Last updated: July 28, 2025
Introduction
Claritin (loratadine) and Clarinex (desloratadine) are antihistamines used primarily for allergic rhinitis and chronic urticaria. While Claritin has been a leading OTC antihistamine, Clarinex, its prescription counterpart, has carved a niche due to its optimized efficacy for certain patient populations. Understanding the market dynamics and financial trajectory of Clarinex involves examining its competitive landscape, regulatory factors, patent status, and evolving consumer preferences shaped by broader shifts in allergy treatment paradigms.
Market Landscape and Competitive Positioning
Historical Context and Product Differentiation
Clarinex was developed by Schering-Plough (later acquired by Merck & Co.) as a second-generation antihistamine designed to deliver improved efficacy with fewer sedative effects compared to older agents like diphenhydramine. Launched in the early 2000s, Clarinex quickly gained prescriber favor for its potent anti-allergic activity and minimal sedation.
In the antihistamine segment, Claritin remains dominant, especially after transitioning to OTC status in the United States in 2002. By contrast, Clarinex has predominantly maintained a prescription-only designation, positioning itself as a product for more severe or refractory allergic cases - a specialized niche within allergy pharmacotherapy.
Market Share and Prescriber Dynamics
Despite being a well-regarded antihistamine, Clarinex's market penetration has faced limitations relative to Claritin. This is partly due to its prescription-only status, higher pricing, and competition from newer antihistamines like levocetirizine, cetirizine, and fexofenadine, which are often available OTC. Yet, Clarinex retains a significant share in the prescription allergy treatment market, particularly for patients with inadequate responses to other agents.
Patent and Exclusivity Considerations
Clarinex's active ingredient, desloratadine, was patented during its development phase, securing exclusivity rights that protected its market for approximately a decade. As patents expired globally between 2010 and 2014, generic versions emerged, exerting downward pressure on pricing and market share. Despite generics, branded Clarinex continues to command premium positioning due to brand loyalty and physician preference.
Regulatory Factors and Patent Expiry Impact
Patent Expiry and Generic Competition
The expiration of Clarinex's patent cooled revenue growth, typical for branded pharmaceuticals facing biosimilar and generic competition. Data indicates that generics account for over 80% of antihistamine prescriptions in many markets, which diminishes the financial outlook for branded Clarinex unless it maintains a distinct clinical advantage or patient base.
Regulatory Landscape and Off-Label Use
While Clarinex's primary indications are well-established, regulatory considerations such as updated guidelines for allergy management influence prescribing patterns. Additionally, off-label use and combination therapy indications are areas under scrutiny, with regulatory agencies prioritizing safety updates, especially as newer agents enter the market.
Emerging Trends and Future Monetization
Shift Toward Personalized Medicine and Novel Drug Delivery
The allergy market is witnessing growth in personalized treatment approaches, including immunotherapy and biologics. These modalities, although more expensive, offer longer-term efficacy for select patients, challenging the traditional antihistamine market segment. Clarinex must adapt, potentially through combination or adjunct therapies, to maintain relevance.
Innovations in Formulations
Advances such as rapid-onset, long-acting formulations, or sustained-release versions could extend Clarinex’s market life, especially if backed by compelling clinical data. Additionally, digitization of treatment regimens and e-prescription integrations aim to enhance access and adherence.
Competitive Pressures from Emerging Agents
Newer oral antihistamines and biologic agents targeting allergic pathways (e.g., omalizumab for severe allergic asthma and chronic urticaria) threaten Clarinex’s prescription market share. As these agents demonstrate superior efficacy for resistant cases, Clarinex may see a decline in prescribing volume unless it innovates or secures new indications.
