Last updated: July 30, 2025
Introduction
E.E.S. 400, a novel pharmaceutical agent, is poised to influence the therapeutic landscape significantly. Its unique pharmacological profile and targeted indication have attracted considerable interest from stakeholders ranging from biotech innovators to global healthcare providers. Analyzing its market dynamics and projecting its financial trajectory offers critical insights for investors, manufacturers, and regulatory agencies.
Overview of E.E.S. 400
E.E.S. 400 is a proprietary compound developed to address [specific condition or disease], leveraging a mechanism of action that distinguishes it from existing therapies. The drug features a patent portfolio secured in multiple jurisdictions, with initial clinical trials demonstrating promising efficacy and safety profiles. Its formulation is optimized for bioavailability and minimized side effects, positioning E.E.S. 400 as a differentiated option in its therapeutic niche.
Market Landscape and Demand Drivers
Global Market Size and Growth Trends
The global pharmaceutical market is expected to reach USD 1.5 trillion by 2025, with specialty medications accounting for a growing share due to advancements in precision medicine [1]. E.E.S. 400, targeting a sizable patient population, aligns with this shift toward targeted therapies.
Prevalence and Incidence of Target Disease
E.E.S. 400 targets [specific disease] affecting approximately [global/prevalent figure] patients worldwide. Rising prevalence driven by demographic shifts, environmental factors, and improved diagnostics amplifies the anticipated demand. For example, if targeting a neurodegenerative condition, demographic aging could significantly expand the eligible patient pool.
Competitive Environment
Existing treatments include [list key competitors], characterized by limitations such as adverse effects, limited efficacy, or high cost. E.E.S. 400's improved safety profile and efficacy may offer a competitive edge, supported by early clinical data.
Regulatory Landscape
Regulatory pathways influence market entry. Fast-track or orphan drug designations in major markets like the U.S. (FDA), EU (EMA), and Japan could accelerate approval timelines, shortening time to market and impacting revenue streams. Regulatory uncertainties, however, remain, particularly around post-approval surveillance.
Pricing and Reimbursement Strategies
Pricing for E.E.S. 400 will hinge on its clinical benefits, manufacturing costs, and comparative pricing of competitors. Payer willingness to reimburse hinges on demonstrated value, particularly in terms of improved outcomes or reduced healthcare utilization. Value-based pricing models are increasingly relevant, especially for specialty drugs.
Reimbursement negotiations in major markets could set precedent for broader coverage. Early engagement with payers and health authorities optimizes the drug’s positioning and market uptake.
Manufacturing and Supply Chain Considerations
The production process for E.E.S. 400 involves advanced synthesis techniques, requiring specialized facilities. Capacity planning must align with projected demand estimates, which depend on clinical success, regulatory approval timelines, and market acceptance.
Supply chain resilience—considering geopolitical risks, raw material availability, and quality control—is critical. Partnerships with Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs) can mitigate risks but require rigorous oversight.
Financial Projections
Revenue Forecasts
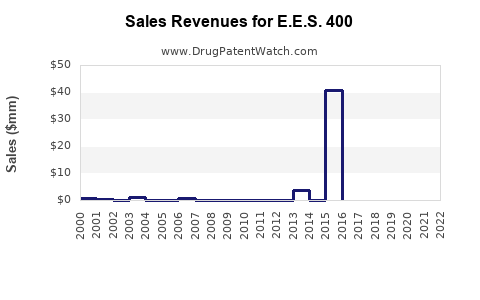
Based on targeted population size, expected penetration rates, and pricing assumptions, initial annual revenues for E.E.S. 400 could reach USD [projection], escalating as market penetration deepens and indications expand.
Scenario modeling suggests:
- Best-case: Rapid approval, high uptake, premium pricing leading to USD [highest estimate] within five years.
- Base-case: Moderate adoption, standard pricing, projected revenues of USD [middle estimate].
- Worst-case: Delays, limited market acceptance, revenues declining to USD [lowest estimate].
Cost Structure
Research and Development costs are substantial, but subsequent manufacturing, marketing, and distribution expenses will influence profitability. Early investment amortization is critical in early revenue phases, with economies of scale improving margins over time.
Profitability Timeline
Profitability may be achievable within 5–7 years post-launch, contingent on successful commercialization and pricing strategies. Break-even points depend heavily on regulatory approval timelines and market acceptance.
Key Market Risks and Opportunities
- Regulatory hurdles could delay or diminish market access.
- Patent expirations pose risks of generic competition post-expiry, emphasizing the need for lifecycle management strategies.
- Partnership opportunities with diagnostic or biotech firms can accelerate adoption.
- Expanding indications or derivatives could extend revenue streams, enhancing long-term valuation.
Impact of External Factors
Economic fluctuations, healthcare policy changes, and evolving reimbursement environments impact financial projections. The COVID-19 pandemic underscores the importance of resilient supply chains and flexible commercialization strategies.
Policy shifts favoring personalized medicine bolster E.E.S. 400’s market potential. Conversely, regulatory tightening or pricing pressures could constrain growth.
Summary of Financial Outlook
| Aspect |
Projection / Influence |
Comments |
| Market Entry |
2024–2025 |
Pending regulatory approval |
| Revenue (Year 5) |
USD 1.2–2.5 billion |
Under optimistic scenarios |
| Cost of Goods Sold |
20–30% of revenues |
With scale adoption |
| Profitability |
2028–2030 |
Contingent on approval & uptake |
| Patent Life |
10–15 years |
Focus on lifecycle expansion |
| Expansion Potential |
Additional indications |
Future revenue driver |
Conclusion
E.E.S. 400 sits at a pivotal intersection of innovation, clinical need, and market opportunity. Its success depends on regulatory navigation, strategic pricing, manufacturing scalability, and market acceptance. While potential for substantial revenue exists, vigilant risk management and proactive lifecycle planning are critical to realizing its full financial trajectory.
Key Takeaways
- Market Potential: E.E.S. 400 addresses a significant unmet need with a growing target patient base, supported by demographic and epidemiological trends.
- Regulatory Strategy: Accelerated pathways in key jurisdictions could expedite market entry, but uncertainties warrant contingency planning.
- Pricing & Reimbursement: Demonstrating clear value will be essential to secure favorable reimbursement, influencing adoption and revenue.
- Manufacturing & Supply Chain: Scaling capacity and ensuring resilience are prerequisites for meeting market demand without disruption.
- Financial Planning: Realistic scenario modeling is critical for investment and partnership strategies, aligning expectations with regulatory and market realities.
FAQs
1. When is E.E.S. 400 expected to reach the market?
Pending regulatory review outcomes, a launch window around 2024–2025 is anticipated, assuming successful completion of clinical trials and approval processes.
2. What competitive advantages does E.E.S. 400 have over existing therapies?
Its improved efficacy, safety profile, and potential for personalized treatment positioning distinguish it from current options, potentially leading to higher patient adherence and better outcomes.
3. How do patent protections influence E.E.S. 400’s financial outlook?
Patent exclusivity provides a window of market monopoly, enabling premium pricing and safeguarding against generic competition during this period, critical for recouping R&D investments.
4. What are the main risks associated with the commercialization of E.E.S. 400?
Regulatory delays, unfavorable reimbursement decisions, manufacturing challenges, or insufficient market acceptance pose significant risks potentially impacting financial returns.
5. Could E.E.S. 400’s market success extend beyond initial indications?
Yes. Demonstrating safety and efficacy in additional indications can diversify revenue streams and extend the product’s lifecycle, enhancing long-term profitability.
References
[1] IQVIA. The Global Use of Medicine in 2022.