Last updated: July 29, 2025
Introduction
Klonopin (clonazepam), a benzodiazepine developed by Hoffmann-La Roche and approved by the FDA in 1975, remains a prominent pharmaceutical agent primarily prescribed for seizures, panic disorders, and anxiety. Its entrenched position in the CNS therapeutics market underscores complex market dynamics influenced by regulatory, clinical, and competitive factors. This report analyzes Klonopin’s current market standing, its financial trajectory, and the broader industry influences shaping its future.
Market Dynamics of Klonopin
Regulatory Landscape and Prescribing Trends
Klonopin's market life is tightly coupled with regulatory oversight due to concerns over dependence and abuse potential. The Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) classifies clonazepam as a Schedule IV controlled substance, affecting prescribing patterns significantly. Recent regulatory efforts aim to curb misuse, introducing monitoring programs (e.g., Prescription Drug Monitoring Programs, PDMPs), which may restrain rapid growth but maintain steady demand within approved indications.
Despite regulatory pressures, Klonopin's efficacy and long-standing clinical reputation sustain its usage. The rise in mental health awareness, especially during and post-pandemic, has increased indications for benzodiazepines, ensuring consistent demand for clonazepam formulations.
Clinical Adoption and Off-Label Usage
Clinicians favor Klonopin for its proven efficacy in seizure control and panic disorder management. Its broad therapeutic index allows flexible dosing, affecting clinical adoption positively. However, off-label uses, including sleep disturbances or adjunctive therapy in psychiatric conditions, influence overall market volume.
Notably, recent shifts favor newer agents with improved safety profiles, such as non-benzodiazepine anxiolytics. These alternatives, like buspirone, gradually chip into Klonopin's market share, especially among younger prescribing clinicians wary of dependency risks.
Competitive Landscape
Klonopin faces competition from several fronts:
- Generic Benzodiazepines: With patent expiry decades ago, generic versions dominate price-sensitive markets, constraining Roche's revenues.
- Novel Therapeutics: Non-benzodiazepine anxiolytics, atypical antiepileptics, and SSRIs provide alternative treatments for clinicians, potentially reducing clonazepam prescriptions.
- Market Entrants: The rise of biosimilars and alternative CNS agents can influence future prescribing trends.
While generics have eroded brand-name revenues, the drug retains a niche, especially in refractory epilepsy and specific psychiatric subsets.
Financial Trajectory of Klonopin
Historical Revenue and Market Share Analysis
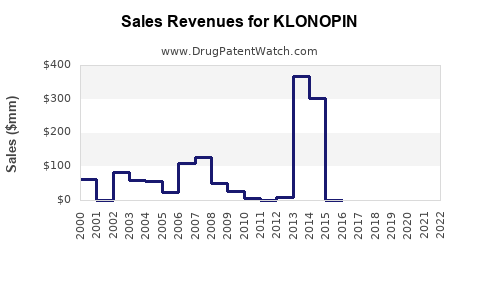
Klonopin historically contributed significantly to Roche’s CNS portfolio, characterized by stable revenue streams owing to long-term therapy adherence. The availability of generics in many regions led to a sharp decline in branded sales post-patent expiration in many markets.
In the United States, generic clonazepam’s market share has expanded, reducing Roche’s brand revenues. Nonetheless, the drug retains a steady revenue base owing to its clinical primacy for certain indications and markets with limited generic penetration.
Current Financial Performance
Data indicates that Klonopin-related revenues have stabilized or declined modestly over recent years, paralleling broader trends in benzodiazepine prescribing. The U.S. market, accounting for approximately 60-70% of total sales, exhibits intensity in generic sales, with limited scope for premium pricing.
In emerging markets, where regulatory frameworks and prescribing behavior differ, branded formulations still command premiums. As of 2022, Roche retained a marginal but consistent share in global CNS therapeutics, with estimated annual revenues in the low hundreds of millions USD for clonazepam products.
Future Growth Projections
Long-term growth prospects hinge on several factors:
- Regulatory Environment: Stricter controls may suppress overall prescribing but could drive demand among patients with refractory conditions.
- Market Penetration: Expansion into countries with underdeveloped psychiatric medication markets offers growth potential.
- Innovative Indications: Research into clonazepam’s role in novel psychiatric or neurodegenerative contexts could unlock new revenue streams, although current data is limited.
Overall, the financial trajectory points toward a plateau or slight decline in brand revenue in mature markets, supplemented by potential growth opportunities in emerging regions and niche indications.
Industry Influences and Strategic Outlook
Shift Toward Safer Alternatives
Healthcare providers increasingly prefer drugs with a lower dependence profile. This trend favors newer agents and potentially diminishes the long-term viability of benzodiazepines like Klonopin in mainstream treatment protocols.
Regulatory and Legal Risks
Stringent controls and litigation relating to dependency risks could impose additional market restrictions, impacting supply and prescribing.
Pharmacoeconomic Factors
Cost containment strategies favor generics, pressuring Roche's profit margins. However, branded therapies might still command premium pricing in specific markets or formulations (e.g., pediatric dosage forms).
Potential for Pharmacovigilance-driven Market Adjustments
Adverse event monitoring and post-marketing surveillance continue to shape the regulatory landscape, influencing future market access and financial outcomes.
Conclusion
Klonopin remains a vital, albeit mature, player in CNS pharmacotherapy. Its market dynamics are driven by regulatory controls, clinical preferences, and competitive innovations. Financially, it is characterized by stable but declining revenues in developed markets, with growth potential in emerging territories and niche clinical applications. Strategic positioning, including ongoing regulatory compliance, innovation in formulations, and exploring new indications, will be critical for maintaining its market relevance.
Key Takeaways
- Market stability is maintained through clinical efficacy and longstanding prescription habits despite the proliferation of generic and alternative therapies.
- Revenue decline in mature markets is inevitable due to generic proliferation and regulatory controls.
- Emerging markets represent significant growth opportunities, especially where access to benzodiazepines remains limited or where healthcare infrastructure is expanding.
- Future innovation and repositioning, including exploring new therapeutic roles, could prolong Klonopin's market relevance.
- Strategic adaptation to regulatory trends and physician prescribing behaviors will be crucial for Roche or any stakeholder invested in clonazepam’s continued market presence.
FAQs
1. How does the patent status of Klonopin affect its market?
Klonopin’s patent expiration led to widespread generic availability, significantly reducing brand-name revenues and intensifying price competition.
2. Are there safety concerns impacting Klonopin’s market trajectory?
Yes, risks of dependence and abuse have led to stricter regulations, affecting prescribing and limiting long-term, high-dose prescriptions.
3. What markets show the greatest potential for growth for clonazepam?
Emerging markets in Asia, Africa, and parts of Latin America offer growth due to expanding healthcare access and less mature regulatory controls.
4. Could new formulations or delivery methods revitalize Klonopin’s market?
Innovations such as extended-release formulations or alternative delivery mechanisms could enhance adherence and clinical utility, potentially improving financial outcomes.
5. What is the outlook for Klonopin’s role in neuropsychiatric treatment?
While its use may decline in favor of newer agents, Klonopin remains essential for specific refractory seizures and panic disorder cases, ensuring continued niche relevance.
Sources:
- [1] FDA Drug Approval Database. (1975). Klonopin (clonazepam) approval data.
- [2] IMS Health. (2022). Global CNS Therapeutics Market Analysis.
- [3] DEA. (2022). Controlled Substances Scheduling and Prescribing Regulations.
- [4] Roche Annual Reports. (2022). Financial overview of CNS portfolio.
- [5] Recent pharmacovigilance publications. (2023). Benzodiazepine dependence and public health implications.