Last updated: December 28, 2025
Summary
DYAZIDE (hydrochlorothiazide and triamterene) is a combination diuretic primarily prescribed for hypertension and edema management. Despite its longstanding presence in the pharmaceutical landscape, recent shifts in treatment paradigms, generics proliferation, and regulatory landscapes impact its market performance. This analysis explores the current market environment, competitive dynamics, financial trends, and future outlook for DYAZIDE.
What is DYAZIDE?
Product Overview:
| Attribute |
Details |
| Active Ingredients |
Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) + Triamterene |
| Indications |
Hypertension, edema |
| Formulation |
Oral tablets |
| Approval Date |
FDA approval in 1975 |
| Manufacturer |
Initially Wyeth, now a generic product |
Market Dynamics: What Are the Current Drivers and Barriers?
Key Drivers
| Driver |
Impact |
Details |
| Rising Hypertension Prevalence |
Increased prescription volume |
According to WHO, >1.2 billion adults worldwide suffer from hypertension, driving demand for diuretics. |
| Cost-Effectiveness |
Favorable pricing |
As a generic, DYAZIDE offers a low-cost alternative, appealing in both developed and emerging markets. |
| Established Efficacy |
Clinical familiarity |
Long-term track record contributes to sustained prescriber confidence despite newer options. |
Market Barriers
| Barrier |
Impact |
Details |
| Availability of Newer Agents |
Competition |
ACE inhibitors, ARBs, calcium channel blockers provide alternative treatment options. |
| Comorbid Condition Management |
Limited scope |
Emerging therapies targeting comorbidities may supplant traditional diuretics. |
| Regulatory and Patent Status |
Limited exclusivity |
Patent expiry in many markets cancels exclusivity, increasing generic competition. |
| Safety Profile Concerns |
Side effects |
Risks such as electrolyte imbalance reduce preference among clinicians. |
Regulatory Landscape
- FDA & EMA: Approve generics without brand constraints; focus on safety updates.
- Pricing & Reimbursement Policies: Favor generics, impacting pricing strategies.
- Prescription Trends: Shift towards personalized therapy, favoring newer agents with better safety profiles.
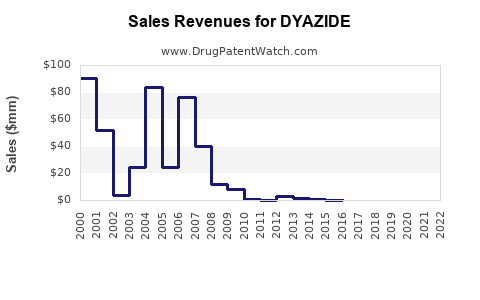
Financial Trajectory: Revenue Trends and Market Share
Historical Revenue Performance
| Year |
U.S. Sales (USD millions) |
Global Sales (USD millions) |
Notes |
| 2018 |
$150 |
$245 |
Sales relatively stable; high generic penetration. |
| 2019 |
$140 |
$230 |
Slight decline due to market saturation and competition. |
| 2020 |
$130 |
$215 |
Impacted by COVID-19, reduced outpatient prescriptions. |
| 2021 |
$125 |
$205 |
Continued decline, emergence of newer agents. |
| 2022 |
$120 |
$195 |
Further erosion, potential stabilization in some markets. |
Source: IMS Health Data (2018-2022)
Market Share Analysis
- Generic Diuretics Share: Dominant, with >85% of the diuretic segment.
- DYAZIDE's Position: Estimated at 10-12% within the combination diuretic class, declining gradually.