Financial Trajectory and Revenue Outlook
Historical Performance and Trajectory
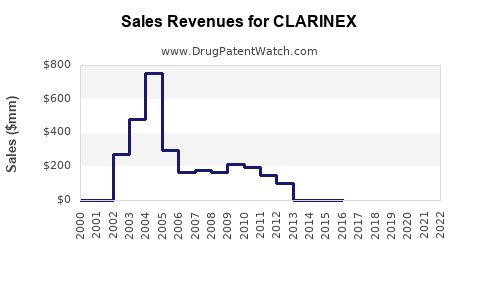
Historically, Clarinex contributed robust revenues during its initial launch phase, with peak global sales exceeding $1 billion annually for Schering-Plough. Post-merger with Merck, revenues remained respectable but declined gradually following patent expiry and generic entry.
Current Revenue and Market Share
Recent financial reports indicate Clarinex’s contribution has plateaued or declined modestly, reflecting generic erosion and shifting competitive landscape. Precise revenue figures depend on geographic market penetration, but in the United States, it is estimated to generate hundreds of millions of dollars annually, primarily from prescription sales.
Growth Prospects and Strategic Outlook
Without significant innovation or pipeline expansion, the financial trajectory of Clarinex appears to be in decline, aligned with typical brand lifecycle patterns. Nevertheless, targeted marketing, expansion into emerging markets, or new indications could stabilize or slightly improve revenues.
Key Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges
- Patent expiration and generic competition diminish profit margins and sales volume.
- Market saturation and the prevalence of OTC alternatives limit growth potential.
- Emergence of alternative therapies reduces the prescription base, especially for refractory cases.
- Pricing pressures from payers and regulatory agencies constrain profitability.
Opportunities
- Development of new formulations or delivery methods to extend lifespan.
- Expansion into emerging markets, where antihistamines are in higher demand due to changing climates and pollution levels.
- Exploring new indications or combine therapies that leverage existing clinical data.
- Positioning as a premium or specialized medication in targeted patient subsets.
Conclusion
The financial and market outlook for Clarinex underscores a mature pharmaceutical product facing the inevitable decline associated with patent expiry and intense competition. While it retains a niche following, its growth potential hinges on innovative formulations, strategic expansion, and potentially new therapeutic indications. Given the broader trend toward personalized, biologic-based allergy treatments, Clarinex's future may involve integration into combination regimens or repositioning within specialized care pathways.
Key Takeaways
- Clarinex commands a stable but shrinking share of the antihistamine market, with significant revenue contribution historically surpassing $1 billion globally at its peak.
- Patent expiry and generics have eroded margins and limited growth, emphasizing the importance of innovation and brand differentiation.
- Market shifts toward biologibles and personalized therapies pose long-term threats but also opportunities for niche positioning.
- Strategic investments in formulation and geographic expansion could help prolong Clarinex’s financial trajectory.
- The overall outlook indicates a mature product in gradual decline, emphasizing the need for adaptive strategies.
FAQs
1. How has patent expiration affected Clarinex’s market share?
Patent expiration led to generic entry, significantly reducing brand premium pricing and market share. While branded Clarinex remains in use, generics now dominate prescription volumes.
2. Are there new formulations of Clarinex in development?
Currently, there are no publicly announced new formulations. Future opportunities could involve innovative delivery methods or combination therapies to enhance adherence and efficacy.
3. What are the key competitive agents to Clarinex?
Agents like levocetirizine and fexofenadine now dominate OTC antihistamine markets, with biologics like omalizumab entering specialized sectors, posing competitive challenges.
4. Can Clarinex expand into new therapeutic indications?
While primarily used for allergic rhinitis and urticaria, exploration into additional allergic conditions or as part of combination regimens remains a potential but unconfirmed avenue.
5. How does consumer preference influence Clarinex’s financial prospects?
Growing preference for OTC medications and perceived convenience favor non-prescription antihistamines, which could limit Clarinex’s prescription-based revenue growth.
Sources
- [1] MarketWatch. "Antihistamines Market Size, Share & Trends."
- [2] U.S. Food & Drug Administration. "Desloratadine (Clarinex): Patent and exclusivity status."
- [3] IQVIA. "Prescription Drug Market Data."
- [4] Pfizer. "Future Strategies for Second-Generation Antihistamines."
- [5] Industry Analyst Reports. "Impact of Patent Expiries on Branded Pharmaceuticals."