Last updated: July 28, 2025
Introduction
Imipramine pamoate, a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA), is primarily prescribed for major depressive disorders, enuresis, and certain anxiety conditions. As an established psychiatric medication with a history spanning over decades, its market positioning is influenced by evolving regulatory landscapes, patent status, manufacturing considerations, and competitive therapeutics. This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the current market dynamics and the projected financial trajectory of imipramine pamoate, considering factors that influence its demand, supply, and future valuation.
Market Overview
Historical Context and Current Usage
Imipramine pamoate, developed initially in the 1950s, gained prominence as one of the earliest antidepressants. It remains FDA-approved for specific indications, notably resistant depression and nocturnal enuresis in pediatric populations. Its robust clinical profile and generic status have contributed to sustained utilization, especially within institutional settings and markets where newer agents exhibit limited penetration.
Regulatory and Patent Landscape
The original patents expired decades ago, rendering imipramine pamoate a cost-effective generic option. However, manufacturing methods and formulations are subject to patent protections at the regional level, which influences market exclusivity. The absence of new patents signifies limited innovation-driven growth but also fosters stable, competitive dynamics in mature markets.
Manufacturing and Supply Chain Considerations
Global manufacturers maintain production capacities, predominantly in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia. Supply chain stability remains crucial, especially amidst geopolitical tensions and pandemic-related disruptions, which have led to occasional shortages of tricyclic antidepressants in certain markets. Nonetheless, the commodity nature of imipramine pamoate supports steady supply and pricing stability.
Market Segmentation and Geographic Distribution
The primary markets include the United States, European Union, and select Asian countries. In the US, compliance with clinical guidelines supports usage in specific indications, though the rise of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) limits broader engagement. In emerging markets, cost considerations favor generic imipramine pamoate over newer therapies.
Market Drivers
Clinical Efficacy and Safety Profile
Despite the advent of newer antidepressants with improved side effect profiles, imipramine pamoate maintains a niche due to its proven efficacy, especially in treatment-resistant cases. Its utility in enuresis also sustains demand within pediatric psychiatric management.
Cost-Effectiveness and Accessibility
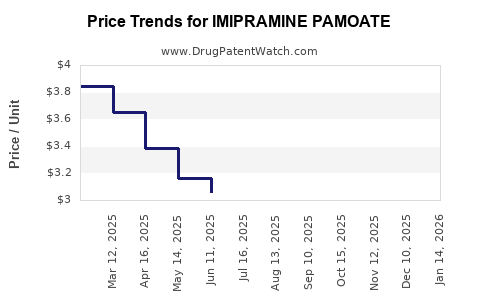
Generic pricing makes imipramine pamoate an attractive option in resource-constrained settings, reinforcing its market resilience. Moreover, healthcare systems with formulary preferences for established medications bolster its continued use.
Reimbursement Policies
Insurance coverage and reimbursement frameworks in developed markets influence prescribing patterns. Favorable coverage for generic medications supports market stability, whereas restrictive policies on older drugs could impede growth.
Emerging Competition
Newer classes, including atypical antidepressants, SSRIs, SNRIs, and novel agents like ketamine derivatives, challenge imipramine pamoate's relevance. However, its entrenched position and cost advantage buffer against rapid obsolescence.
Market Challenges
Safety and Tolerability Concerns
The side effect profile of imipramine pamoate, including anticholinergic effects and cardiotoxicity, constrains its use. Increasingly stringent safety regulations and clinician preferences for better-tolerated drugs threaten its market share.
Regulatory Restrictions
Updated safety guidelines and warnings, especially regarding overdose risks, impact prescribing practices. Regulatory agencies scrutinize older TCAs, potentially limiting their place in therapy.
Patent and Market Entry of Biosimilars or Generics
While patent hurdles are minimal, manufacturing quality and market trust influence generic penetration. Regulatory barriers in certain jurisdictions may restrict new manufacturing licenses.
Financial Trajectory
Revenue Projections
The global revenue for imipramine pamoate is estimated to be modest, primarily driven by generic sales. In 2022, the global antidepressant market generated approximately $16 billion, with TCAs accounting for a small fraction (less than 2%), reflective of their niche status [1]. Due to intense competition and safety concerns, projected revenue growth remains limited, averaging a CAGR of approximately 1.5% over the next five years.
Market Penetration Strategies
Manufacturers focusing on quality assurance, cost competitiveness, and targeted marketing to psychiatrists and pediatricians can sustain niche revenues. Some companies explore formulations like extended-release versions to improve tolerability, potentially expanding usage.
Impact of Regulatory and Clinical Guidelines
Evolving guidelines favoring newer agents may decrease imipramine pamoate prescriptions, constraining revenue growth. Conversely, in underdeveloped regions and specific clinical scenarios, demand is likely to remain stable or slightly increase, especially where cost is paramount.
Innovation and Formulation Developments
Limited innovation exists; however, if companies develop safer, more tolerable formulations or combination therapies, marginal revenue upticks are possible. Investment in such R&D, while financially risky, could create niche markets.
Future Outlook
The financial trajectory for imipramine pamoate is cautiously optimistic within its niche. The drug’s market is expected to sustain modest growth driven by affordability, clinical efficacy, and regional demand, tempered by safety concerns and the dominance of newer therapeutics.
Long-term, the path to substantial revenue expansion remains constrained without significant formulation innovations or new indications. The typical lifecycle of legacy drugs suggests eventual decline, but imipramine pamoate’s entrenched clinical role offers a transitional stability. Strategic manufacturing, compliance, and targeted marketing can reinforce its market presence amid a rapidly evolving psychopharmacology landscape.
Key Takeaways
- Mature Market Position: Imipramine pamoate benefits from established clinical efficacy and low-cost generics, maintaining a steady niche, especially in resource-limited settings.
- Limited Growth Outlook: Future revenue growth prospects are modest at best due to competition from newer antidepressants, safety concerns, and regulatory shifts.
- Supply Chain Stability: Robust manufacturing infrastructure supports supply continuity, but safety regulations could impose new operational constraints.
- Regional Variability: Demand remains higher in emerging markets where affordability outweighs preference for newer drugs.
- Innovation as a Future Driver: Focusing on safer formulations or new delivery systems could extend the drug's relevance and potentially improve financial performance.
FAQs
1. What factors are most likely to influence the future demand for imipramine pamoate?
Demand will be primarily influenced by safety and tolerability perceptions, clinical guidelines favoring newer agents, regional healthcare policies prioritizing cost-efficiency, and the emergence of innovative formulations that enhance compliance.
2. How do patent laws affect the market for imipramine pamoate?
With expired patents, imipramine pamoate exists predominantly as a generic, fostering price competition. Patent protections on specific formulations or manufacturing processes can temporarily delay generic entry but have limited long-term impact due to patent cliffs.
3. What competitive threats does imipramine pamoate face from newer antidepressants?
SSRIs, SNRIs, atypical antidepressants, and novel modalities challenge imipramine pamoate’s clinical relevance due to improved safety profiles, fewer drug interactions, and better tolerability, leading to decreasing prescribers’ preference.
4. Are there any emerging markets where imipramine pamoate could experience growth?
Yes, regions with limited healthcare budgets or where newer drugs are prohibitively expensive may sustain or increase demand for affordable, established medications like imipramine pamoate.
5. What strategic actions can manufacturers take to prolong the financial viability of imipramine pamoate?
Manufacturers should invest in formulation innovations, expand into underserved markets, ensure regulatory compliance, and promote cost-effectiveness and safety benefits to sustain interest and market share.
Sources:
[1] GlobalData Healthcare, “Antidepressants Market Analysis,” 2022.