Last updated: July 28, 2025
Introduction
CELEXA (generic name: citalopram) is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) primarily prescribed for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD). Since its debut in the late 1980s, CELEXA has established itself as a significant player in the psychopharmacology sector, impacting both market dynamics and pharmaceutical revenues. This analysis explores the evolving landscape of CELEXA, examining market trends, competitive pressures, regulatory influences, and financial projections essential for stakeholders aiming to understand its current and future significance.
Market Overview of CELEXA
Historical Market Position
CELEXA received FDA approval in 1989 (under the brand name Celexa), quickly capturing a considerable market share due to its efficacy and tolerability profile. As a first-generation SSRI, it was positioned as a safer alternative to older antidepressants like tricyclics and monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs). Its initial success was driven by the rising prevalence of depression, high prescribing rates, and favorable safety profile, especially regarding overdose toxicity.
Market Segmentation and Usage Patterns
The primary segment for CELEXA encompasses adult patients diagnosed with MDD, often co-presenting with comorbid anxiety disorders. Increasing awareness around mental health issues has amplified prescription volumes. Additionally, CELEXA's use extends to off-label applications, including premature ejaculation and hot flashes, diversifying its market reach.
Competitor Landscape
CELEXA faces intense competition from both branded and generic SSRIs, including fluoxetine (Prozac), sertraline (Zoloft), escitalopram (Lexapro), and paroxetine (Paxil). Generics have significantly reduced branded drug revenues, with many pharmaceutical companies shifting focus toward biosimilars and new antidepressants.
Market Dynamics Influencing CELEXA
Patent Expirations and Generic Competition
CELEXA's patent protection ended in the early 2000s, catalyzing a wave of generic manufacturing. Generic versions now dominate the market, eroding profits for originator companies like Lundbeck and Forest Laboratories (acquired by AbbVie). As a result, the revenue contribution from CELEXA has diminished, with generic sales often outweighing branded sales.
Regulatory and Safety Issues
Concerns over safety profiles, notably QT interval prolongation associated with higher doses of citalopram, prompted FDA warnings in 2011. These advisories have influenced prescribing patterns, with clinicians favoring alternative SSRIs perceived as safer—affecting CELEXA’s market penetration. Regulatory scrutiny remains an ongoing influence, particularly with evolving guidelines for safe prescribing.
Prescriber Preferences and Market Trends
The advent of newer antidepressants with broader indication profiles and shorter side effect profiles has shifted prescriber preferences. For instance, escitalopram (Lexapro) has gained popularity due to its improved tolerability and lower dosing requirements, subtly encroaching on CELEXA’s market share.
Health Insurance and Reimbursement Policies
Insurance formularies favor cost-effective generics, favoring CELEXA's generic versions. Reimbursement policies influence prescribing behavior significantly, with payers promoting generic over branded drugs, further cementing CELEXA's position within the market.
Emerging Treatments and Biologics
The expanding pipeline of novel antidepressants, including ketamine derivatives and digital therapeutics, could disrupt traditional SSRI markets. While CELEXA remains a mainstay, its long-term financial trajectory is contingent upon how well it adapts or maintains relevance amid these innovations.
Financial Trajectory of CELEXA
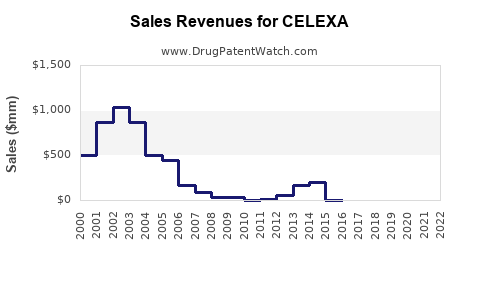
Revenue Trends and Market Share
Following patent expiration, CELEXA’s revenues declined sharply. According to IMS Health data, US branded sales peaked at approximately $800 million in the late 2000s, with generics subsequently capturing the majority of sales. Current estimates place CELEXA’s annual revenue at substantially lower levels, often less than $100 million globally, predominantly from legacy prescribers and specific patient subsets.
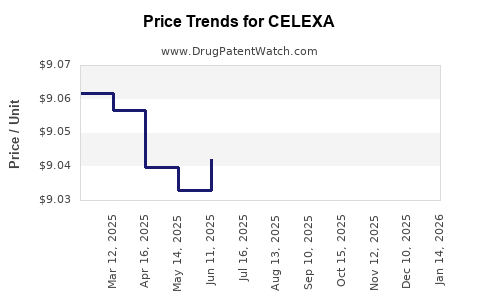
Pricing and Profitability
Generic entry has driven down the price per prescription by over 80%, with current average wholesale prices (AWP) for generics averaging around $0.20–$0.50 per tablet. While profit margins for manufacturing generics are thin, volume sales sustain profitability for larger pharmaceutical companies. For originator companies, declining revenues necessitate strategic repositioning.
