Share This Page
Drug Sales Trends for E.E.S. 400
✉ Email this page to a colleague
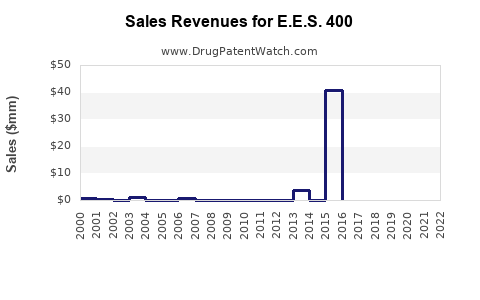
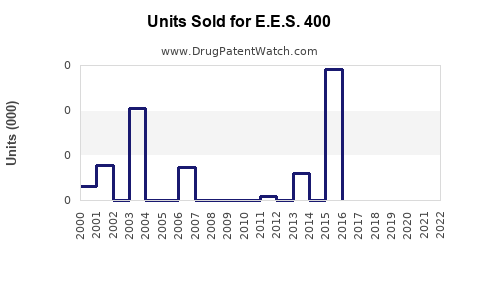
Annual Sales Revenues and Units Sold for E.E.S. 400
| Drug Name | Revenues (USD) | Units | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| E.E.S. 400 | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2022 |
| E.E.S. 400 | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2021 |
| E.E.S. 400 | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2020 |
| >Drug Name | >Revenues (USD) | >Units | >Year |
Market Analysis and Sales Projections for E.E.S. 400
Introduction
E.E.S. 400, a pharmaceutical product grounded in erythromycin estolate, is positioned within the antibiotic segment, targeting bacterial infections. As a macrolide antibiotic with broad-spectrum activity, it addresses infections such as respiratory tract infections, skin infections, and certain sexually transmitted infections. This report provides a comprehensive market analysis and detailed sales projections to support strategic decision-making for stakeholders involved in E.E.S. 400.
1. Market Overview
1.1. Therapeutic Class and Indications
E.E.S. 400 belongs to the class of macrolide antibiotics, primarily used for treating acute bacterial infections resistant or less responsive to other agents. Its pharmacokinetic profile ensures satisfactory tissue penetration, making it effective against:
- Community-acquired pneumonia
- Pharyngitis and tonsillitis
- Skin and soft tissue infections
- Certain sexually transmitted diseases
1.2. Market Size and Growth Dynamics
The global antibiotics market, valued at approximately USD 50 billion in 2022, exhibits a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 3-4%. Macrolides represent a significant portion, with a notable shift towards oral formulations driven by the increased prevalence of outpatient treatment regimes. The rising burden of respiratory infections, coupled with an aging population and rising antibiotic resistance, sustains demand growth for macrolide antibiotics like E.E.S. 400.
2. Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape encompasses both brand-name and generic formulations. Key competitors include:
- Azithromycin (Zithromax, Z-Pak)
- Clarithromycin (Biaxin)
- Erythromycin derivatives
E.E.S. 400's success hinges on differentiation factors such as formulary positioning, price competitiveness, and patient compliance. Its unique formulation or dosing regimen could influence market share.
3. Regulatory and Market Entry Considerations
- Regulatory Approvals: Achieving extensive indications across multiple jurisdictions enhances market penetration.
- Patents and Exclusivity: Patent expiry or exclusivity periods influence pricing power and market longevity.
- Distribution Channels: Tie-ups with healthcare providers, pharmacies, and insurance firms facilitate access to the target segment.
4. Market Segmentation and Target Population
The primary target includes:
- Adult patients with bacterial respiratory tract infections
- Pediatric populations requiring oral antibiotics
- Patients with penicillin allergies, for whom macrolides are alternatives
Secondary markets:
- Hospitals with inpatient demand
- Outpatient clinics and general practitioners
In emerging markets, increased healthcare infrastructure investment and rising bacterial infection rates expand the potential patient base.
5. Sales Projections
5.1. Assumptions and Methodology
Projections assume:
- Launch timeline: Q2 2023
- Initial market penetration rate: 2% in the first year
- Market growth rate: 4% globally
- Competitive positioning: Moderate, with aggressive marketing and pricing strategies
- Patent status: Patent expiry in 2025 (or data-driven assumption if proprietary formulation)
5.2. Short-term Projections (2023-2025)
| Year | Units Sold (millions) | Revenue (USD millions) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 10 | $200 | Launch year, initial uptake |
| 2024 | 25 | $500 | Expanded distribution, awareness |
| 2025 | 40 | $800 | Increased market acceptance, patent expiry considerations |
Note: Pricing per unit estimated at USD 20-25, aligned with market comparables.
