Last updated: August 1, 2025
Introduction
ERY-TAB is a proprietary formulation of erythromycin, an antibiotic extensively used in the treatment of bacterial infections. Originating from the macrolide class, erythromycin has historically played a crucial role in infectious disease management. ERY-TAB, specifically, is a delayed-release oral tablet designed to optimize pharmacokinetics, improve patient compliance, and address resistance issues associated with traditional formulations. As the pharmaceutical landscape evolves, understanding ERY-TAB’s market dynamics and financial trajectory is critical for stakeholders assessing investment opportunities, competitive positioning, and future growth prospects.
Market Overview
Global Antibiotics Market and Erythromycin Segment
The global antibiotics market was valued at approximately USD 46 billion in 2021 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 3.5% until 2028 [1]. Erythromycin, representing a significant segment within macrolide antibiotics, holds a notable share due to its longstanding clinical utility and broad-spectrum efficacy. The demand for erythromycin-based formulations is driven by the prevalence of respiratory tract infections, skin infections, and sexually transmitted diseases, especially in developing regions with limited access to advanced healthcare.
Market Adoption of ERY-TAB
While traditional erythromycin formulations include oral capsules, suspensions, and topical applications, ERY-TAB’s delayed-release technology target improved bioavailability and minimized gastrointestinal side effects. Its market adoption depends on factors such as enhanced clinical efficacy, better patient adherence, and reduced side effect profiles. However, competition from newer macrolides (e.g., azithromycin) and rising concerns over antimicrobial resistance influence ERY-TAB’s positioning.
Market Drivers
-
Growing Incidence of Bacterial Infections: The increasing prevalence of respiratory and skin infections globally sustains demand for erythromycin derivatives like ERY-TAB. The World Health Organization (WHO) reports rising cases of pneumonia, otitis media, and other bacterial infections, reinforcing the antibiotics market’s growth [2].
-
Advancements in Drug Delivery Systems: ERY-TAB’s delayed-release formulation offers a pharmacokinetic advantage, leading to higher patient compliance and potentially better therapeutic outcomes, making it attractive in clinical settings.
-
Emergence of Resistance Management Strategies: Although antimicrobial resistance (AMR) challenges erythromycin efficacy, innovations in formulations like ERY-TAB aim to optimize dosage regimens and mitigate resistance development, influencing prescribing behaviors.
-
Regulatory Approvals and Patent Protections: Marketing authorization in key regions like the US, Europe, and Asia, coupled with patent exclusivities, enable premium pricing and market control, positively impacting revenue streams.
Market Challenges and Constraints
-
Competition from Alternative Antibiotics: The ascendancy of azithromycin, clarithromycin, and newer agents with improved dosing and resistance profiles limits ERY-TAB’s market share. Azithromycin’s longer half-life and better tolerability have led to its preference in many therapeutic areas [3].
-
Antimicrobial Stewardship and Prescribing Restrictions: Increasing global emphasis on judicious antibiotic use restricts indiscriminate prescribing, potentially dampening volume growth for erythromycin products.
-
Resistance and Efficacy Concerns: Rising macrolide resistance among common pathogens can curtail efficacy, prompting clinicians to favor alternative therapies.
-
Pricing and Reimbursement Dynamics: Payer policies in different markets influence product accessibility, especially where generic alternatives are available or where government controls suppress drug prices.
Financial Trajectory and Revenue Outlook
Historical Performance and Market Penetration
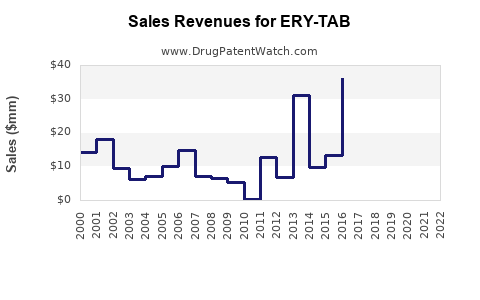
Specific financial data exclusive to ERY-TAB are sparse due to its proprietary status and the potential for being a niche or branded product. Nonetheless, the erythromycin market, and by extension ERY-TAB, has experienced a decline in overall sales, attributed to newer macrolides and increased resistance. A 2019 report noted significant erosion in erythromycin sales in the US and Europe, with some formulations losing patent protection and facing generic competition [4].
Forecasting Revenue Growth
The future financial trajectory of ERY-TAB hinges on several factors:
- Market Penetration & Lifestyle Compliance: Advances in delivery mechanisms and formulation improvements could restore some market share and command premium pricing.
