IDHIFA Drug Patent Profile
✉ Email this page to a colleague
When do Idhifa patents expire, and when can generic versions of Idhifa launch?
Idhifa is a drug marketed by Bristol Myers Squibb and is included in one NDA. There are six patents protecting this drug.
This drug has one hundred and fourteen patent family members in forty countries.
The generic ingredient in IDHIFA is enasidenib mesylate. One supplier is listed for this compound. Additional details are available on the enasidenib mesylate profile page.
DrugPatentWatch® Generic Entry Outlook for Idhifa
Idhifa was eligible for patent challenges on August 1, 2021.
By analyzing the patents and regulatory protections it appears that the earliest date
for generic entry will be September 16, 2034. This may change due to patent challenges or generic licensing.
Indicators of Generic Entry
AI Deep Research
Questions you can ask:
- What is the 5 year forecast for IDHIFA?
- What are the global sales for IDHIFA?
- What is Average Wholesale Price for IDHIFA?
Summary for IDHIFA
| International Patents: | 114 |
| US Patents: | 6 |
| Applicants: | 1 |
| NDAs: | 1 |
| Finished Product Suppliers / Packagers: | 1 |
| Raw Ingredient (Bulk) Api Vendors: | 66 |
| Clinical Trials: | 12 |
| Patent Applications: | 860 |
| Drug Prices: | Drug price information for IDHIFA |
| Patent Litigation and PTAB cases: | See patent lawsuits and PTAB cases for IDHIFA |
| What excipients (inactive ingredients) are in IDHIFA? | IDHIFA excipients list |
| DailyMed Link: | IDHIFA at DailyMed |
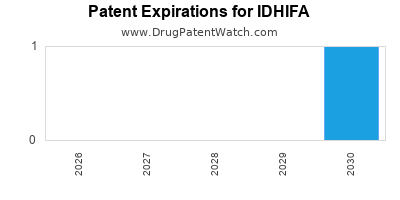

DrugPatentWatch® Estimated Loss of Exclusivity (LOE) Date for IDHIFA
Generic Entry Date for IDHIFA*:
Constraining patent/regulatory exclusivity:
NDA:
Dosage:
TABLET;ORAL |
*The generic entry opportunity date is the latter of the last compound-claiming patent and the last regulatory exclusivity protection. Many factors can influence early or later generic entry. This date is provided as a rough estimate of generic entry potential and should not be used as an independent source.
Recent Clinical Trials for IDHIFA
Identify potential brand extensions & 505(b)(2) entrants
| Sponsor | Phase |
|---|---|
| University of Chicago | Phase 1 |
| AbbVie | Phase 1/Phase 2 |
| University Health Network, Toronto | Phase 1/Phase 2 |
Pharmacology for IDHIFA
| Drug Class | Isocitrate Dehydrogenase 2 Inhibitor |
| Mechanism of Action | Isocitrate Dehydrogenase 2 Inhibitors |
US Patents and Regulatory Information for IDHIFA
IDHIFA is protected by six US patents.
Based on analysis by DrugPatentWatch, the earliest date for a generic version of IDHIFA is ⤷ Get Started Free.
This potential generic entry date is based on patent 9,732,062.
Generics may enter earlier, or later, based on new patent filings, patent extensions, patent invalidation, early generic licensing, generic entry preferences, and other factors.
| Applicant | Tradename | Generic Name | Dosage | NDA | Approval Date | TE | Type | RLD | RS | Patent No. | Patent Expiration | Product | Substance | Delist Req. | Exclusivity Expiration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bristol Myers Squibb | IDHIFA | enasidenib mesylate | TABLET;ORAL | 209606-001 | Aug 1, 2017 | RX | Yes | No | 9,512,107 | ⤷ Get Started Free | Y | Y | ⤷ Get Started Free | ||
| Bristol Myers Squibb | IDHIFA | enasidenib mesylate | TABLET;ORAL | 209606-002 | Aug 1, 2017 | RX | Yes | Yes | 9,512,107 | ⤷ Get Started Free | Y | Y | ⤷ Get Started Free | ||
| Bristol Myers Squibb | IDHIFA | enasidenib mesylate | TABLET;ORAL | 209606-001 | Aug 1, 2017 | RX | Yes | No | 10,610,125 | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | ||||
| Bristol Myers Squibb | IDHIFA | enasidenib mesylate | TABLET;ORAL | 209606-002 | Aug 1, 2017 | RX | Yes | Yes | 9,738,625 | ⤷ Get Started Free | Y | ⤷ Get Started Free | |||
| >Applicant | >Tradename | >Generic Name | >Dosage | >NDA | >Approval Date | >TE | >Type | >RLD | >RS | >Patent No. | >Patent Expiration | >Product | >Substance | >Delist Req. | >Exclusivity Expiration |
International Patents for IDHIFA
When does loss-of-exclusivity occur for IDHIFA?
