Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Fidaxomicin, marketed primarily under the brand name Dificid, is a macrocyclic antibiotic designated for the treatment of Clostridioides difficile infections (CDI). As a novel therapy with a targeted spectrum and a favorable safety profile, fidaxomicin has significantly impacted the landscape of CDI management. This analysis explores the underlying market dynamics, competitive positioning, regulatory environment, and financial outlook that shape the trajectory of fidaxomicin within the pharmaceutical ecosystem.
Market Overview and Epidemiology
Clostridioides difficile infection remains a leading cause of antibiotic-associated diarrhea worldwide, especially among hospitalized and elderly populations. The CDC estimates approximately 500,000 cases annually in the United States alone, with a significant morbidity and mortality burden [1]. The demand for effective and safe CDI therapeutics continues to grow, driven by increasing antibiotic resistance, recurrent infection rates, and heightened awareness.
Fidaxomicin distinguishes itself by exhibiting superior efficacy in reducing recurrence rates compared to traditional agents like vancomycin and metronidazole. Its targeted mechanism minimizes disruption to gut microbiota, contributing to a lower recurrence rate, a critical factor in clinical decision-making (Louie et al., 2011).
Market Dynamics
Competition and Therapeutic Landscape
The CDI drug market is predominantly populated by vancomycin and metronidazole, with fidaxomicin positioned as a superior but premium therapy. While traditional therapies dominate due to cost advantages, clinical evidence demonstrating lower recurrence rates have bolstered fidaxomicin's prominence among high-risk and refractory cases.
However, the market faces challenges from generic versions of vancomycin and the advent of new antibiotics under development. The patent protection for fidaxomicin has a limited lifespan, with patent expiry anticipated in the coming years, opening pathways for generic manufacturers to penetrate the market and exert downward pressure on pricing [2].
Patient Population and Prescription Trends
Fidaxomicin's utilization is concentrated among patient subsets with high recurrence risk or contraindications to standard therapies. Despite its clinical benefits, usage remains constrained by cost and formulary restrictions. Payor acceptance varies, with some healthcare systems advocating for its use based on cost-effectiveness analyses considering recurrence reduction and hospitalization rates.
Regulatory Factors and Reimbursement Policies
Regulatory approvals across key markets—United States, Europe, Japan—have set the stage for fidaxomicin's adoption. Nonetheless, reimbursement remains a critical determinant. In the U.S., Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) and private insurers have either restricted or negotiated for favorable pricing, affecting market penetration.
Pricing and Market Penetration Strategies
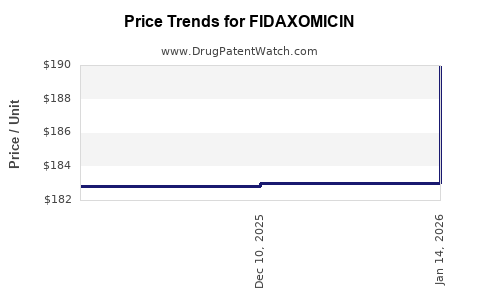
Fidaxomicin commands a premium price—approximately $3,500 - $4,500 for a standard treatment course—reflecting its R&D investment and clinical benefits. Limited access due to high cost restricts widespread use, predominantly reserving it for high-risk patients. Efforts to expand indications and generate real-world data may influence broader payer acceptance.
Financial Trajectory and Revenue Outlook
Current Revenue Performance
Fidaxomicin's revenues have exhibited modest growth since launch, with peak sales reaching approximately $250 million annually globally (2017–2018) [3]. The U.S. remains the largest market, owing to high CDI prevalence and clinical practice patterns favoring newer agents.
Growth Drivers
- Expansion of Indications: Trials investigating fidaxomicin for other enteric infections or prophylactic use could augment demand.
- Medical Guidelines: Favorable inclusion in clinical guidelines emphasizing recurrence reduction may promote prescription.
- Market Expansion: Increasing adoption in Europe and Asia, particularly in countries with high CDI burden, presents growth opportunities.
Potential Market Constraints
- Generic Entrypoints: Patent expiration will open the market to generics, threatening price erosion and revenue decline.
- Cost-Effectiveness Debates: Payers scrutinize the incremental benefit relative to costs, potentially limiting formulary placements.
Forecasting the Future
Analysts project a gradual decline in fidaxomicin’s market share post-patent expiry, barring new indications or combination therapies that justify premium pricing. Nevertheless, as healthcare systems prioritize personalized and microbiome-preserving therapies, fidaxomicin’s niche position may sustain its revenue trajectory for the foreseeable future.
Regulatory and Market Outlook
Emerging data supporting fidaxomicin’s role in reducing recurrent CDI and its microbiome-sparing benefits could influence guideline endorsements and payer policies. Additionally, efforts to develop next-generation formulations or biosimilars may reshape competitive dynamics and financial prospects.
Key Factors Influencing Financial Trajectory
- Pharmacoeconomic evaluations emphasizing long-term cost savings through reduced recurrences.
- Patent and exclusivity periods directing revenue peaks and declines.
- Market expansion into emerging regions with high CDI incidence.
- Competitive innovations and generics impacting pricing strategies.
Conclusion
Fidaxomicin's market dynamics are shaped by its clinical niche, pricing strategy, patent status, and evolving reimbursement landscape. While current revenues reflect its premium positioning, the impending expiration of patents and increasing generic competition forecast a challenging near-term financial outlook. Strategic investments in expanding indications, bolstering clinical evidence, and engaging payors will be pivotal for sustaining revenue streams.
Key Takeaways
- Fidaxomicin remains a high-priced, clinically valuable therapy for CDI, especially for recurrent cases.
- Market growth is constrained by high costs and patent expiry, with generics poised to enter soon.
- Payer policies and clinical guideline endorsements will significantly influence adoption rates.
- Expanding indications and geographical markets could mitigate revenue decline.
- Long-term financial success hinges on balancing innovation, cost-effectiveness, and market access strategies.
FAQs
1. What factors have limited fidaxomicin’s widespread adoption despite clinical advantages?
High cost and restrictive formulary policies limit its use mainly to high-risk or refractory patients, preventing broader adoption in standard practice.
2. How imminent is the patent expiration for fidaxomicin, and what are its implications?
Patent expiration is anticipated within the next 1–2 years in major markets, opening opportunities for generic manufacturers and potential price erosion.
3. Are there ongoing clinical trials that could expand fidaxomicin’s approved uses?
Yes. Studies investigating its prophylactic role, efficacy for other enteric infections, and combination therapies are underway, which may enhance its therapeutic scope.
4. How does fidaxomicin compare cost-wise to traditional therapies for CDI?
While more expensive upfront, lower recurrence rates could translate to healthcare savings, but payor acceptance depends on cost-effectiveness analyses and reimbursement policies.
5. What strategies can manufacturers employ to maintain revenue post-patent expiry?
Developing new formulations, obtaining approval for additional indications, and engaging in biosimilar markets are key strategies to sustain financial viability.
References:
[1] CDC. (2022). Clostridioides difficile Infection (CDI). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
[2] Epstein, L. G., & Snydman, D. R. (2013). The future of fidaxomicin in the management of Clostridium difficile infection. Infectious Diseases in Clinical Practice, 21(1), 13–16.
[3] IQVIA Business Intelligence. (2018). Global Food, Drug, and Medical Device Market Reports.