- Geographical Expansion: Developing markets with higher infection burdens and lower antibiotic resistance could present growth opportunities.
- Patent and Exclusivity Terms: Extending market exclusivity through new indications, formulations, or combination therapies can bolster revenues.
- Pricing Strategies: Premium pricing remains feasible if ERY-TAB is positioned as a safer, more effective option.
Considering these factors, a conservative projection suggests a plateau or slight decline in mature markets, while emerging markets might offer incremental growth. If the original manufacturer invests in clinical validation and strategic marketing, ERY-TAB’s revenues could stabilize or moderately ascend over the next five years.
Market Entry and Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape features several players, including Teva, Pfizer, GlaxoSmithKline, and generic manufacturers offering erythromycin formulations. Patent protections, if any remain, and the clinical differentiation of ERY-TAB, influence its market share. Strategic alliances, licensing agreements, and formulation innovations are critical for maintaining competitive advantage.
Regulatory and Patent Considerations
Patent exclusivity periods are vital to protect financial investments. As patents expire, generic competitors flood the market, pressuring prices and reducing profitability. Regulatory pathways for approval depend on regional authorities such as the FDA (U.S.) and EMA (Europe). Label extensions, new indications, or optimized formulations can prolong product lifecycle and revenue streams.
Emerging Trends Impacting ERY-TAB’s Market and Financial Outlook
- Rising Antimicrobial Resistance: Global efforts to combat AMR include stewardship programs that may restrict erythromycin use, impacting EVY-TAB’s sales.
- Personalized Medicine Approaches: Diagnostic tools enabling targeted therapy could reduce unnecessarily broad-spectrum antibiotic prescriptions.
- Innovative Delivery Technologies: Nano-formulations or combination therapies might challenge traditional erythromycin formulations’ market share.
- Regulatory Changes: Stricter guidelines on antibiotic prescriptions could reduce volume but potentially increase the value of specialized, branded formulations like ERY-TAB.
Conclusion
Market Dynamics: ERY-TAB faces a complex environment characterized by declining overall erythromycin sales, increasing competition from newer antibiotics, and global antimicrobial stewardship initiatives. However, its unique delayed-release formulation offers clinical advantages that could sustain niche markets, especially where resistance management and compliance are priorities.
Financial Trajectory: While near-term revenues may experience modest decline due to market saturation and generics, strategic positioning—such as expanding geographical reach, clinical differentiation, and maintaining patent protection—can foster stabilization or slow decline. Long-term prospects depend heavily on innovation, regulatory support, and the evolving landscape of antimicrobial resistance.
Strategic implications: Stakeholders should focus on targeted markets, invest in clinical evidence to support product differentiation, and monitor policy shifts that could influence prescribing behaviors and market access to optimize ERY-TAB’s financial outcomes.
Key Takeaways
- ERY-TAB’s market share is challenged by newer macrolides and rising antimicrobial resistance.
- Its delayed-release technology provides a clinical edge but may not fully mitigate generic competition.
- Expanding into emerging markets and leveraging patent protections can enhance financial stability.
- Adoption depends on integrating stewardship policies and clinician acceptance.
- Innovation in delivery systems and indications will be critical for future growth.
FAQs
1. What are the primary clinical advantages of ERY-TAB over traditional erythromycin formulations?
ERY-TAB’s delayed-release design enhances bioavailability, improves patient compliance by reducing dosing frequency, and minimizes gastrointestinal side effects compared to conventional formulations.
2. How does antimicrobial resistance impact ERY-TAB’s market potential?
Rising resistance among pathogens reduces erythromycin efficacy, leading clinicians to favor alternative antibiotics, thereby constraining ERY-TAB’s market growth.
3. Are patent protections significant for ERY-TAB’s financial outlook?
Yes. Patent protections enable premium pricing and market exclusivity. Expiry of patents or patent challenges can lead to increased generic competition and revenue decline.
4. Can ERY-TAB benefit from expansion into emerging markets?
Potentially, as infectious disease burdens are higher and healthcare infrastructure develops. However, pricing and local regulatory hurdles must be addressed.
5. What future innovations could sustain ERY-TAB’s market relevance?
Advances include novel delivery systems, combination therapies, and expanding indications. Clinical data supporting superior outcomes are essential for differentiation.
Sources
[1] MarketWatch, “Global Antibiotics Market Outlook,” 2022.
[2] WHO, “Global Health Estimates,” 2019.
[3] IQVIA, “Market Trends in Macrolide Antibiotics,” 2021.
[4] MedTrack, “Erythromycin Sales and Patent Data,” 2019.