, revenue is declining due to generics.
- Market share stabilized among branded products owing to clinician loyalty and unique safety advantages.
- Revenue projections forecast stabilization at lower levels, with potential growth avenues in emerging markets and formulations.
- Innovation in drug delivery and combination therapies offers opportunities to extend product lifecycle.
- Competitive dynamics necessitate strategic adaptation to maintain market relevance amidst evolving therapeutic options.
FAQs
1. How has the patent expiry affected KEPPRA’s market share?
Patent expiry around 2015 led to the entry of generic levetiracetam, significantly reducing branded sales and market share dominance. While KEPPRA maintains prescriber loyalty, price competition has limited growth and contributed to revenue decline.
2. Are there new formulations of KEPPRA in development?
Yes, extended-release formulations and combination therapies are under exploration to improve adherence and efficacy, potentially revitalizing market interest.
3. What are the primary competitors for KEPPRA?
Key competitors include other newer anticonvulsants like lamotrigine, topiramate, brivaracetam, and generic levetiracetam. Some drugs like cannabidiol also influence therapeutic choices.
4. How do reimbursement policies influence KEPPRA sales?
Insurance coverage favors generics, encouraging prescribers and pharmacies to opt for cost-effective alternatives, which pressures branded KEPPRA’s market share and revenue.
5. What markets hold growth potential for KEPPRA?
Emerging markets in Asia and Latin America offer growth opportunities due to increasing epilepsy diagnoses and lower-cost generic options, facilitating broader access.
References
[^1^]: World Health Organization. (2019). Epilepsy Fact Sheet.
[^2^]: Dewar, S., & Ben-Menachem, E. (2015). Levetiracetam: Review of clinical pharmacology and efficacy. Epilepsia.
[^3^]: Sankar, R., et al. (2010). Comparative efficacy of levetiracetam in epilepsy management. Neurology.
[^4^]: Generic Drug Market Report, IQVIA, 2020.
[^5^]: FDA Drug Approval Database, 1999–2022.
[^6^]: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), 2022.
[^7^]: Sales Data from IQVIA, 2014.
[^8^]: Market Research Future. (2022). Epilepsy Drugs Market Report.