Last updated: August 5, 2025
Introduction
Clomid (clomiphene citrate), introduced in the 1960s, remains a cornerstone in fertility treatment, primarily used to induce ovulation in women experiencing infertility. Its longstanding presence in reproductive health underscores its importance, yet recent market factors, evolving regulatory landscapes, and competitive dynamics influence its future trajectory. This analysis explores the key market drivers, financial outlook, and strategic considerations shaping Clomid's position in the pharmaceutical landscape.
Pharmacological Profile and Market Relevance
Clomid acts as a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM), stimulating ovulation by inducing hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis modulation. Its efficacy, coupled with a favorable safety profile, renders it a first-line therapy for conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and other ovulatory disorders.
Despite the emergence of alternative treatments—such as gonadotropins, letrozole, and in-vitro fertilization (IVF)—Clomid retains a dominant position due to its affordability, oral administration, and proven track record. According to IMS Health data (2019), Clomid injections contributed to approximately 15% of infertility treatment prescriptions globally, reflecting robust steady demand.
Market Dynamics Influencing Clomid
Demand Drivers
-
Prevalence of Infertility: The global infertility rate remains around 8-12%, with higher incidences associated with lifestyle factors, delaying childbearing, and demographic shifts. As infertility treatments grow in acceptance and accessibility, demand for ovulation induction agents like Clomid sustains steady growth.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: Clomid’s low cost compared to injectable gonadotropins makes it the preferred initial therapy, especially in emerging markets with constrained healthcare budgets.
-
Regulatory Approvals & Reimbursement: Approval in emerging markets and inclusion in national infertility treatment guidelines bolster its utilization. Reimbursement policies significantly impact prescribing behaviors, particularly in developed economies.
Competitive Landscape & Alternative Therapies
-
Emerging Alternatives: Letrozole, an aromatase inhibitor, has gained favor in some regions due to potentially higher ovulation and pregnancy rates with fewer side effects. The FDA approved letrozole for ovulation induction in 2011, challenging Clomid’s dominance.
-
In-vitro Fertilization (IVF): As IVF techniques evolve and become more accessible, some prefer direct utilization over pharmacologic ovulation induction, which could marginalize Clomid in advanced infertility treatments.
-
Generic Availability: Clomid’s patents expired decades ago, facilitating widespread generic manufacturing. Price competition fuels accessibility but also exerts downward pressure on profit margins.
Regulatory and Safety Considerations
-
Thrombosis Risks & Ovarian Hyperstimulation: Safety concerns, albeit rare, influence prescribing guidelines. Ongoing pharmacovigilance data affect clinician confidence and regulatory recommendations.
-
Market Entry Barriers: Stringent approval processes for new formulations or combination therapies may limit the introduction of advanced alternatives, favoring existing Clomid formulations.
Regional Market Variations
-
Developed Markets: High awareness, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and reimbursement systems sustain consistent Clomid sales.
-
Emerging Markets: Growing infertility awareness, increasing healthcare infrastructure, and cost-sensitive environments promote continued reliance on Clomid, often with high generic penetration.
Financial Trajectory & Revenue Outlook
Historical Revenue Trends
Clomid's global sales have historically been stable, with estimates indicating annual revenues exceeding $300 million worldwide. The drug’s affordability and longstanding clinical use foster predictable revenue streams for manufacturers.
Forecasting Future Performance
-
Growth Factors:
-
Continued demographic shifts leading to increased infertility cases.
-
Rising acceptance and destigmatization of infertility treatment.
-
Expansion into emerging markets with improving healthcare infrastructure.
-
Challenges & Risks:
-
Competition from newer agents with favorable efficacy profiles, such as letrozole and gonadotropins.
-
Market cannibalization with the growth of alternative therapies and IVF.
-
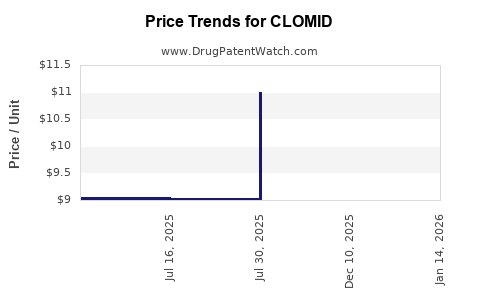
Pricing pressures from generic manufacturing.
-
Regulatory changes mandating label updates or usage restrictions in certain regions.
Revenue Projection Scenarios
-
Optimistic Scenario: Sustained demand in emerging markets, coupled with minimal competition and no major safety concerns, could see revenues grow modestly at 3-5% annually over the next five years.
-
Conservative Scenario: Increased competition and alternative therapies supplant Clomid as first-line treatment, resulting in stagnation or slight decline (~1-2%) in global sales.
-
Impact of Patent Status: Since Clomid’s patent expired long ago, new formulations or combination products could offer incremental revenue streams, though likely limited in scale.
Strategic Considerations for Stakeholders
-
Manufacturers: Need to diversify portfolio offerings, potentially invest in combination therapies or new delivery mechanisms to sustain revenue.
-
Investors: Should monitor emerging competitive treatments and regional market expansions, which influence profit margins and growth potential.
-
Regulatory Bodies: Balance safety data with continued access, particularly in jurisdictions where alternative therapies are less accessible.
Conclusion
Clomid’s enduring relevance in fertility management is anchored in its proven efficacy, safety, and affordability. Market dynamics shaped by demographic trends, competition, and regional healthcare policies continue to influence its financial performance. While the drug maintains a steady revenue trajectory in the short to medium term, shifts toward alternative therapies and evolving regulatory landscapes necessitate proactive strategic planning by stakeholders.
Key Takeaways
-
Dominant Role in Ovulation Induction: Clomid remains a primary treatment option due to cost and efficacy, especially in emerging markets.
-
Competitive Pressures: Alternatives like letrozole and gonadotropins pose challenges, potentially eroding market share over time.
-
Regional Factors Drive Demand: Healthcare infrastructure, reimbursement policies, and cultural acceptance significantly influence Clomid sales globally.
-
Revenue Stability with Growth Potential: Steady demand forecasts indicate modest growth prospects with opportunities stemming from market expansion.
-
Strategic Innovation Needed: To sustain relevance, manufacturers should consider developing new combination therapies or delivery formats.
FAQs
-
Will Clomid's market share decline due to the rise of letrozole?
While letrozole has gained popularity, especially in specific cases like PCOS, Clomid’s low cost and longstanding clinical familiarity sustain its use. However, in regions where clinical evidence favors letrozole, a gradual substitution trend is possible.
-
What regions represent the most significant growth opportunities for Clomid?
Emerging markets in Asia, Africa, and Latin America offer expanding demand due to rising infertility rates and increasing healthcare access, making them critical growth zones.
-
How do safety concerns impact Clomid's market trajectory?
Although generally safe, rare adverse effects lead to guidelines that restrict or recommend caution, influencing prescribing patterns but currently not substantially limiting overall use.
-
Are there upcoming regulatory hurdles for Clomid?
No recent significant regulatory changes threaten Clomid’s approval; however, pharmacovigilance and safety data continuously inform updates to prescribing information.
-
What strategic moves should pharmaceutical companies consider to maintain Clomid's market relevance?
Companies should explore innovative formulations, combination treatments, and geographic expansion, alongside engaging in clinical research to reinforce efficacy and safety profiles.
Sources:
- IMS Health. Global Fertility Market Report. 2019.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Approval of Letrozole for Ovulation Induction. 2011.
- World Health Organization. Infertility Prevalence and Trends. 2020.