Based on analysis by DrugPatentWatch, the following patents block generic entry in the countries listed below:
Argentina
Patent: 0411
Patent: COMPUESTOS TERAPEUTICAMENTE ACTIVOS Y SUS METODOS DE USO
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Australia
Patent: 13207289
Patent: Therapeutically active compounds and their methods of use
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 17265096
Patent: THERAPEUTICALLY ACTIVE COMPOUNDS AND THEIR METHODS OF USE
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Brazil
Patent: 2014016805
Patent: compostos terapeuticamente ativos e seus métodos de uso
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Canada
Patent: 60623
Patent: COMPOSES THERAPEUTIQUEMENT ACTIFS ET LEURS PROCEDES D'UTILISATION (THERAPEUTICALLY ACTIVE COMPOUNDS AND THEIR METHODS OF USE)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Chile
Patent: 14001793
Patent: Compuestos derivados de 1,3,5-triazinas sustituidas y sus sales, como inhibidores de la idh2 mutante; composicion farmaceutica que los comprende; y su uso para el tratamiento del cancer.
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
China
Patent: 4114543
Patent: Therapeutically active compounds and their methods of use
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 7417667
Patent: 治疗活性化合物及其使用方法 (Therapeutically active compounds and their methods of use)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 8912066
Patent: 治疗活性化合物及其使用方法 (THERAPEUTICALLY ACTIVE COMPOUNDS AND THEIR METHODS OF USE)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 4933585
Patent: 治疗活性化合物及其使用方法 (Therapeutically active compounds and methods of use thereof)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 5521264
Patent: 治疗活性化合物及其使用方法 (Therapeutically active compounds and methods of use thereof)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 5536635
Patent: 治疗活性化合物及其使用方法 (Therapeutically active compounds and methods of use thereof)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Colombia
Patent: 30962
Patent: Compuestos terapéuticamente activos y sus métodos de uso
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Costa Rica
Patent: 140377
Patent: COMPUESTOS TERAPÉUTICAMENTE ACTIVOS Y SUS MÉTODOS DE USO
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Croatia
Patent: 0180844
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Cyprus
Patent: 20506
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Denmark
Patent: 00743
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Ecuador
Patent: 14012726
Patent: COMPUESTOS TERAPÉUTICAMENTE ACTIVOS Y SUS MÉTODOS DE USO
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Eurasian Patent Organization
Patent: 0187
Patent: ТЕРАПЕВТИЧЕСКИ АКТИВНЫЕ СОЕДИНЕНИЯ И СПОСОБЫ ИХ ИСПОЛЬЗОВАНИЯ (THERAPEUTICALLY ACTIVE COMPOUNDS AND METHODS OF USE THEREOF)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 1491330
Patent: ТЕРАПЕВТИЧЕСКИ АКТИВНЫЕ СОЕДИНЕНИЯ И СПОСОБЫ ИХ ИСПОЛЬЗОВАНИЯ
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
European Patent Office
Patent: 00743
Patent: COMPOSÉS THÉRAPEUTIQUEMENT ACTIFS ET LEURS PROCÉDÉS D'UTILISATION (THERAPEUTICALLY ACTIVE COMPOUNDS AND THEIR METHODS OF USE)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 06608
Patent: COMPOSÉS THÉRAPEUTIQUEMENT ACTIFS ET LEURS PROCÉDÉS D'UTILISATION (THERAPEUTICALLY ACTIVE COMPOUNDS AND THEIR METHODS OF USE)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 84997
Patent: COMPOSÉS THÉRAPEUTIQUEMENT ACTIFS ET LEURS PROCÉDÉS D'UTILISATION (THERAPEUTICALLY ACTIVE COMPOUNDS AND THEIR METHODS OF USE)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Hong Kong
Patent: 03942
Patent: 治療活性化合物及其使用方法 (THERAPEUTICALLY ACTIVE COMPOUNDS AND THEIR METHODS OF USE)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Hungary
Patent: 38403
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Israel
Patent: 3503
Patent: מדכאי איזוציטראט דהידרוגנאז, תכשירים המכילים אותם ושימושים בהם (Isocitrate dehydrogenase inhibitors, compositions comprising same and uses thereof)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Japan
Patent: 09081
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 11895
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 15503571
Patent: 治療活性化合物およびその使用方法
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 17075193
Patent: 治療活性化合物およびその使用方法 (THERAPEUTICALLY ACTIVE COMPOSITIONS AND THEIR METHODS OF USE)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Lithuania
Patent: 00743
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Malaysia
Patent: 5206
Patent: THERAPEUTICALLY ACTIVE COMPOUNDS AND THEIR METHODS OF USE
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Mexico
Patent: 8940
Patent: COMPUESTOS TERAPÉUTICAMENTE ACTIVOS Y SUS MÉTODOS DE USO. (THERAPEUTICALLY ACTIVE COMPOUNDS AND THEIR METHODS OF USE.)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 14008350
Patent: COMPUESTOS TERAPEUTICAMENTE ACTIVOS Y SUS METODOS DE USO. (THERAPEUTICALLY ACTIVE COMPOUNDS AND THEIR METHODS OF USE.)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