Forecasted Growth and Decline
Given the current landscape, CELEXA’s financial future appears characterized by gradual decline absent significant new indications or formulations. However, niche uses or line extensions may provide pockets of revenue stability. Based on industry patterns, sustained revenues are expected for the next 3–5 years, after which market saturation and competition could further diminish sales.
Pipeline Developments and Market Opportunities
While dedicated development efforts for CELEXA have waned, there remains potential in leveraging existing formulations for new delivery mechanisms or combination therapies. Strategic licensing, drug repurposing, and digital health integrations represent avenues to prolong financial relevance.
Regulatory and Market Challenges
Patent and Exclusivity Considerations
Since CELEXA’s patent expiry, no new patent protections are in place for the molecule, limiting monopolistic pricing ability. Future exclusivity depends on formulation patents or new therapeutic claims, which are challenging given the generic landscape.
Legal and Safety Litigation
Legal liabilities related to adverse effects and off-label marketing can influence market perception and access. Regulatory agencies’ warnings and adverse event reporting may further shape prescriber confidence.
Market Saturation and Physician Prescribing Behavior
Decreased physician reliance on older SSRIs in favor of newer agents with purported better safety and tolerability profiles constrains CELEXA’s growth potential.
Strategic Outlook and Future Market Position
Niche Market Focus
Targeting specific patient populations, such as those requiring long-term maintenance or with particular side effect profiles, may sustain CELEXA’s relevance. Education campaigns highlighting cost-effectiveness can influence prescriber choices within formulary constraints.
Potential for Line Extensions and Formulation Innovations
Developing extended-release formulations or combining CELEXA with other therapies might open new avenues for revenue. However, development costs and regulatory hurdles must be balanced against expected benefits.
Partnerships and Licensing Opportunities
Collaborations with digital health companies leveraging CELEXA’s profile within mental health management could create synergistic revenue streams. Licensing agreements to develop newer indications or formulations also present opportunities.
Key Takeaways
- Market decline post-patent expiration has markedly reduced CELEXA’s revenue, with generics dominating worldwide sales.
- Regulatory safety concerns and evolving prescriber preferences favor newer SSRIs like escitalopram, further constraining CELEXA’s market share.
- Price suppression due to generic competition has resulted in significantly lower per-unit revenues, although volume maintains profitability for manufacturers.
- Market opportunities remain limited; targeted niche use, formulation innovations, and digital health integrations are avenues for future growth.
- Long-term financial outlook suggests continued gradual decline unless new indications, formulations, or strategic partnerships are pursued.
Conclusion
CELEXA’s journey exemplifies the typical lifecycle of a branded pharmaceutical after patent expiry—initial dominance giving way to generic competition, regulatory challenges, and shifting prescriber preferences. While its overarching market trajectory points towards decline, strategic repositioning and innovation could sustain niche relevance. Business professionals must monitor regulatory developments, competitive innovations, and evolving consumer health trends to navigate CELEXA’s future landscape effectively.
FAQs
1. Will CELEXA regain market share with new formulations or indications?
Unlikely without significant clinical breakthroughs; current trends favor newer antidepressants or combination therapies. However, niche formulations or approved new indications could provide limited opportunities.
2. How do safety concerns impact CELEXA’s prescribing patterns?
FDA warnings on QT prolongation have led clinicians to favor other SSRIs, especially at higher doses. This cautious approach diminishes CELEXA’s market share.
3. What role do insurance providers play in CELEXA’s market?
Payers heavily favor generics due to lower costs, incentivizing prescriptions of low-cost alternatives over branded CELEXA, thereby compressing revenues.
4. Can CELEXA’s digital health integration offer new revenue streams?
Potentially, particularly within mental health management platforms, but competitive integration and proof of efficacy are essential.
5. What strategies can pharmaceutical companies employ to extend CELEXA’s market life?
Focusing on targeted niche markets, developing novel formulations, leveraging licensing agreements, and pursuing new therapeutic claims are viable strategies.
References
[1] U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2011). FDA Drug Safety Communication: QT prolongation possible with high doses of Celexa (citalopram) and Lexapro (escitalopram).
[2] IMS Health. (2019). Global Trends in Antidepressant Market Sales.
[3] Lundbeck A/S. (2010). Celexa (citalopram) product monograph.