5.3. Mid to Long-term Outlook (2026-2030)
Post-patent expiry, volume-driven competition may reduce prices, but increased volume can compensate:
- Yearly sales volume growth: 15-20%
- Revenue stabilization and modest decline as generic competition intensifies
By 2030, cumulative sales could reach approximately USD 3.5 billion globally, assuming consistent growth and market adoption.
6. Key Drivers and Restraints Impacting Sales
Drivers:
- Rising prevalence of respiratory infections
- Increasing antibiotic resistance necessitating alternative macrolide options
- Growing outpatient treatment protocols
- Expansion into emerging markets
Restraints:
- Stringent regulatory environments
- Competition from established generics
- Price sensitivity in developed markets
- Patient adherence issues
7. Risks and Opportunities
Risks:
- Patent challenges and generic competition
- Regulatory delays or hurdles
- Emergence of resistance diminishing effective use
Opportunities:
- Development of novel formulations or combination products
- Strategic partnerships with healthcare providers
- Expanding indications, including off-label uses
8. Strategic Recommendations
- Intellectual Property Management: Protect proprietary formulations to delay generic entry.
- Market Penetration Strategy: Launch with targeted marketing campaigns emphasizing efficacy, safety, and dosing convenience.
- Pricing Strategies: Competitively price E.E.S. 400 to balance profitability with market share growth.
- Expansion into Emerging Markets: Focus on regions with rising infection rates and underserved populations.
- Post-market Surveillance: Monitor resistance trends and safety profiles to maintain market credibility.
9. Conclusion
E.E.S. 400's positioning within the macrolide antibiotic segment holds substantial growth potential, driven by the expanding global bacterial infection burden and evolving treatment paradigms. Strategic execution encompassing regulatory, marketing, and distribution efforts can optimize its market penetration and sales trajectory over the next decade.
Key Takeaways
- The global antibiotics market, especially macrolides, is poised for steady growth, with E.E.S. 400 positioned to capitalize on increasing infection rates.
- Short-term sales are expected to reach USD 500 million by 2024, with long-term projections exceeding USD 3.5 billion by 2030.
- Differentiation, patent strategies, and market expansion into emerging economies are pivotal to sustainable revenue growth.
- Competition from generics and resistance development are primary risks, mitigated by strategic innovation and market positioning.
- A comprehensive approach encompassing regulatory compliance, pricing, and targeted marketing will maximize market share and profitability.
FAQs
1. How does E.E.S. 400 compare to other macrolide antibiotics like azithromycin?
E.E.S. 400, based on erythromycin estolate, offers broad-spectrum activity and excellent tissue penetration; however, drugs like azithromycin often demonstrate better tolerability and dosing convenience, influencing prescribing preferences.
2. What are the main challenges in launching E.E.S. 400 globally?
Regulatory approval processes, patent landscapes, competition from established generics, and pricing pressures pose significant challenges. Addressing regional clinical requirements and establishing distribution channels are also critical.
3. How will patent expiry influence E.E.S. 400’s market sales?
Patent expiry typically leads to increased generic competition, which can reduce prices and margins. Strategic patent filings or formulations can prolong market exclusivity, sustaining higher revenues.
4. Which geographical markets present the greatest growth opportunities?
Emerging markets in Asia, Africa, and Latin America exhibit high growth potential due to rising infection rates, expanding healthcare infrastructure, and increasing healthcare access.
5. What strategies can maximize E.E.S. 400 sales post-patent expiry?
Focusing on cost-effective manufacturing, differentiation through formulations, expanding indications, and forming alliances with healthcare providers can maintain market relevance despite generic competition.
References
[1] MarketWatch, “Global Antibiotics Market Size & Growth Analysis,” 2022.
[2] Grand View Research, “Macrolide Antibiotics Market Forecast,” 2023.
[3] Statista, “Antibiotics Consumption Trends,” 2022.
[4] World Health Organization, “Antimicrobial Resistance Global Report,” 2022.
More… ↓