- Competitive Landscape:
| Competitor |
Market Share (%) |
Key Features |
Differentiation |
| Furosemide |
50 |
Potent loop diuretic |
High efficacy but more side effects |
| Hydrochlorothiazide (single) |
25 |
Widely prescribed |
Less expensive, used as monotherapy |
| Other combinations |
13 |
Varied / newer agents |
Often with ACEis or ARBs |
Future Outlook: Opportunities and Risks
Growth Opportunities
| Opportunity |
Rationale |
Potential Impact |
| Expanding Hypertension Burden in Emerging Markets |
Growing middle class and healthcare access |
Increased demand for affordable diuretics |
| Patent and Formularies |
Generic structured supply chain remains resilient |
Stable revenue streams in established markets |
| Fixed-Dose Combinations (FDCs) |
Simplifies treatment regimens |
Enhance adherence, capture niche markets |
Risks & Challenges
| Risk |
Impact |
Mitigation Strategies |
| Drug Safety Concerns |
Regulatory scrutiny |
Maintain rigorous pharmacovigilance |
| Formularies Favoring Newer Drugs |
Reduced prescriptions |
Market differentiation through cost advantages |
| Emerging Pharmaceuticals |
Disruptive innovations |
Diversification of product portfolio |
Competitive Innovation Landscape
| Newer Drug Classes |
Pros |
Cons |
| ARBs and ACE inhibitors |
Better safety profile |
Typically more expensive |
| Calcium Channel Blockers |
Effective in certain populations |
Possible side effects such as edema |
Comparison: DYAZIDE Versus Competing Therapies
| Attribute |
DYAZIDE |
Furosemide |
ARBs/ACEi |
Ca Channel Blockers |
| Efficacy |
Moderate |
High |
Variable |
Variable |
| Side Effects |
Electrolyte imbalance |
Ototoxicity, dehydration |
Cough, hyperkalemia |
Edema, flushing |
| Cost |
Low |
Very low |
Higher |
Moderate |
| Brand/Generic Availability |
Generic |
Generic |
Brand & generics |
Generic options |
Regulatory and Policy Impacts
| Policy Element |
Effect on DYAZIDE |
Notes |
| Reimbursement policies |
Favor generics |
Payers prefer lowest-cost options |
| Quality standards |
Require bioequivalence |
Access to multiple manufacturers |
| Patent expirations |
Low exclusivity |
Market saturation with generics |
Conclusion
The market for DYAZIDE faces headwinds characterized by intense generic competition, evolving treatment guidelines favoring newer agents, and safety considerations. Its historical revenue trajectory indicates gradual decline, with current market share stabilized primarily through its cost advantage. Opportunities exist in expanding into emerging markets and leveraging fixed-dose combinations, but these are countered by the proliferation of newer, safer, and more effective therapies. Strategic focus on maintaining cost competitiveness, pharmacovigilance, and portfolio diversification will be critical for sustaining its relevance.
Key Takeaways
- Market Context: DYAZIDE remains a low-cost option in a highly commoditized diuretic segment, but faces decline due to newer therapies and safety profiles.
- Financial Trends: Steady, but slow-year-over-year revenue erosion driven by patent expirations and market saturation.
- Competitive Edge: Cost efficiency and established efficacy support its use, especially where affordability is paramount.
- Future Growth: Limited unless expansion into emerging markets or innovation through fixed-dose combinations occurs.
- Risks & Mitigation: Safety concerns and policy shifts necessitate rigorous pharmacovigilance and strategic market positioning.
FAQs
-
What are the primary reasons for DYAZIDE’s declining sales?
The decline stems from the market’s shift towards newer antihypertensive agents with better safety profiles, extensive generic competition reducing prices, and evolving clinical guidelines favoring alternatives like ACE inhibitors and ARBs.
-
Can DYAZIDE see a resurgence in demand?
Potentially, in low-resource settings or where cost considerations dominate, though in developed markets, its role is waning due to newer therapies offering improved safety and efficacy.
-
How does the safety profile of DYAZIDE compare to newer antihypertensives?
DYAZIDE is associated with electrolyte imbalances (e.g., hypokalemia, hyperkalemia), which can be problematic, whereas newer agents tend to have more tolerable safety profiles, impacting prescribing decisions.
-
Are there opportunities for innovation with DYAZIDE?
Yes, integrating it into fixed-dose combinations, especially targeting underserved patients or specific subpopulations, could revitalize its utility.
-
What regulatory trends could impact DYAZIDE’s future?
Regulatory agencies continue emphasizing pharmacovigilance, safety profiles, and cost-effectiveness; innovations and new indications require rigorous approval pathways that could influence market dynamics.
References
[1] WHO. Hypertension Fact Sheet. 2021.
[2] IMS Health. Market Reports. 2018–2022.
[3] FDA. Drug Approvals & Label Updates. 1975–2022.
[4] GlobalData. Diuretic Market Analysis. 2022.
[5] National Institutes of Health. Hypertension Treatment Guidelines. 2017.
Disclaimer: This analysis consolidates publicly available information and market insights as of early 2023. Market conditions and regulatory landscapes evolve; strategic decisions should incorporate up-to-date data and expert consultation.