New Zealand
Patent: 7096
Patent: Triazinyl compounds and their methods of use
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 2582
Patent: Methods of preparing 2-methyl-1-[(4-[6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-yl]-6-{ [2-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-4-yl]amino} -1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)amino]propan-2-ol
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Nicaragua
Patent: 1400073
Patent: COMPUESTOS TERAPÉUTICAMENTE ACTIVOS Y SUS MÉTODO
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Norway
Patent: 97546
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Peru
Patent: 142098
Patent: COMPUESTOS TERAPEUTICAMENTE ACTIVOS Y SUS METODOS DE USO
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Philippines
Patent: 014501561
Patent: THERAPEUTICALLY ACTIVE COMPOUNDS AND THEIR METHODS OF USE
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Poland
Patent: 00743
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Portugal
Patent: 00743
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Serbia
Patent: 401
Patent: TERAPEUTSKI AKTIVNA JEDINJENJA I POSTUPCI ZA NJIHOVU UPOTREBU (THERAPEUTICALLY ACTIVE COMPOUNDS AND THEIR METHODS OF USE)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Singapore
Patent: 201602862R
Patent: Therapeutically Active Compounds And Their Methods Of Use
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 201403878Q
Patent: THERAPEUTICALLY ACTIVE COMPOUNDS AND THEIR METHODS OF USE
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Slovenia
Patent: 00743
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
South Africa
Patent: 1405163
Patent: THERAPEUTICALLY ACTIVE COMPOUNDS AND THEIR METHODS OF USE
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
South Korea
Patent: 1893112
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 140113712
Patent: THERAPEUTICALLY ACTIVE COMPOUNDS AND THEIR METHODS OF USE
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Spain
Patent: 75760
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 01430
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Taiwan
Patent: 53228
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 1329054
Patent: Therapeutically active compounds and their methods of use
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Turkey
Patent: 1809228
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Ukraine
Patent: 7451
Patent: ТЕРАПЕВТИЧНО АКТИВНІ СПОЛУКИ І СПОСОБИ ЇХ ЗАСТОСУВАННЯ (THERAPEUTICALLY ACTIVE COMPOUNDS AND THEIR METHODS OF USE)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Generics may enter earlier, or later, based on new patent filings, patent extensions, patent invalidation, early generic licensing, generic entry preferences, and other factors.
See the table below for additional patents covering IDHIFA around the world.
| Country | Patent Number | Title | Estimated Expiration |
|---|---|---|---|
| European Patent Office | 3932408 | COMPOSÉS THÉRAPEUTIQUEMENT ACTIFS ET LEURS MÉTHODES D'UTILISATION (THERAPEUTICALLY ACTIVE COMPOUNDS AND THEIR METHODS OF USE) | ⤷ Get Started Free |
| European Patent Office | 3406608 | COMPOSÉS THÉRAPEUTIQUEMENT ACTIFS ET LEURS PROCÉDÉS D'UTILISATION (THERAPEUTICALLY ACTIVE COMPOUNDS AND THEIR METHODS OF USE) | ⤷ Get Started Free |
| Taiwan | 201932455 | Therapeutically active compounds and their methods of use | ⤷ Get Started Free |
| Croatia | P20180844 | ⤷ Get Started Free | |
| >Country | >Patent Number | >Title | >Estimated Expiration |
Market Dynamics and Financial Trajectory for IDHIFA (Enasidenib)
More… ↓
Make Better Decisions: Try a trial or see plans & pricing
Drugs may be covered by multiple patents or regulatory protections. All trademarks and applicant names are the property of their respective owners or licensors. Although great care is taken in the proper and correct provision of this service, thinkBiotech LLC does not accept any responsibility for possible consequences of errors or omissions in the provided data. The data presented herein is for information purposes only. There is no warranty that the data contained herein is error free. We do not provide individual investment advice. This service is not registered with any financial regulatory agency. The information we publish is educational only and based on our opinions plus our models. By using DrugPatentWatch you acknowledge that we do not provide personalized recommendations or advice. thinkBiotech performs no independent verification of facts as provided by public sources nor are attempts made to provide legal or investing advice. Any reliance on data provided herein is done solely at the discretion of the user. Users of this service are advised to seek professional advice and independent confirmation before considering acting on any of the provided information. thinkBiotech LLC reserves the right to amend, extend or withdraw any part or all of the offered service without notice.
