Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Carbinoxamine maleate, a first-generation antihistamine, is primarily employed to treat allergy symptoms such as hay fever, urticaria, and conjunctivitis. Despite its longstanding presence in the pharmaceutical landscape, its market trajectory is subject to evolving therapeutic preferences, regulatory landscapes, and competitive dynamics. This analysis examines key market drivers, challenges, and financial prospects, providing a comprehensive outlook for stakeholders considering investment or strategic positioning in this niche.
Pharmaceutical Profile and Regulatory Status
Carbinoxamine maleate belongs to the ethanolamine class of antihistamines and functions by antagonizing H1 histamine receptors, thus alleviating allergic reactions. It is available in various formulations including tablets, syrups, and injectable forms.
Regulatory approval in jurisdictions such as the U.S. often categorizes it as an over-the-counter (OTC) medication. The FDA classifies many first-generation antihistamines as generally recognized as safe (GRAS) for OTC use, though newer agents with improved safety profiles have gained prominence.
Notably, in recent years, regulatory agencies have implemented rigorous safety reviews due to concerns over sedative effects and anticholinergic side effects common to first-generation antihistamines. This shift influences the clinical and commercial usage of carbinoxamine maleate.
Market Dynamics
1. Evolving Therapeutic Paradigms
The antihistamine market has experienced significant shifts toward second- and third-generation agents like loratadine, cetirizine, and fexofenadine, which offer comparable efficacy with reduced sedative effects. This transition has constricted the market share for first-generation compounds such as carbinoxamine maleate.
2. Competitive Landscape
Market players include generic pharmaceutical companies and niche formulators. The generic nature of carbinoxamine maleate limits pricing power, with prevalent competition from other first-generation antihistamines. The entry of modern antihistamines has further compressed revenues, especially in developed markets.
3. Regulatory and Safety Considerations
Regulatory agencies’ increased emphasis on safety profiles diminishes the broader adoption of sedating antihistamines. Marketing restrictions, labeling changes, and safety warnings attenuate demand among sensitive patient populations.
4. Market Penetration and Consumer Preferences
Current consumer preferences favor medications with minimal sedation and broader safety profiles, favoring second-generation drugs. Consequently, OTC sales of carbinoxamine maleate are diminishing. However, certain niche applications—such as in specific formulations or in regions with less regulatory oversight—may sustain limited demand.
5. New Formulations and Delivery Systems
Innovations such as combination therapies, extended-release formulations, or novel delivery mechanisms could revive some interest in carbinoxamine maleate. Nonetheless, such developments are limited and face stiff clinical competition.
Financial Trajectory
1. Revenue Trends
The global antihistamine market size was valued approximately at USD 6.5 billion in 2022, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3–4% [1]. Within this, first-generation antihistamines account for a decreasing proportion due to safety concerns and market preferences.
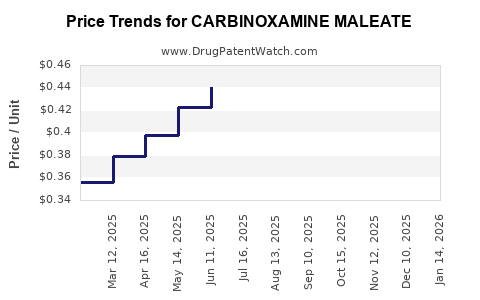
Carbinoxamine maleate, as a legacy drug, exhibits declining revenues aligned with general market shrinkage for first-generation antihistamines. Its revenue contribution is limited mainly to generic off-patent sales, which are often volatile and margin-compressed.
2. Market Forecast
Predictive models suggest a continued decline in demand over the next five years unless novel formulations or niche strategies emerge. The rising adoption of newer agents is expected to reduce its market share in developed markets, especially North America and Europe.
However, in emerging markets with less regulatory rigor and lower awareness of safety issues, sales may stabilize in the short term. Generics manufacturers targeting these regions could sustain modest revenues.
3. Investment and R&D Outlook
Limited R&D activity centers on improving or reformulating carbinoxamine maleate. Innovators primarily focus on later-generation antihistamines. As a result, investment optimism remains subdued, restricting opportunities for substantial financial growth.
4. Licensing and Strategic Alliances
License agreements from patent holders, historical patent expirations, and regional distribution arrangements influence financial performance. Since carbinoxamine maleate has been off patent for decades, revenues are predominantly driven by generic manufacturers.
Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges:
- Increased safety concerns lead to regulatory restrictions.
- Dominance of second-generation antihistamines diminishes market share.
- Pricing pressures from generic competition.
- Limited scope for innovation or differentiation.
Opportunities:
- Niche pharmaceutical applications or combination therapies.
- Expanding sales in regions with less stringent regulations.
- Developing formulations targeting specific patient groups with minimal sedative effects.
- Repositioning for off-label uses if supported by clinical data.
Regulatory and Market Outlook
The regulatory environment favors safer antihistamines, which hampers growth prospects for first-generation drugs like carbinoxamine maleate. Market dynamics indicate a gradual contraction in mainstream demand, emphasizing the importance of strategic repositioning.
Stakeholders must monitor regional regulatory updates, evolving clinical guidelines, and consumer preferences. Investment in new formulations or therapeutic niches presents potential but remains limited by overall industry momentum favoring newer agents.
Key Takeaways
- The global market for carbinoxamine maleate is in decline, driven mainly by safety concerns and the dominance of second-generation antihistamines.
- Limited innovation and generic competition constrain revenue potential, with most sales concentrated within niche markets or regions with lax regulations.
- Future growth prospects hinge on selective niche applications, formulation innovations, and regional market opportunities, rather than broad mainstream expansion.
- Regulatory trends toward safer medications will continue to restrict the use of first-generation antihistamines, including carbinoxamine maleate.
- Strategic focus should pivot to identifying underserved markets or developing combination therapies that leverage existing safety profiles.
FAQs
1. Is there still a significant market for carbinoxamine maleate globally?
The overall market is shrinking, with demand mainly confined to niche markets and regions with lax regulations. Its decline is driven by competition from safer, second-generation antihistamines.
2. Can reformulation or innovation revive the market prospects of carbinoxamine maleate?
Potential exists through niche formulation strategies or combination therapies, but widespread commercial viability remains limited given regulatory and competitive pressures.
3. What regulatory challenges does carbinoxamine maleate face?
Regulatory agencies are increasingly scrutinizing sedative antihistamines for safety concerns, leading to restrictions, warnings, and decline in OTC availability in many markets.
4. Who are the main competitors in the antihistamine space affecting carbinoxamine maleate?
Second- and third-generation antihistamines like loratadine, cetirizine, and fexofenadine dominate market share due to better safety profiles and marketing support.
5. Are there emerging markets that could provide growth opportunities?
Yes, regions with less regulatory oversight may sustain some demand, but global growth remains constrained by the dominant position of newer antihistamines.
References
[1] Market Data Forecast. “Antihistamines Market Size and Trends.” 2022.