Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Glipizide, a second-generation sulfonylurea, has been a cornerstone in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) for decades. As an oral hypoglycemic agent, it stimulates insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells, thereby reducing blood glucose levels. Despite the advent of newer drug classes, glipizide remains significant in global diabetes treatment paradigms due to its efficacy, cost-effectiveness, and extensive clinical history. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of the current market dynamics and financial trajectory of glipizide, emphasizing factors influencing its demand, competitive landscape, regulatory environment, and future outlook.
Market Overview
Globally, the burden of T2DM has surged, with the International Diabetes Federation estimating approximately 537 million adults living with diabetes in 2021—a figure projected to reach 783 million by 2045[1]. This escalating prevalence sustains the demand for affordable antidiabetic medications such as glipizide.
Historically, glipizide's popularity stems from its low cost, proven efficacy, and availability across various markets. It is widely incorporated into treatment guidelines, especially in resource-constrained settings. Notably, in countries like India, where a significant portion of the population relies on cost-effective medications, glipizide maintains a substantial market share.
Market Dynamics
Driving Factors
1. Prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity Trends
Rising T2DM prevalence directly translates into increased demand for oral hypoglycemics. According to the CDC, nearly 90% of adult diabetes cases are T2DM, and lifestyle factors such as sedentary habits and obesity accelerate disease incidence. As a result, the market for agents like glipizide remains buoyant, especially in areas with limited access to advanced therapies.
2. Cost-Effectiveness and Affordability
Generics dominate the glipizide market, significantly reducing manufacturing and distribution costs. This affordability positions it as a primary treatment option in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), where healthcare budgets are constrained. Market penetration in these regions underpins its steady demand.
3. Established Clinical Track Record
Decades of clinical use have built clinician confidence in glipizide’s safety and efficacy. Its inclusion in numerous national guidelines reinforces its role as a first-line agent, maintaining its relevance in the therapeutic landscape.
4. Regulatory Approvals and Expanded Indications
While primarily indicated for T2DM, ongoing research into glipizide’s pharmacodynamics minimizes regulatory barriers for ongoing use. Still, newer formulations or combination products continue to be evaluated, potentially expanding its application.
Restraining Factors
1. Safety Concerns and Side Effect Profile
Hypoglycemia risk is a notable adverse effect, particularly in elderly patients or those with renal impairment. Such safety concerns prompt clinicians to consider alternative agents, especially newer drugs with better safety profiles.
2. Competition from Novel Drug Classes
The past decade has seen the rise of newer oral agents—DPP-4 inhibitors, SGLT2 inhibitors, and GLP-1 receptor agonists—that offer better cardiovascular and renal profiles. While more expensive, these drugs are gradually encroaching on glipizide’s market share, especially in markets prioritizing safety and long-term outcomes.
3. Strict Regulatory Guidelines
Stringent regulatory scrutiny concerning hypoglycemia risk and cardiovascular safety evaluations has led some countries to favor newer drugs, reducing glipizide’s use.
Market Segmentation and Geography
Regional Market Dynamics
-
North America & Europe: Predominantly containment of glipizide use to traditional, cost-sensitive segments. The trend is shifting away in favor of newer drugs owing to safety and efficacy concerns.
-
Asia-Pacific: The dominant market for glipizide, driven by high diabetes prevalence, large patient populations, and cost-sensitive healthcare systems.
-
Latin America and Africa: Growing markets where affordability remains paramount. Generics, including glipizide, continue to be widely prescribed.
Market Player Landscape
Major pharmaceutical firms, such as Sanofi and Mylan, manufacture generic glipizide. These players benefit from established supply chains, extensive distribution networks, and patent expirations that facilitate affordable pricing strategies.
Financial Trajectory and Revenue Trends
Historical Performance
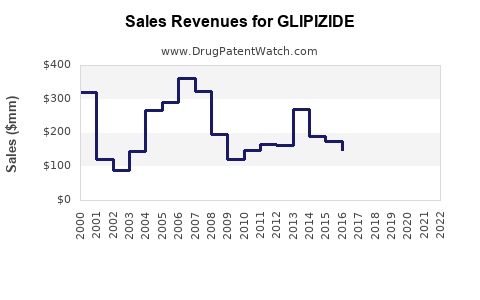
The global glipizide market experienced steady growth through the 2000s, aligning with the global diabetes boom[2]. However, its revenue trajectory plateaued in the late 2010s as sales shifted toward newer agents and formulations.
Current Revenue Analysis
While precise global sales figures are proprietary, estimates suggest that generic glipizide maintains a multi-billion-dollar market globally, primarily driven by LMICs. For instance, India’s robust generic sector sustains a significant portion of glipizide consumption, with an estimated regional market size exceeding US$200 million annually[3].
Future Financial Outlook
Projected growth is modest but stable, primarily fueled by:
- Ongoing diabetes prevalence increases, especially in emerging markets.
- Continued acceptance in low-income settings due to affordability.
- Potential formulation innovations (combination pills, extended-release versions) that could enhance adherence and market appeal.
However, the influx of newer, cost-effective alternatives and potential regulatory hurdles may cap long-term revenue growth. The expiration of patents for branded versions could further intensify price competition, pressuring profit margins.
Regulatory Considerations
In recent years, safety Data from cardiovascular outcome trials (CVOTs) have influenced the regulatory landscape. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European Medicines Agency (EMA) emphasize post-marketing surveillance, especially given hypoglycemia concerns. Regulatory bodies may impose stringent labeling or usage recommendations, affecting market dynamics.
In developing markets, regulatory adaptations focus on ensuring the availability of affordable generics, with minimal restrictions to maintain accessibility.
Competitive Landscape
While glipizide faces competition from newer drug classes, it retains a unique position as an economical, long-established therapy. Its major competitors include:
- Oral agents: Metformin (first-line), glimepiride, and other sulfonylureas.
- Newer agents: DPP-4 inhibitors (sitagliptin), SGLT2 inhibitors (empagliflozin), and GLP-1 receptor agonists.
The choice among these depends on patient-specific factors, safety considerations, and healthcare resource availability.
Future Outlook
Innovation and Formulation Development
Research focuses on modified-release formulations of glipizide to improve adherence and reduce hypoglycemia risk. Combination therapies with metformin or other agents may enhance efficacy, creating niche markets.
Market Evolution
In markets prioritizing safety and resistant to increased healthcare costs, glipizide’s role may diminish, supplanted by newer agents with superior profiles. Nevertheless, in cost-sensitive regions, its market remains resilient.
Impact of Healthcare Policy and Digital Health
Government initiatives promoting affordable diabetes management, including drug price regulation and generic medication promotion, will sustain glipizide’s market. Telemedicine and improved diabetes screening can increase early diagnosis, consequently maintaining demand.
Key Takeaways
- Stable Demand in Emerging Markets: Due to affordability and high diabetes prevalence, glipizide continues to command steady sales, especially in LMICs.
- Competitive Threats from Newer Agents: Advances in safety and efficacy profiles of newer drugs challenge glipizide’s market dominance in developed regions.
- Regulatory and Safety Factors: Hypoglycemia risk and cardiovascular safety concerns influence prescribing practices and regulatory policies.
- Patent Expiry and Price Competition: The expiration of patents leads to increased generic competition, driving down prices and profit margins.
- Innovation Opportunities: Development of extended-release formulations and combination therapies could prolong market relevance.
FAQs
1. Is glipizide still a preferred treatment for T2DM worldwide?
Glipizide remains a preferred choice in resource-limited settings due to its cost-effectiveness and proven efficacy. However, in developed countries, newer medications with better safety profiles are increasingly favored.
2. What are the primary safety concerns associated with glipizide?
The predominant safety concern is hypoglycemia, especially in elderly patients or those with renal impairment. Weight gain and cardiovascular risks are also considerations, monitored through ongoing research.
3. How does patent expiration influence glipizide’s market?
Patent expirations enable multiple manufacturers to produce generic versions, increasing supply and reducing prices. This subsidizes continued accessibility, particularly in LMICs, but also intensifies market competition.
4. Are there ongoing innovations related to glipizide?
Yes, research focuses on extended-release formulations and fixed-dose combination therapies aimed at improving adherence and safety.
5. What is the future of glipizide in the evolving diabetes treatment landscape?
While its role in high-income countries may decline, it will likely remain pivotal in low-income regions due to affordability. Its future depends on formulation innovations, regulatory policies, and the evolving standard of care emphasizing safety.
References
[1] International Diabetes Federation. "IDF Diabetes Atlas, 9th Edition," 2021.
[2] Market Research Future. "Global Glipizide Market Research Report," 2022.
[3] Indian Pharmaceutical Market Overview, 2021. Directorate General of Drugs & Pharmacy, India.